Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yagi, Masahiro; Horiguchi, Hironori; Yokoo, Kenji; Oyama, Koji; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2008-072, 79 Pages, 2008/09
A crack had been found on the weld of one reflector element in JRR-4. A survey revealed that the cause for the crack was the expansion of graphite reflector in the reflector element. It appeared that the expansion of graphite reflector was caused by fast neutron irradiation at low temperature. The survey confirmed radiographically that graphite reflectors in the other reflector elements without the crack expanded similarly by the irradiation growth. Irradiated graphite reflectors were carefully observed and were precisely measured the three dimensions after dismantling the irradiated reflector elements in order to understand quantitatively the irradiation growth behavior of IG-110 graphite under the JRR-4 operation condition. As the results, it was confirmed that growth of graphite reflectors increased with increasing of fast neutron fluence. The maximum irradiation growth per fast neutron fluence was 7.13 10
10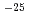 %m
%m /n, the minimum was 4.21
/n, the minimum was 4.21 10
10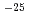 %m
%m /n, the average was 5.71
/n, the average was 5.71 10
10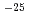 %m
%m /n in the range of fast neutron fluence below 2.5
/n in the range of fast neutron fluence below 2.5 10
10 n/m
n/m .
.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Kenji; Yokoo, Takeshi*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.434 - 442, 2007/09
In Japan, the partitioning and transmutation (PT) technology is being studied and developed to reduce the burden of the high-level radioactive waste (HLW) management. To demonstrate clearly the benefit of the PT technology on the waste management of future nuclear fuel cycles, the repository area necessitated to dispose of the HLW was discussed quantitatively for spent fuels from UO -LWR, MOX-LWR and MOX-FBR. Four options of separation process were assumed in the analysis: (1) Conventional PUREX reprocessing, (2) Transmutation of minor actinide (MA), (3) Partitioning of FP, and (4) PT for both MA and FP. The results showed that MA transmutation would be necessary to keep the emplacement area for MOX fuel at the same level as that for UO
-LWR, MOX-LWR and MOX-FBR. Four options of separation process were assumed in the analysis: (1) Conventional PUREX reprocessing, (2) Transmutation of minor actinide (MA), (3) Partitioning of FP, and (4) PT for both MA and FP. The results showed that MA transmutation would be necessary to keep the emplacement area for MOX fuel at the same level as that for UO fuel. The adoption of PT for both MA and FP was effective to further reduce the repository area independently on the fuel type, the reactor type and the cooling period.
fuel. The adoption of PT for both MA and FP was effective to further reduce the repository area independently on the fuel type, the reactor type and the cooling period.
Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Yagi, Masahiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Sasajima, Fumio; Oyama, Koji; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Sasaki, Tsutomu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-018, 104 Pages, 2007/03
Reactor operation training using JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4) was started in FY 1969, one of the curriculums of Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC). After that, the program was updated and carried out for reactor operation training, control rod calibration, and measurement of various kind of characteristics. JRR-4 has been contributed for nuclear engineer training that is over 1,700 trainees from bother domestic and foreign countries. JRR-4 can be used for experiment from zero power to 3500kW, and the trainees can make experience to operate the reactor from start up to shut down, not only zero-power experiments (critical approach, control rod calibration, reactivity measurement, etc.) but also other experiments under high power operation (xenon effect, temperature effects, reactor power calibration, etc.). This report is based on various kinds of guidance texts using for training, and collected for operation and experiments for reactor physics.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Yokoo, Takeshi*; Nishihara, Kenji; Morita, Yasuji; Ikeda, Takao*; Takaki, Naoyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(3), p.398 - 404, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Benefit of implementing Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) technology was parametrically surveyed in terms of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal by discussing possible reduction of the geological repository area. The results showed that, by recycling minor actinides (MA), the placement area could be reduced by 17-29% in the case of UO -LWR and by 63-85% in the case of MOX-LWR in comparison with the conventional PUREX reprocessing. This significant impact in MOX fuel was caused by the recycle of
-LWR and by 63-85% in the case of MOX-LWR in comparison with the conventional PUREX reprocessing. This significant impact in MOX fuel was caused by the recycle of  Am which was a long-term heat source. Further 70-80% reduction of the placement area in comparison with the MA-recovery case could be expected by partitioning the fission products (FP) into several groups for both fuel types.
Am which was a long-term heat source. Further 70-80% reduction of the placement area in comparison with the MA-recovery case could be expected by partitioning the fission products (FP) into several groups for both fuel types.
Hirane, Nobuhiko; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Nemoto, Takumi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Yagi, Masahiro; Arai, Nobuyoshi; Watanabe, Shukichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-028, 115 Pages, 2006/03
JRR-4, a light-water-moderated and cooled, swimming pool type research reactor using high-enriched uranium plate-type fuels had been operated from 1965 to 1996. In order to convert to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels, modification work had been carried out for 2 years, from 1996 to 1998. After the modification, start-up experiments were carried out to obtain characteristics of the low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel core. The measured excess reactivity, reactor shutdown margin and the maximum reactivity addition rate satisfied the nuclear limitation of the safety report for licensing. It was confirmed that conversion to low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuels was carried out properly. Besides, the necessary data for reactor operation were obtained, such as nuclear, thermal hydraulic and reactor control characteristics. This report describes the results of start-up experiments and burnup experiments. The first criticality of low-enriched-uranium-silicied core was achieved on 14th July 1998, and the operation for joint-use has been carried out since 6th October 1998.
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Yokoo, Takeshi*; Nishihara, Kenji; Morita, Yasuji; Ikeda, Takao*; Takaki, Naoyuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The benefit of implementing Partitioning and Transmutation (P&T) of high-level wastes was parametrically surveyed. The possible reduction of the geological repository area was estimated. By recycling minor actinides (MA), the repository area required for unit spent fuel was reduced significantly in the case of MOX-LWR. This effect was caused by removal of  Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO
Am which is a long-term heat source. By partitioning the fission products, in addition to MA recycling, further 70-80% reduction from the MA-recovery case can be expected for both UO and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
and MOX. This significant reduction was independent of the cooling time before the partitioning process.
*; Nakajima, Teruo; ; ; ;
Advances in Neutron Capture Therapy, 1, p.326 - 330, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Yamane, Yoshihiro*; *;
JAERI-Research 95-059, 83 Pages, 1995/09
no abstracts in English
; Torii, Yoshiya; ; Ichimura, Shigeju; *; Sasajima, Fumio; *; *; *; Takahashi, Hidetake
JAERI-M 94-058, 45 Pages, 1994/03
no abstracts in English
Horiguchi, Hironori; Shibata, Taiju; Yagi, Masahiro; Yokoo, Kenji; Oyama, Koji; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
The Japan Research Reactor No.4 (JRR-4) are used for medical irradiation (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy), education and training for engineers, activation analysis and researches in various fields. A crack was found on the weld of aluminum cladding of a reflector element, in which graphite reflector was set. A survey on the reflector element confirmed that the crack was caused by growth of graphite. The growth of graphite was observed in the other reflector elements by the radiographic testing (RT). In order to understand the relations between irradiation fluence and irradiation growth, the dimensions of irradiated graphite reflectors were precisely measured after dismantling the reflector elements. We revealed that the growth of graphite increased with fast neutron fluence at low temperature which was estimated below 200 C under JRR-4 operation condition.
C under JRR-4 operation condition.
Yokoo, Kenji; Yagi, Masahiro; Horiguchi, Hironori; Oyama, Koji; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English