Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Hashimoto, Makoto; Maeda, Koji; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1437 - 1446, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The aerodynamic radioactive median diameter (AMAD) is necessary information to assess the internal exposure. On June 6, 2017, at a plutonium handling facility in Oarai site of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), during the inspection work of a storage container that contains nuclear fuel materials, accidental contamination occurred and five workers inhaled radioactive materials including plutonium. Some smear papers and an air sampling filter were measured with the imaging plate, and we conservatively estimated minimum AMADs for two cases, plutonium nitrate and plutonium dioxide. As a result of AMAD estimation, even excluding a giant particle of a smear sample, the minimum AMADs of plutonium nitrate from smear papers were 4.3 - 11.3  m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1
m and those of plutonium dioxide were 5.6 - 14.1  m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0
m. Also, the minimum AMAD of plutonium nitrate from an air sampling filter was 3.0  m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9
m and that of plutonium dioxide was 3.9  m.
m.
Shimada, Kazumasa; Nagai, Haruyasu; Hashimoto, Makoto; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 65(5), P. 290, 2023/05
, 65(5), P. 290, 2023/05
This article is part of the special feature article "What should be done from now on after the 1F accident and what should be conveyed to the next generation after the 1F accident?" of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan, which summarizes the discussions and future proposals on nuclear disaster prevention in which the members of the Health Physics and Environment Science Subcommittee have been involved. In view of the recommendations of the Accident Investigation Committee of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan and the Meteorological Society of Japan, the behavior of radioactive plumes and the prediction of residents' evacuation behavior should be studied to support decision-making on evacuation and other protective measures for residents in and outside the UPZ. Furthermore, decision-making on protective measures and practical risk communication to residents based on radiation health risks to residents and ethical aspects are newly proposed.
Hamaguchi, Takumi; Yamada, Junya; Komatsuzaki, Naoya*; Hatakeyama, Takumi; Seya, Natsumi; Muto, Yasunobu; Miyauchi, Hideaki; Hashimoto, Makoto
JAEA-Technology 2022-038, 65 Pages, 2023/03
New regulatory requirements were developed taking into account the lessons-learnt from the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station on March 2011. The new regulatory standards required that monitoring posts should be diversified in transmission systems and equipped with backup power supply equipment for design basis accidents. In this report, we look back on the history of monitoring posts in Oarai Research and Development Institute, explained the application for the permission of reactor installment license, application for approval of the design and construction method, pre-use operator's inspection and improvement design of monitoring posts. This report also includes about inspection based on act on special measures concerning nuclear emergency preparedness and the installation of KURAMA-II, which was carried out in conjunction with the improvement of monitoring post for new regulatory standards. As an appendix, application document for approval of the design and construction method are included.
Watanabe, Seiya*; Kawahara, Jun*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Sugihara, Kenta; Takase, Shinsuke*; Moriguchi, Shuji*; Hashimoto, Hirotada*
Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics, 17(1), p.2211143_1 - 2211143_23, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.52(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)In tsunami inundations or slope disasters of heavy rain, a lot of floating debris or driftwood logs are included in the flows. The damage to structures from solid body impacts is more severe than the damage from the water pressure. In order to study free-surface flows that include floating debris, developing a high-accurate simulation code of free-surface flows with high performance for large-scale computations is desired. We propose the single-phase free-surface flow model based on the cumulant lattice Boltzmann method coupled with a particle-based rigid body simulation. The discrete element method calculates the contact interaction between solids. An octree-based AMR (Adaptive Mesh Refinement) method is introduced to improve computational accuracy and time-to-solution. High-resolution grids are assigned near the free surfaces and solid boundaries. We conducted two kinds of tsunami flow experiments in the 15 and 70 m water tanks at Hachinohe Institute of Technology and Kobe University to validate the accuracy of the proposed model. The simulation results have shown good agreement with the experiments for the drifting speed, the number of trapped wood pieces, and the stacked angles.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.1 - 7, 2022/03
Background: In Japan, new regulations that revise the dose limit for the lens of the eye (the lens), operational quantities, and measurement positions for the lens dose were enforced in April 2021. Based on the international safety standards, national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of the Nuclear Regulatory Authority, and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) developed a guideline for radiation dose monitoring for the lens. Materials and Methods: The Working Group of the JHPS discussed the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit for the lens. Results and Discussion: In July 2020, the JHPS guideline was published. The guideline consists of three parts: main text, explanations, and 26 questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were provided to enable similar cases to be addressed. Conclusion: With the development of guideline on radiation dose monitoring of the lens, radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimise radiation protection.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Matsuoka, Amane; Yasumune, Takashi; Kojima, Nobuhiro; Miyauchi, Hideaki; Takasaki, Koji; Hashimoto, Makoto
JAEA-Review 2021-055, 11 Pages, 2021/12
The dose limit for the eye lens was lowered on April 1 2021, and a 3 mm dose equivalent was added to the calculation. The guidelines require that lens dosimeters be worn and managed when there is a risk of exceeding control standards. In this report, in order to examine future management methods, we investigated whether work that might exceed the equivalent dose limit was performed in the past. As a result of the investigation, the exposure dose for all works after fiscal year 2008 was sufficiently low compared to the equivalent dose limit. For this reason, it is considered that there is no need for additional management of wearing a personal dosimeter near the eyes for the work that is normally performed. In the future, as in the past, the basic management method will be to wear a dosimeter only on the basic part of the trunk under uniform exposure conditions, and to wear a dosimeter on the basic part of the trunk and the maximum dose part under nonuniform exposure conditions. When performing work with a high exposure dose to the eye lens, a dosimeter should be worn near the eye to measure the 3 mm dose equivalent.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Kinase, Sakae; Munakata, Masahiro; Murayama, Takashi; Takahashi, Masa; Takada, Chie; Okamoto, Akiko; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Sukegawa, Masato; Kume, Nobuhide*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-071, 53 Pages, 2021/03
In the case of a nuclear accident or a radiological emergency, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), as a designated public corporation assigned in the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and the Armed Attack Situation Response Law, undertakes technical supports to the national government and local governments. The JAEA is requested to support to evaluate radiation doses to residents in a nuclear emergency, which is specified in the Basic Disaster Management Plan and the Nuclear Emergency Response Manual. For the dose evaluation, however, its strategy, target, method, structure and so on have not been determined either specifically or in detail. This report describes the results of investigation and consideration discussed in the "Working Group for Radiation Dose Evaluation at a Nuclear Emergency" established within the Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center to discuss technical supports for radiation dose evaluation to residents in the case of a nuclear emergency, and aims at contributing to specific and detailed discussion and activities in the future for the national government and local governments, also within the JAEA.
Nakano, Masanao; Hosomi, Kenji; Nishimura, Shusaku; Matsubara, Natsumi; Okura, Takehisa; Kuramochi, Akihiko; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Takeuchi, Erina; Fujii, Yutaka*; Jinno, Tsukasa*; et al.
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 55(2), p.102 - 109, 2020/06
After the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) Accident in March 2011, the increase was significantly observed in a part of the result of the environmental radiation monitoring in Ibaraki prefecture. "The review meeting of the environmental effect from 1F accident" was established to discuss technically the fluctuation of monitoring data. The review meeting collected the monitoring data from the four nuclear operators, and discussed a fluctuating trend,  Cs/
Cs/ Cs activity ratio, and so on. In this report, the results of the dose rate and
Cs activity ratio, and so on. In this report, the results of the dose rate and  Cs in fallout, surface soil, flatfish and seabed sediment are introduced. Also the problem solving in the review meeting is introduced.
Cs in fallout, surface soil, flatfish and seabed sediment are introduced. Also the problem solving in the review meeting is introduced.
Hashimoto, Makoto
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(7), p.525 - 528, 2019/07
, 61(7), p.525 - 528, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Hashimoto, Makoto; Maeda, Koji; Kato, Masato; Yoshizawa, Michio; Momose, Takumaro
JAEA-Review 2019-003, 48 Pages, 2019/03
June 6, 2017, at Plutonium Fuel Research Facility in Oarai Research and Development Center of JAEA, when five workers were inspecting storage containers containing plutonium and uranium, resin bags in a storage container ruptured, and radioactive dust spread. Though they were wearing a half face mask respirator, they inhaled radioactive materials. In the evaluation of the internal exposure dose, the aerodynamic radioactive median diameter (AMAD) is an important parameter. We measured 14 smear samples and a dust filter paper with imaging plates, and estimated the AMAD by image analysis. As a result of estimating the AMAD, from the 14 smear samples, the AMADs are 4.3 to 11  m or more in the case of nitrate plutonium, and the AMADs are 5.6 to 14
m or more in the case of nitrate plutonium, and the AMADs are 5.6 to 14  m or more in the case of the oxidized plutonium. Also, from the dust filter paper, the AMAD is 3.0
m or more in the case of the oxidized plutonium. Also, from the dust filter paper, the AMAD is 3.0  m or more in the case of nitrate plutonium, and the AMAD is 3.9
m or more in the case of nitrate plutonium, and the AMAD is 3.9  m or more in the case of the oxidized plutonium.
m or more in the case of the oxidized plutonium.
 I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas counts
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas countsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Hoken Butsuri, 52(1), p.5 - 12, 2017/03
The purpose of this study is to improve a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of
I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of  I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The
I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The  I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for
I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for  I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
 I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring posts
I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring postsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Radioisotopes, 65(10), p.403 - 408, 2016/10
The purpose of this study is to develop a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m
I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m /cps.
/cps.
Seya, Natsumi; Hashimoto, Makoto; Nemoto, Koji*; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji
Hoken Butsuri, 49(1), p.29 - 38, 2014/03
Evaluation of annual average of radionuclide concentration in surface air obtained from atmospheric dispersion factor is intended to determine a public dose as a primary source for the safety analysis of nuclear facilities in normal operation. Oarai Research and Development Center (ORDC) of the JAEA have used fixed 5-year meteorological statistics for derivation of atmospheric dispersion factors as average conditions. To show that the meteorological statistics for any 5-year period could be used as representative data for evaluation of average conditions, annual average (1-year average) and 5-year average of evaluated radionuclide concentrations derived from the meteorological data observed from 1991 to 2010 at ORDC were analyzed. The fluctuations of evaluated radionuclide concentrations of any 5-year averages were smaller than those of 1-year averages during 20 years, and any 5-year averages contained no rejections by the F-test (5% significance level). It means that any 5-year averages of radionuclide concentration evaluations are well representative for the safety analysis under normal condition in ORDC.
Usui, Toshihide; Mikami, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Makoto; Nakayama, Naoto; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tani, Kotaro*; Yamasaki, Keizo*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*
KURRI Progress Report 2010, P. 209, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Makoto; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.65 - 68, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)A dose evaluation using multiple radiation detector outputs can be improved by the convex optimisation. It enables flexible dose evaluation corresponding to the radiation field. The neutron ambient dose equivalent is evaluated using a mixed-gas proportional counter. The reliability of evaluated dose values are comparable with current dosimeter. An application to neutron individual dose equivalent measurement is also investigated. The combination of dosimeters with high orthogonality of response characteristics tends to show good suitability for dose evaluation.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 136(1), p.1 - 10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.22(Environmental Sciences)A novel neutron dose measurement method which flexibly responds to variations of neutron field is being developed in JAEA. This is an implementation of the multi-detector method (first introduced in early 1970s) for neutron dose evaluation using convex hull in the response space defined for multiple detectors. The convex hull provides range of possible neutron dose corresponding to the incident neutron spectrum. Feasibility of the method was studied using simulated response of mixed-gas proportional counter. Monochromatic neutrons are shown to be fundamentally suitable for mapping the convex hull. The convex hull can be further reduced taking into consideration 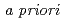 information about physically possible incident neutron spectra, for example, theoretically derived moderated neutron spectra originated from a fission neutron source.
information about physically possible incident neutron spectra, for example, theoretically derived moderated neutron spectra originated from a fission neutron source.
 rays
raysHashimoto, Makoto; Otaka, Masahiko; Ara, Kuniaki; Kanno, Ikuo; Imamura, Ryo*; Mikami, Kenta*; Nomiya, Seiichiro*; Onabe, Hideaki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 46(1), p.76 - 82, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A photon detector for unfolding X-ray energy distribution has been previously reported. Simulation studies on the unfolding method for this detector are discussed for diagnostic X-rays and mixed-source  rays of
rays of  Cs/
Cs/ Co. Response functions for diverse diagnostic X-rays are almost indistinguishable and an unfolding using error reduction method is not sufficiently worked. The spectrum surveillance method is effective in this case. However, a simple error reduction method is useful for mixed
Co. Response functions for diverse diagnostic X-rays are almost indistinguishable and an unfolding using error reduction method is not sufficiently worked. The spectrum surveillance method is effective in this case. However, a simple error reduction method is useful for mixed  rays. For both techniques, the neural network method is promising.
rays. For both techniques, the neural network method is promising.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kosako, Toshiso*
Proceedings of International Symposium commemorating the First Anniversary of the Foundation of GoNERI "Key to the Future; Energy Security and Nuclear Education & Research", p.247 - 252, 2008/10
Neutron dose evaluation method which flexibly respond to an alteration of neutron field is developing. The mulitidetector method is introduced. The method uses a convex hull in a topological vector space composed of the ratio of multi detector outputs and objective quantities. The convex hull provides range of possible conversion factor to obtain objective quantity based on the circumstance condition. The convex hull is sophisticated with elemental neutron spectra group of respective neutron field. Mixed gas proportional counter is applied to validate the effectively of the dose evaluation method with a convex hull.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Usui, Toshihide
Proceedings of 2nd Asian and Oceanic Congress Radiological Protection (AOCRP-2) (CD-ROM), p.1175 - 1181, 2006/10
no abstracts in English