Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kikuchi, Norihiro; Doda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Dai-23-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2018/06
For the thermal-hydraulic design regarding a fuel assembly of sodium-cooled fast reactors, a subchannel analysis code ASFRE has been developed by JAEA. ASFRE was applied to numerical simulations of several kinds of water and sodium experiments as its validation studies and it was confirmed that pressure drops and temperature distributions measured in the experiments can be well reproduced. To enhance safety of sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is required to evaluate thermal-hydraulics in a core during decay heat removal by natural circulation. It is necessary to estimate radial heat transfer phenomena between fuel assemblies. In this study, a numerical simulation of a 37-pin bundle sodium experiment with radial heat flux was carried out and it was confirmed that ASFRE can be qualitatively reproduced temperature distributions in a fuel assembly affected by radial heat transfer.
Kikuchi, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*
Dai-21-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2016/06
For the thermal-hydraulic design and safety assessment regarding a fuel assembly of sodium-cooled fast reactors, a subchannel analysis code ASFRE has been and is continuously developed in JAEA. In the numerical simulation of ASFRE confirmed that the tendency to overestimate the maximum coolant temperature in a fuel assembly still remains. In this study, Distributed Resistance Model (DRM), which deals with wire-spacer wrap volumetric effect in subchannels on peripheral and axial directions, was modified and its calibration factor was optimized in order to improve the prediction accuracy of the maximum coolant temperature. A numerical simulation of a 37-pin bundle sodium experiment was also carried out and the result showed the validity of the modified DRM.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Imai, Yasutomo*; Ito, Masahiro*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1702, p.040011_1 - 040011_4, 2015/12
A numerical simulation system, which consists of a deformation analysis program and three kinds of thermal-hydraulics analysis programs, is being developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to offer methodologies to clarify thermal-hydraulic phenomena in fuel assemblies of sodium-cooled fast reactors under various operating conditions including fuel deformation. This paper gives a summary of numerical methods of component programs of the system and their validation studies.
 Li(d,t)
Li(d,t) Li reaction
Li reactionHashimoto, Takashi; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Jeong, S.-C.*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Nomura, Toru*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 674(4-5), p.276 - 280, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.15(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The excitation function of the  Li(d,t)
Li(d,t) Li reaction was directly measured using
Li reaction was directly measured using  Li beams at E
Li beams at E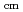 = 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, 0.8, 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2 MeV with CD
= 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, 0.8, 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2 MeV with CD targets. The beam energies covered the Gamow peaks for 1
targets. The beam energies covered the Gamow peaks for 1 3
3 10
10 K. Large cross sections were observed at around E
K. Large cross sections were observed at around E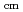 = 0.8 MeV, implying a resonance state located at 22.4 MeV in
= 0.8 MeV, implying a resonance state located at 22.4 MeV in  Be. The present astrophysical reaction rate is higher in one order magnitude than the presently adopted rate at around 1
Be. The present astrophysical reaction rate is higher in one order magnitude than the presently adopted rate at around 1 10
10 K.
K.
Takata, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Akira; *
JNC TN9400 2001-125, 184 Pages, 2002/03
In a steam generator using liquid sodium, water intensely reacts with sodium when it leaked out from a heat transfer tube. It is important to evaluate thermal influence of the sodium-water reaction to surrounding tubes and the shell. In the past, evaluations of this phenomenon have been carried out based on experimental evidence. However it is difficult to predict the phenomena in different conditions such as configuration of a heat tube and change of operating condition. Furthermore, experiments using sodium are expensive in general. Hence, the quantification of the sodium-water reaction by a numerical method is desirable. In this study, a multi-dimensional sodium-water reaction analysis code SERAPHIM (Sodium-watEr Reaction Analysis : PHysics of Interdisciplinary Multi-phase flow) has been developed. This code has two sodium-water reaction models. 0ne is a surface reaction model, which is assumed that liquid sodium reacts with steam vapor on the surface. The other is a gas-phase reaction, in that vaporized sodium reacts with steam vapor. As a result of preliminary analyses of sodium-water reaction in a steam generator (SG) of LMFR with SERAPHIM code, (1)Surface reaction is dominant within 100msec after steam is leaked. (2)Maximum temperature is approximately 1200 C in analyses. (3)Maximum temperature has little sensitivity on a initial pressure in SG and a heat coefficient between liquid and gas phase. (4)Configuration of the tube and leak ratio have affected with a expansion of gas area. And it has been demonstrated that a sodium-water reaction in SG can be comprehended and integrity of the tube can be estimated by SERAPHIM code.
C in analyses. (3)Maximum temperature has little sensitivity on a initial pressure in SG and a heat coefficient between liquid and gas phase. (4)Configuration of the tube and leak ratio have affected with a expansion of gas area. And it has been demonstrated that a sodium-water reaction in SG can be comprehended and integrity of the tube can be estimated by SERAPHIM code.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; *
JNC TN9400 2001-114, 100 Pages, 2001/10
A whole core thermal-hydraulic analysis program ACT is being developed for the purpose of evaluating detailed in-core thermal hydraulic phenomena of fast reactors including the effect of the flow between wrapper-tube walls (inter-wrapper flow) under various reactor operation conditions. As appropriate boundary conditions in addition to a detailed modeling of the core are essential for accurate simulations of in-core thermal hydraulics, ACT consists of not only fuel assembly and inter-wrapper flow analysis modules but also a heat transport system analysis module that gives response of the plant dynamics to the core model. This report describes incorporation of a simplified model to the fuel assembly analysis module and program parallelization by a message passing method toward large-scale simulations. ACT has a fuel assembly analysis module which can simulate a whole fuel pin bundle in each fuel assembly of the core and, however, it may take much CPU time for a large-scale core simulation. Therefore, a simplified fuel assembly model that is thermal-hydraulically equivalent to the detailed one has been incorporated in order to save the simulation time and resources. This simplified model is applied to several parts of fuel assemblies in a core where the detailed simulation results are not required. With regard to the program parallelization, the calculation load and the data flow of ACT were analyzed and the optimum parallelization has been done including the improvement of the numerical simulation algorithm of ACT. Message Passing Interface (MPI) is applied to data communication between processes and synchronization in parallel calculations. Parallelized ACT was verified through a comparison simulation with the original one. In addition to the above works, input manuals of the core analysis module and the heat transport system analysis module have been prepared.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; ; *; *
JNC TN9400 2001-111, 192 Pages, 2001/09
The feasibility study (Phase I) has been carried out at JNC to build up new design concepts of commercialized fast reactors from the viewpoint of economy, safety, effective use of resources, reduction of environmental burden and nuclear non-proliferation. This report describes the results of the investigation related to core/fuel-assembly thermal-hydraulics that was performed in fiscal 2000 as a part of the feasibility study. A numerical analysis method was developed for the coated-particle-type fuel assembly in the helium-gas-cooled fast reactor and a parametric study was performed using it. It revealed that with proper form pressure losses at inlet and outlet surfaces of the fuel region it is possible to control flow distribution under the rated power operation condition and that the decay heat removal may fail if the natural circulation is driven only by heat generation in the fuel region. A detailed numerical analysis of local fuel region was also carried out. The characteristics of coolant flow/temperature fields, particle-surface temperature distribution and the maximum temperature in the fuel particle were grasped and the applicability of the pressure drop correlation to such porous media was onfirmed. A subchannel analysis code ASFRE was applied to calculations of flow and temperature fields in a fuel assembly with inner duct in sodium cooled reactors, which is examined for re-criticality elimination. The calculation results showed that the peak coolant temperature was higher than that of the normal fuel assembly (without inner duct) under the same power-to-flow ratio condition and its temperature difference becomes much larger as the number of fuel pins decreases.The same tendency was observed in the case of lateral skew power profile in the fuel assembly.In this case, the difference of the peak temperatures between fuel assemblies with/without inner duct is almost proportional to the peaking factor. A parametric analysis was carried out for an ...
 IWGAR ] Benchmark calculation)
IWGAR ] Benchmark calculation)Takata, Takashi; Yamaguchi, Akira; *
JNC TN9400 2001-086, 60 Pages, 2001/09
A benchmark problem was proposed to reproduce an experiment for target membrane structure cooling of Accelerator Driven System at the 10th meeting of IWGAR (International Working Group of Advanced Nuclear Reactors Thermal Hydraulic) by the fluid Phenomena in Energy Exchnges Section of IAHR (International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research). THe benchmark calculation has been carried out with AQUA and FLUENT codes to estimate the code validity for liquid metal thermal-hydraulics application. As a result of comparison between numerical analyses and experiment, it is concluded as follows: (1)Inlet flow rate at the distributing grid much affects a coolant temperature and temperature pulsation near the membrane. The coolant temperature descreases and the pulsation decays rapidly as the flow rate toward the membrane center increases. (2)On downstream of the distributing grid, numerical results agree with experimental data except that numerical analysis tends to overestimate the coolant temperature pulsation. Numerical results show that the decrease of coolant temperature and the dissipation of pulsation tend to be underestimated when the flow rate toward the membrane center increases. (3)In FLUENT code, the dissipation of coolant temperature is underestimated more than in AQUA code because FLUENT code tends to overestimate the flow rate toward the membrane center. But the same tendency of the dissipation behavior is shown in AQUA code. (4)A turbulent model is less influenced on the coolant behavior in this benchmark analysis. Because Prandtl (Pr) number of liquid metal is low and the turbulent flow is not developed sufficiently in the condition of the experiment.
Koike, Kazuhiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Satoru; Namekawa, Takashi; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Hashimoto, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyatake, Hiroari; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; Nomura, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Li(d,t)(d,p)(d,
Li(d,t)(d,p)(d, ) reaction cross sections
) reaction cross sectionsHashimoto, Takashi; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Jeong, S.-C.*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Nomura, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Naganuma, Masayuki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Li(d,t)
Li(d,t) Li reaction
Li reactionHashimoto, Takashi; Miyatake, Hiroari; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Osa, Akihiko; Matsuda, Makoto; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Li(d,t),(d,p),(d,
Li(d,t),(d,p),(d, ) reactions
) reactionsHashimoto, Takashi; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Jeong, S.-C.*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Nomura, Toru*; Okada, Masayuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Imai, Yasutomo*
no journal, ,
A numerical simulation system is being developed in order to offer methodologies to clarify thermal-hydraulic phenomena in fuel subassemblies of sodium-cooled fast reactors under various operating conditions such as normal operation, transient condition or deformed geometry condition from the viewpoint of the assessment of fuel pin structure integrity. As a part of this simulation system development, a coupling method of thermal-hydraulic analysis with fuel deformation analysis was implemented and was applied to a high burn-up fuel assembly analysis for the method verification.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
Adoption of higher burn-up core can be considered as one of effective methods to enhance economic competitiveness for the commercialization of sodium-cooled fast reactors and it becomes possible with evaluating and confirming structural integrity of fuel assemblies under high burn-up conditions. A numerical simulation system, which consists of a deformation analysis program and three kinds of thermal-hydraulics analysis programs, is being developed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in order to offer methodologies to clarify thermal-hydraulic phenomena in fuel assemblies under various operating conditions. In this paper, an analysis method of thermal-hydraulics in a wire-wrapped and deformed fuel pin bundle using two kinds of component programs of the numerical simulation system and its application to an irradiated fuel assembly analysis are described.
Yamada, Fumiaki; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Kato, Mitsuya*; Arikawa, Mitsuhiro*
no journal, ,
In this report that review on the safety evaluation for the consequence of Large Pipe Break in Primary Heat Transport System on the Monju used experimental data.
Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Sakae, Kazuaki*; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Nagae, Yuji
no journal, ,
Sakae, Kazuaki*; Hashimoto, Akihiko*; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English