Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Naka, Yasuhito*; Nishijima, Haruyuki*; Imabayashi, Shinichiro*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji
Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 51(9), p.726 - 731, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.13(Engineering, Chemical)Thermochemical hydrogen production by the iodine-sulfur process decomposes water into hydrogen and oxygen by combining the chemical reactions of iodine and sulfur. Two types of acids are produced through the Bunsen reaction. To improve the performance of this reaction, ion-exchange membranes for the membrane Bunsen reaction should be developed. In the present study, a cation-exchange membrane was prepared by using a radiation-graft polymerization method. It was found that a divinylbenzene crosslinking procedure was very effective in reducing water permeation through the membrane, and the membrane Bunsen reaction was successfully carried out by using the developed crosslinked membrane. Therefore, the developed crosslinked membrane is a potential candidate for cation-exchange membranes for the membrane Bunsen reaction.
 -permselective silica membrane for the separation of H
-permselective silica membrane for the separation of H from the hydrogen iodide decomposition reaction in the iodine-sulfur process
from the hydrogen iodide decomposition reaction in the iodine-sulfur processMyagmarjav, O.; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(9), p.6012 - 6023, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:49.58(Chemistry, Physical)Gonda, Mayuki; Kunii, Katsuhiko; Nakajima, Hidemitsu; Ikeda, Kiyoshi; Itabashi, Keizo; Koike, Akemi*; Igarashi, Ayumi*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Grey Literature (GL-12), p.113 - 117, 2011/00
Circulation of scientific information improves internationally today, and English which is "universal language" takes the leading part for scientific communication. On the other hand, non-English articles are still "gray literatures" due to language barriers though physical circulation improves as well as English articles. In the International Nuclear Information System (INIS) database operated by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), bibliographic information such as title and abstract etc. is written in English. This feature of the INIS database contributes to international circulation of scientific information of the nuclear field. However, titles of journals written by non-English language were described by transliterated Roman alphabet, non-native users cannot understand natures and subjects of journals written by non-English language. Non-native users cannot understand the nature of the journal with this journal title description, and then they fail to get the useful article. This language barrier should be broken through as soon as possible for circulation improvement of journals written by non-English language. So we develop a special journal titles translation list of journals written in Japanese for the INIS database, as attempt to improve circulation of articles in journals written by non-English language. We will release this list on the INIS database for circulation improvement of journals written by non-English language, and we will implement the list into the database for user's convenience in the future.
Kodaira, Takahide; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,  , ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting.
, ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting.
Kodaira, Takahide; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by using methods of radiation crosslinking and/or radiation graft polymerization. Our preliminary experiments made it possible to confirm controllability of the degree of grafting,  , ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting. Importantly, controlling the fixed-charge density of the membrane should both lower permeability of SO
, ion exchange capacity by varying the conditions of the grafting. Importantly, controlling the fixed-charge density of the membrane should both lower permeability of SO and enhance the transport number of H
and enhance the transport number of H .
.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
There has been a strong motivation to develop new cation exchange membranes suitable for the Bunsen reaction in the thermochemical water splitting IS process. We prepared cation exchange membranes by a radiation grafting polymerization method. The grafting reaction into a poly(ethylene-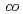 -tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The membrane had an ion exchange capacity of 2.17 mmol g
-tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The membrane had an ion exchange capacity of 2.17 mmol g while Nafion212 possessed 0.90 mmol g
while Nafion212 possessed 0.90 mmol g that is less than half of that for the grafted membrane. Both these membranes exhibited a similar water uptake, but the grafted membrane showed lower water permeation than Nafion212.
that is less than half of that for the grafted membrane. Both these membranes exhibited a similar water uptake, but the grafted membrane showed lower water permeation than Nafion212.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by radiation-induced graft polymerization. The water permeation of the grafted membrane was lower than that of Nafion 212 under the condition of a similar water uptake.
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane, which renders separation procedures unnecessary. As part of a JST-ALCA project, therefore, we have been developing ion exchange membranes for this application by radiation-induced graft polymerization. The water permeation of the grafted membrane was lower than that of Nafion 212 under the condition of a similar water uptake.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Kono, Nobuho*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
In the thermochemical water splitting IS process, the Bunsen reaction (SO + I
+ I + 2H
+ 2H O = H
O = H SO
SO + 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane. As part of an ongoing JST-ALCA project, therefore, we developed ion exchange membranes for this reaction by radiation-induced graft polymerization, investigating their water permeation properties by the pervaporation method. Our membrane preparation involves the
+ 2HI) needs to be achieved in an electrochemical cell with an ion exchange membrane. As part of an ongoing JST-ALCA project, therefore, we developed ion exchange membranes for this reaction by radiation-induced graft polymerization, investigating their water permeation properties by the pervaporation method. Our membrane preparation involves the  -ray-induced grafting of styrene and divinylbenzene into poly(ethylene-
-ray-induced grafting of styrene and divinylbenzene into poly(ethylene-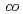 -tetrafluoroethylene) films and the subsequent sulfonation. Water permeate flux values at 25
-tetrafluoroethylene) films and the subsequent sulfonation. Water permeate flux values at 25 C were 7.4 and 19 kg/m
C were 7.4 and 19 kg/m h through the grafted membrane and Nafion 212 at the same water uptake (37%), respectively.
h through the grafted membrane and Nafion 212 at the same water uptake (37%), respectively.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Oura, Kotone*; Ono, Ryuhei*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kodaira, Takahide*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Oura, Kotone*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nomura, Mikihiro*
no journal, ,
There has been a strong motivation to develop new cation exchange membranes suitable for the Bunsen reaction in the thermochemical water splitting IS process. We prepared cation exchange membranes by a radiation grafting polymerization method. The grafting reaction into a poly(ethylene-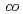 -tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film was performed in a mixture of styrene and divinylbenzene (DVB). The grafted membrane showed two times lower water permeation flux and three times higher activation energy of water diffusion than Nafion212 though both the membranes exhibited a similar water uptake. Therefore, the DVB-based crosslinking in the graft polymer would restrict water permeation through the membrane.
Ikeda, Ayumi*; Ono, Ryuhei*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
In the IS process, the improvement of efficiency and the downsizing can be achieved if equilibrium inversion rate of HI decomposition is improved by using membrane reactor with hydrogen separation membrane. In this paper, the application to the silica hybrid membrane prepared by counter diffusion CVD method was investigated. As a result, we can obtain the H /HI permeation rate, 6820 and the H
/HI permeation rate, 6820 and the H permeance, 5.0
permeance, 5.0 10
10 mol m
mol m s
s Pa
Pa at 400
at 400  C, indicating that this membrane can be applied to this system. In addition, relation between SF
C, indicating that this membrane can be applied to this system. In addition, relation between SF and HI permeance of membrane was investigated and verified to show the positive correlation. This result indicates that HI permeance of membrane can be evaluated by using SF
and HI permeance of membrane was investigated and verified to show the positive correlation. This result indicates that HI permeance of membrane can be evaluated by using SF permeance, which can be easily treated.
permeance, which can be easily treated.
Kodaira, Takahide*; Oura, Kotone*; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Ono, Ryuhei*; Matsuyama, Emi*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
Bunsen reactor in the IS process has a potential of the downsizing and the improvement of efficiency by using redox type reactor with an ion exchange membrane. The key to the performance of redox reactor is the development of the high performance ion exchange membrane. In this paper, we investigated the performance (proton transport number (t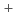 ) and water permeation factor (
) and water permeation factor ( )) of Nafion 212, which is the reference. As a result, t
)) of Nafion 212, which is the reference. As a result, t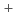 and
and  were 0.63 and 2.82, respectively, indicating that not only H
were 0.63 and 2.82, respectively, indicating that not only H but also I
but also I and water permeate through the membrane. The permeation of these components might cause the precipitation of sulfur and the rising of the voltage. Aftertime, we must new ion exchange membrane which can restrict the permeation of I
and water permeate through the membrane. The permeation of these components might cause the precipitation of sulfur and the rising of the voltage. Aftertime, we must new ion exchange membrane which can restrict the permeation of I and water.
and water.
 production from HI decomposition in the IS process
production from HI decomposition in the IS processMyagmarjav, O.; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
In this study, we have developed a highly hydrogen permeable silica membrane derived from hexyltrimethoxysilane as a Si precursor using porous alumina support. Modification of alumina support tubes in the absence of and in the presence of  -alumina coating was carried out by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition (CVD). A membrane with intermediate
-alumina coating was carried out by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition (CVD). A membrane with intermediate  -alumina layer showed higher H
-alumina layer showed higher H permeance (7.7
permeance (7.7  10
10 mol m
mol m s
s Pa
Pa ) than that formed directly on the
) than that formed directly on the  -alumina tube (3.8
-alumina tube (3.8  10
10 mol m
mol m s
s Pa
Pa ). It was found that the thickness of
). It was found that the thickness of  -alumina layer played an important role in the improvement of membrane permeation performance. Modified membrane based on
-alumina layer played an important role in the improvement of membrane permeation performance. Modified membrane based on  -alumina coating with a thickness of 1.5
-alumina coating with a thickness of 1.5  m exhibited H
m exhibited H /SF
/SF selectivity over 3000 at 270
selectivity over 3000 at 270 C, while maintaining H
C, while maintaining H permeance in the order of 10
permeance in the order of 10 mol m
mol m s
s Pa
Pa . The results led to the conclusion that the modified membrane is a promising candidate for further enhancement of HI decomposition in membrane reactor.
. The results led to the conclusion that the modified membrane is a promising candidate for further enhancement of HI decomposition in membrane reactor.
Myagmarjav, O.; Ikeda, Ayumi*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
no journal, ,
The thermal decomposition of hydrogen iodide (HI) to produce hydrogen in a membrane reactor was investigated using the separation characteristics of a silica membrane with the aim of improving the one-pass decomposition rate of HI decomposition reaction in the thermochemical IS process. The silica membranes were prepared by a counter diffusion chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of hexyltrimethoxysilane (HTMOS) using alumina porous support. The membrane reactor phenomenon was evaluated using determined H production rate from HI decomposition at 400
production rate from HI decomposition at 400 C. It was found from experiments that produced H
C. It was found from experiments that produced H rate was approximately 1.5 mL min
rate was approximately 1.5 mL min in permeated site. Hydrogen was successfully produced and extracted from the HI decomposition membrane reactor with a utilization of the HTMOS silica membrane. The HTMOS silica membrane was effective for the HI decomposition at higher reaction temperature of 400
in permeated site. Hydrogen was successfully produced and extracted from the HI decomposition membrane reactor with a utilization of the HTMOS silica membrane. The HTMOS silica membrane was effective for the HI decomposition at higher reaction temperature of 400 C in the membrane reactor.
C in the membrane reactor.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Matsumoto, Ayumu; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ikeda, Yuji*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
For the decommissioning of "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (F1NPS)", widely basic R&D and matting for actual application for decommissioning technology will be strongly required. CLADS/JAEA is one of the key institute for strategic promotion of Decommissioning Science on F1NPS. As for the development of rapid, easy, onsite and in-situ remote diagnostic/analysis techniques under extremely high radioactive condition, the concept of probing by light and diagnostic by light with radiation resistant optical fiber will be one of the simple, powerful and applicable choices as the innovative development based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology. Optical fiber based LIBS is developed for in-core and in-situ elemental analysis of debris and its activity is performed under severe environmental conditions such as high radiation field of about 10kGy/h and under water. Long pulse laser, microwave assisted LIBS and microchip laser are also introduced for more high sensitivity.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Oba, Hironori; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa; Matsumoto, Ayumu*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Ikeda, Yuji*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Matsumoto, Ayumu*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Taira, Takunori*; Ikeda, Yuji*
no journal, ,
Masuda, Shiho; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakai, Eiichi; Nemoto, Hideyuki; Ikeda, Yujiro; Haga, Katsuhiro
no journal, ,
In the Materials and Life science experimental Facility at J-PARC, pulsed neutrons are provided by a mercury target via spallation reactions. During the target vessel replacement, gaseous spallation products are released from the mercury circulation system to outside. The release of radioactive gases needs to be reduced to a negligibly small level by a purging process in advance of replacement. The radioactivity of noble gases decreased by the purging process while that of tritium was almost unchanged. It is considered that most of tritium produced in mercury is accumulated in the vessel made of stainless-steel and is gradually desorbed during the purging and the vessel replacement. However, there have been no effective data associated with tritium behavior in an environment of mercury spallation target. Then, authors decided to develop an experimental system to understand these phenomena quantitatively and to discuss procedures to minimize tritium release during the vessel replacement. As a first step, we start experiments using deuterium before using tritium. Accumulation and release behaviors of deuterium to stainless-steel are examined under vacuum, controlled humidity and mercury coexistence conditions. Results are expected to be used to establish safer the target vessel replacement.