Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Ikeda, Atsushi; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
Results of the URASOL project aimed at evaluating the generation and dispersion of radioactive aerosols during the cutting of fuel debris, a key issue in the decommissioning of the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), are presented in this report. Characterization of aerosols generated during heating and mechanical cutting of simulated fuel debris in terms of mass concentration, real-time number density, mass-based particle size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties is reported. In the heating tests, an increase in particle size with increasing temperature was observed, and in terms of particle number density, the case using depleted uranium simulated fuel debris had a smaller number density than the test using Hf-containing simulated fuel debris. In mechanical cleavage, the aerodynamic median mass diameter of the aerosol was almost the same for the radioactive and non-radioactive samples (about 3.7 4.4
4.4  m).
m).
Ikeda, Yoichi*; Umemoto, Yoshihiko*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Hashimoto, Yuki*; Kitazawa, Takafumi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Zn
Zn
Kitazawa, Takafumi; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Matsuo, Akira*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kindo, Koichi*; Nambu, Yusuke*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(8), p.085105_1 - 085105_7, 2023/08
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
One of the important challenges for the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is the fuel debris retrieval. The URASOL project, which is undertaken by a French consortium consisting of ONET Technologies, CEA, and IRSN for JAEA/CLADS, is dedicated to acquiring basic scientific data on the generation and characteristics of radioactive aerosols from the thermal or mechanical processing of fuel debris simulant. Heating process undertaken in the VITAE facility simulates some representative conditions of thermal cutting by LASER. For mechanical cutting, the core boring technique is implemented in the FUJISAN facility. Fuel debris simulants have been developed for inactive and active trials. The aerosols are characterized in terms of mass concentration, real time number concentration, mass size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties. The chemical characterization aims at identifying potential radioactive particles released and the associated size distribution, both of which are important information for assessing possible safety and radioprotection measures during the fuel debris retrieval operations at 1F.
 continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates (
continuous air monitor for the measurement of highly radioactive alpha-emitting particulates ( -aerosols) under high humidity environment
-aerosols) under high humidity environmentTsubota, Yoichi; Honda, Fumiya; Tokonami, Shinji*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Ikeda, Atsushi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1030, p.166475_1 - 166475_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the long-lasting decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), the dismantling of nuclear fuel debris (NFD) remaining in the damaged reactors is an unavoidable but significant issue with many technical difficulties. The dismantling is presumed to involve mechanical cutting, generating significant concentrations of particulates containing  -radionuclides (
-radionuclides ( -aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with
-aerosols) that pose significant health risk upon inhalation. In order to minimize the radiation exposure of workers with  -aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of
-aerosols during the dismantling/decommissioning process at 1F, it is essential to monitor the concentration of  -aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an
-aerosols at the point of initial generation, i.e. inside the primary containment vessels (PCV) of the damaged reactors. Toward this end, an  monitoring system for
monitoring system for  -aerosols (
-aerosols ( alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of
alpha air monitor: IAAM) was developed and its technical performance was investigated under the conditions expected for the actual environments at 1F. IAAM was confirmed to fulfill four technical requirements: (1) steady operation under high humidity, (2) operation without using filters, (3) capability of measuring a high counting rate of  -radiation, and (4) selective measurement of
-radiation, and (4) selective measurement of  -radiation even under high radiation background with
-radiation even under high radiation background with  /
/ -rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring
-rays. IAAM is capable of selectively measuring  -aerosols with a concentration of 3.3
-aerosols with a concentration of 3.3  10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with
or higher without saturation under a high humid environment (100%-relative humidity) and under high background with  /
/ -radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of
-radiation (up to 100 mSv/h of  -radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for
-radiation). These results demonstrate promising potential of IAAM to be utilized as a reliable monitoring system for  -aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
-aerosols during the dismantling of NFD, as well as the whole long-lasting decommissioning of 1F.
Sombillo, D. L. B.*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Sato, Toru*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 104(3), p.036001_1 - 036001_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:61.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics) O
O (R: Y, Lu) investigated by transmission electron microscopy
(R: Y, Lu) investigated by transmission electron microscopyHoribe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Maeno, Hiroshi*; Murakami, Yasukazu*
Ferroelectrics, 584(1), p.20 - 30, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Temperature dependence of charge-ordered crystal structures and domain structures in RFe O
O (R: Y and Lu) was investigated by energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy, combined with conventional transmission electron microscopy. The presence of three-dimensional to two-dimensional charge ordering transition were observed in both RFe
(R: Y and Lu) was investigated by energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy, combined with conventional transmission electron microscopy. The presence of three-dimensional to two-dimensional charge ordering transition were observed in both RFe O
O on heating. Furthermore, real-space images obtained with the energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy revealed that YRFe
on heating. Furthermore, real-space images obtained with the energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy revealed that YRFe O
O has less anisotropic nanometer-scale charge-ordered domains than LuRFe
has less anisotropic nanometer-scale charge-ordered domains than LuRFe O
O . These findings in RFe
. These findings in RFe O
O indicate the importance of the interchange interactions between Fe-O bilayers in addition to those within bilayers in the structural phase transitions associated with charge ordering in this system.
indicate the importance of the interchange interactions between Fe-O bilayers in addition to those within bilayers in the structural phase transitions associated with charge ordering in this system.

Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ueta, Daichi*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Nakao, Akiko*; Munakata, Koji*; Ohara, Takashi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Single-crystal neutron diffraction study was performed for anomalous antiferromagnetic ordering in a heavy-electron superconductor CeNiGe . We observed incommensurate magnetic Bragg reflections characterized with the propagation vector of
. We observed incommensurate magnetic Bragg reflections characterized with the propagation vector of 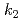 = (0; 0:41; 1=2) below the N
= (0; 0:41; 1=2) below the N el temperature of 5 K, while there is no significant magnetic reflection at the commensurate propagation vector of
el temperature of 5 K, while there is no significant magnetic reflection at the commensurate propagation vector of 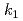 = (1; 0; 0) at which another magnetic reflection was observed in the previous neutron diffraction study with a polycrystalline sample. From the single crystal study, we suggest that the magnetic phase of CeNiGe
= (1; 0; 0) at which another magnetic reflection was observed in the previous neutron diffraction study with a polycrystalline sample. From the single crystal study, we suggest that the magnetic phase of CeNiGe at ambient pressure is characterized only by the incommensurate propagation vector
at ambient pressure is characterized only by the incommensurate propagation vector 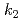 .
.
Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
 P
P
Araki, Shingo*; Hayashida, Minami*; Nishiumi, Naoto*; Manabe, Hiroki*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Kobayashi, Tatsuo*; Murata, Keizo*; Inada, Yoshihiko*; Wi niewski, P.*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
niewski, P.*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(2), p.024705_1 - 024705_8, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary) P
P under high pressure
under high pressureAraki, Shingo*; Hayashida, Minami*; Nishiumi, Naoto*; Manabe, Hiroki*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Kobayashi, Tatsuo*; Murata, Keizo*; Inada, Yoshihiko*; Wi niewski, P.*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
niewski, P.*; Aoki, Dai*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.011081_1 - 011081_6, 2014/06
 by precise dc magnetization measurements
by precise dc magnetization measurementsShimizu, Yusei*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Letters, 109(21), p.217001_1 - 217001_5, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:67.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Nishihata, Yasuo; Maeda, Daisuke*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kano, Jun*; Kambe, Takashi*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(3), p.033704_1 - 033704_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.37(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Exchange bias (EB) behavior has been observed for multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small 
 ions (
ions ( =Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (
=Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (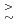 1 kOe) below
1 kOe) below  100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller
100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller 
 ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the
ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the  -site in this series.
-site in this series.

Shimizu, Yusei*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Wakabayashi, Takumi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Tenya, Kenichi*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(9), p.093701_1 - 093701_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.77(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Shimizu, Yusei*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Wakabayashi, Takumi*; Tenya, Kenichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA100_1 - SA100_3, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Shimizu, Yusei*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Wakabayashi, Takumi*; Tenya, Kenichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 273, p.012084_1 - 012084_4, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.76(Physics, Condensed Matter) O
O
Horibe, Yoichi*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 82(18), p.184119_1 - 184119_5, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The low-temperature superstructure of YFe O
O was carefully investigated by transmission electron microscopy. We found that the unique superstructure at about 100 K is characterized by
was carefully investigated by transmission electron microscopy. We found that the unique superstructure at about 100 K is characterized by  /14 2/7 1/14-type superlattice reflection spots, suggesting the presence of charge reordering process. The low-temperature high-resolution images clearly show superlattice modulations in Y-O layers as well as Fe-O layers. The modification of intra-bilayer charge interactions due to lattice distortions in Y-O layers is discussed to play a crucial role in the stabilization of long-periodic superstructures at low temperatures.
/14 2/7 1/14-type superlattice reflection spots, suggesting the presence of charge reordering process. The low-temperature high-resolution images clearly show superlattice modulations in Y-O layers as well as Fe-O layers. The modification of intra-bilayer charge interactions due to lattice distortions in Y-O layers is discussed to play a crucial role in the stabilization of long-periodic superstructures at low temperatures.
 O
O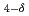
Horibe, Yoichi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Physical Review B, 80(9), p.092104_1 - 092104_4, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:57.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effects of oxygen deficiency on charge ordering were investigated by transmission electron microscopy at various deficiencies and temperatures of YFe O
O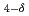 . We found that the detailed nature of the charge ordering structures is associated with changes in the superlattice reflections and diffuse scattering. They go from (1/3 1/3 1/2)-type superlattice reflection to (1/3 1/3
. We found that the detailed nature of the charge ordering structures is associated with changes in the superlattice reflections and diffuse scattering. They go from (1/3 1/3 1/2)-type superlattice reflection to (1/3 1/3 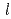 )-type straight-type diffuse scattering, then to zigzag-type diffuse scattering. With the oxygen deficiencies increased, the interchange correlation of Fe-O bilayers obviously decreases, yet the triple super periodicity along [110]
)-type straight-type diffuse scattering, then to zigzag-type diffuse scattering. With the oxygen deficiencies increased, the interchange correlation of Fe-O bilayers obviously decreases, yet the triple super periodicity along [110] remains unchanged. These findings on frustrated ferritesindicate the stability of in-plane threefold charge ordering and the importance of the interchange interaction between bilayers in the structural phase transitions.
remains unchanged. These findings on frustrated ferritesindicate the stability of in-plane threefold charge ordering and the importance of the interchange interaction between bilayers in the structural phase transitions.
 O
O (
( =Cu, Co) revealed by energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy
=Cu, Co) revealed by energy-filtered transmission electron microscopyMatsuo, Yoji*; Hirata, Akihiko*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Ferroelectrics, 380(1), p.56 - 62, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Diluted effect on the charge ordered (CO) structure in dielectric materials LuFe O
O (
( =Cu, Co) were investigated by an energy-filtered transmission electron microscope (TEM), in combination with a conventional TEM. It is revealed that partial substitution of Cu
=Cu, Co) were investigated by an energy-filtered transmission electron microscope (TEM), in combination with a conventional TEM. It is revealed that partial substitution of Cu and Co
and Co for Fe
for Fe in LuFe
in LuFe O
O destabilized the CO structure. In LuFeCuO
destabilized the CO structure. In LuFeCuO , there exist characteristic zigzag-shaped diffuse streaks and diffuse spots at the h/3-
, there exist characteristic zigzag-shaped diffuse streaks and diffuse spots at the h/3- h/3-
h/3- 0-type positions (h: integer,
0-type positions (h: integer,  =0.06) in reciprocal space, which originate from static cationic ordering of Fe
=0.06) in reciprocal space, which originate from static cationic ordering of Fe and Cu
and Cu ions in the triangular lattice. Moreover, real-space images by the energy-filtered TEM revealed that nanometer-sized domain structures with the 5
ions in the triangular lattice. Moreover, real-space images by the energy-filtered TEM revealed that nanometer-sized domain structures with the 5 10 nm size are formed. In contrast, honeycomb-shaped diffuse streaks were found in LuFeCoO
10 nm size are formed. In contrast, honeycomb-shaped diffuse streaks were found in LuFeCoO , in which no domain structures are observed in real-space images.
, in which no domain structures are observed in real-space images.
 Mn
Mn O
O (0
(0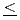 x
x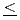 1)
1)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Michiuchi, Takamasa*; Yokota, Yusuke*; Okajima, Yuka; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Matsuo, Yoji*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 182(7), p.1611 - 1618, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:51.45(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have investigated the magnetic and dielectric properties of YbFe Mn
Mn O
O (0
(0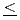 x
x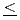 1), which is an Fe-site-substituted system of new multiferroic oxides RFe
1), which is an Fe-site-substituted system of new multiferroic oxides RFe O
O (R=Y, Ho-Lu). X-ray diffraction measurements show that a solid solution is formed between YbFe
(R=Y, Ho-Lu). X-ray diffraction measurements show that a solid solution is formed between YbFe O
O (x=0) and YbFeMnO
(x=0) and YbFeMnO (x=1) for 0
(x=1) for 0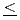 x
x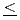 1. The valence of the Mn ion is determined to be
1. The valence of the Mn ion is determined to be  2+, consistently with the suppression of low-temperature magnetization by the Mn substitution. The magnetic transition temperature and the dielectric constant decrease monotonically with increasing x. This result plausibly confirms that the magnetic and dielectric properties in oxides isostructural with RFe
2+, consistently with the suppression of low-temperature magnetization by the Mn substitution. The magnetic transition temperature and the dielectric constant decrease monotonically with increasing x. This result plausibly confirms that the magnetic and dielectric properties in oxides isostructural with RFe O
O are governed by the electron transfer between Fe-site ions, unlike ordinary ferroelectrics and dielectrics, in which the ionic displacement plays a key role. The possibility for application is briefly discussed.
are governed by the electron transfer between Fe-site ions, unlike ordinary ferroelectrics and dielectrics, in which the ionic displacement plays a key role. The possibility for application is briefly discussed.