Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi; Yamasaki, Keizo*; Oki, Yuichi*; Osada, Naoyuki*
Hoken Butsuri, 43(4), p.333 - 340, 2008/12
To assess internal exposure due to inhalation of radioactive aerosols and gases generated in high-energy accelerator facilities, physicochemical properties such as particle size of aerosols and chemical form of gases are important information. We measured the particle size distribution and concentration of aerosols coexisting with radionuclide formed by high-energy radiation emission in the target room of LINAC and estimated the long term variation of particle size and concentration of radioactive aerosols in high-energy acceleration facilities.
Nakai, Satoru; Aoyama, Takafumi; Ito, Chikara; Yamamoto, Masaya; Iijima, Minoru; Nagaoki, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Atsuko; Onoda, Yuichi; Ohgama, Kazuya; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; et al.
Kosoku Jikkenro "Joyo" Rinkai 30-Shunen Kinen Hokokukai Oyobi Gijutsu Koenkai, 154 Pages, 2008/06
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Manabe, Kentaro; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Oki, Yuichi*; Iida, Takao*; Tanaka, Susumu*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 127(1-4), p.392 - 397, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)To estimate internal doses due to the inhalation of radionuclides produced by the nuclear spallation of the air nuclei in high-energy proton accelerator facilities, the physicochemical properties of radionuclides are very important. However, there is not enough information of the properties for airborne radioactive chlorine formed from argon gas in the air of a high-energy proton irradiation field. Thus we have measured the ratio of aerosol and gases of radioactive chlorine which are formed by irradiating argon gas-added air with a 48 MeV proton beam. In addition, the particle size distribution and chemical form of non-radioactive aerosol were examined. It was found that Cl-38 and Cl-39 exist as aerosol, acidic and non-acidic gases. The percentages of Cl-38 and Cl-39 aerosols are more than 70%. In total radioactive chlorine gas, about 30% and 70% are acidic and non-acidic gases, respectively. The concentration of non-radioactive aerosol had a peak at an aerodynamic diameter of 20-30 nm in the early irradiation period. The particle size of non-radioactive aerosol shifted to larger with time. After 10 min, the aerosols grew very slowly and many of the non-radioactive aerosols were distributed widely under 200 nm. This suggests that the diameter of the radioactive chlorine aerosol formed by the attachment of the radioactive chlorine to the non-radioactive aerosol around a beam line of the accelerator is much smaller than the default value adopted in ICRP Publication 66.
Takamura, Shuichi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Fujii, Takashi*; Fujiyama, Hiroshi*; Takabe, Hideaki*; Adachi, Kazuo*; Morimiya, Osamu*; Fujimori, Naoji*; Watanabe, Takayuki*; Hayashi, Yasuaki*; et al.
Kara Zukai, Purazuma Enerugi No Subete, P. 164, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu*; Iida, Takao*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 74(5), p.338 - 340, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.8(Chemistry, Physical)The operation of high-energy accelerators leads to the production of radiolytic noxious gases, such as ozone and nitrogen compounds in the air of the beam-line tunnels. Among nitrogen compounds, nitric acid is a principal radiolytic compound produced in large quantities. In the high-intensity proton accelerator, such as J-PARC, a very strong radiation environment leads to an abundant production of nitric acid. A quantitative assessment of the damage due to corrosion with nitric acid is essential for machine maintenance and information concerning the formation of nitric acid is a requisite for that. In this work, the G-value for nitric acid production was measured by irradiating atmospheric air with 48MeV-protons. The G-value was obtained to be 1.46 0.12. The G-value for nitric acid production obtained in this experiment was larger than the estimated value, but very close to the value of 1.5 given by irradiating the air with Co-60-
0.12. The G-value for nitric acid production obtained in this experiment was larger than the estimated value, but very close to the value of 1.5 given by irradiating the air with Co-60- rays.
rays.
Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Kaneto, Taihei*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 116(1-4), p.401 - 405, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.45(Environmental Sciences)The physicochemical property of radionuclides suspended in the air is an important parameter to evaluate internal doses due to the inhalation of the airborne radionuclides and to develop the air monitoring system in high-energy proton accelerator facilities. This study focuses on the property of radioactive airborne chlorine ( Cl and
Cl and 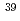 Cl) and sulfur (
Cl) and sulfur ( S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,
S) formed from Ar gas by irradiation with high-energy neutrons. As a result of the irradiation to a mixture of Ar gas and dry air,  Cl and
Cl and 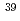 Cl existed as non-acidic gas and
Cl existed as non-acidic gas and  S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
S was present as acidic gas. Further, it was found that in the high-energy neutron irradiation to aerosol containing-Ar gas, the higher the amount of radioactive aerosols becomes, the lower that of radioactive acidic gas becomes.
Endo, Akira; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 256(2), p.231 - 237, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.83(Chemistry, Analytical)Size distributions of  Cl,
Cl, 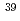 Cl,
Cl, 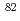 Br and
Br and 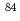 Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Iida, Takao*; Sato, Kaoru; Tsuda, Shuichi
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 56(4), p.615 - 620, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.41(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Formation mechanism and size distribution of radioactive aerosol particles generated in a high-energy neutron field were studied in order to evaluate a particle size parameter for internal dose evaluation in high-energy accelerator facilities. Argon gas containing DOP aerosols was irradiated by a 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron beam of TIARA. The number size distribution of the DOP aerosols and the activity-weighted size distribution of  Cl and
Cl and 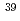 Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of
Cl aerosols, formed from the (n, 2np) and (n, np) reactions of  Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
Ar, were measured using an electrical low-pressure impactor. The activity-weighted size distribution of the radioactive aerosols was well explained by the simple attachment model of the radioactive atoms to the DOP aerosols.
 N species and noxious gases produced at the 12GeV proton synchrotron
N species and noxious gases produced at the 12GeV proton synchrotronKanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*; Endo, Akira; Numajiri, Masaharu*; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 247(1), p.25 - 31, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:56.08(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
 C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnels
C produced in the air in high energy proton accelerator tunnelsEndo, Akira; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 93(3), p.223 - 230, 2001/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.09(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
 C,
C,  N and
N and  O produced in air through nuclear spallation reactions by high energy protons
O produced in air through nuclear spallation reactions by high energy protonsEndo, Akira; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Kondo, Kenjiro*
Proceedings of 10th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-10) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2000/05
no abstracts in English
Endo, Akira; *; *; Kanda, Yukio*; *
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(3), p.210 - 218, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Manabe, Kentaro; Endo, Akira; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Kaneko, Hirohisa; Oki, Yuichi*; Osada, Naoyuki*; Kanda, Yukio*; Iida, Takao*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Osada, Naoyuki*; Oki, Yuichi*; Kanda, Yukio*; Yokoyama, Sumi; Sato, Kaoru; Manabe, Kentaro; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Endo, Akira; Tanaka, Susumu*; Kaneko, Hirohisa; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamasaki, Keizo*; Oki, Yuichi*; Osada, Naoyuki*; Yokoyama, Sumi; Yamada, Yuji*; Tokonami, Shinji*; Fukutsu, Kumiko*; Iida, Takao*; Rahman, N. M.*; Shimo, Michikuni*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Makino, Takayoshi; Okita, Takatoshi; Kato, Akebumi*; Suzuki, Yuichiro*; Minakawa, Susumu; Kashimura, Motoaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Osada, Naoyuki*; Oki, Yuichi*; Yamasaki, Keizo*; Yokoyama, Sumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamasaki, Keizo*; Oki, Yuichi*; Osada, Naoyuki*; Iida, Takao*; Shimo, Michikuni*; Yamada, Yuji*; Tokonami, Shinji*; Fukutsu, Kumiko*; Yokoyama, Sumi
no journal, ,
The physicochemical properties of radioactive aerosols are important factors to assess internal dose at high energy accelerator facilities. In Kyoto University Research Reactor Institute, a generation of radioactive aerosols in ADSR (Accelerator-Driven Subcritical Reactor) facilities was studied as part of the research project of ADSR. The generation of radioactive aerosols in high intensity irradiation fields of ADSR was simulated by irradiation of the target room air at LINAC. We measured the particle size of radioactive aerosols in the target room during the acceleration period. Natural radon aerosols in the target room grew to the larger size because of an attachment of radon daughters to non-radioactive aerosols. The particle size of the produced radioactive aerosols was also larger with time. This would mean that a formation mechanism of the radioactive aerosols produced at high energy accelerator facilities is the same as radon one.