Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.12025_1 - 12025_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:90.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)Recently, intensive neutron sources using deuteron accelerator have been proposed for various applications. Accurate and comprehensive deuteron nuclear data library over wide ranges of target mass number and incident energy are indispensable for the design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources. Thus, we have developed an integrated code system dedicated for analysis and prediction of deuteron-induced reactions, which is called DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System (DEURACS). In the present work, the analysis of  reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to
reactions is extended to higher incident energy up to nearly 100 MeV and also DEURACS is applied to 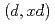 reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the
reactions at 80 and 100 MeV. The DEURACS calculations reproduce the experimental double-differential cross sections for the  and
and 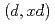 reactions well.
reactions well.
 reactions on
reactions on  Be and
Be and  C
CNakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
RCNP Annual Report 2016 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2017/05
We are conducting a theoretical research on deuteron-induced reaction together with Kyushu University and Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. The research outcomes achieved in fiscal year 2016 are summarized as a part of the annual report of RCNP. In recent years, accelerator neutron sources using  reactions on light nuclei (Li, Be, C, etc.) are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires accurate prediction of
reactions on light nuclei (Li, Be, C, etc.) are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires accurate prediction of  reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. Therefore, we have developed a physics-based computational code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In fiscal year 2016, we calculated double-differential neutron yields from deuteron bombardment on thick
reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. Therefore, we have developed a physics-based computational code system dedicated for deuteron-induced reactions, called DEURACS. In fiscal year 2016, we calculated double-differential neutron yields from deuteron bombardment on thick  Be and
Be and  C targets, and the calculation reproduced the experimental data quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. From the results, it has been found that DEURACS can accurately predict
C targets, and the calculation reproduced the experimental data quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. From the results, it has been found that DEURACS can accurately predict  reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. In addition, component-by-component analysis has revealed that the nonelastic breakup reactions make the most dominant contribution to neutron production.
reactions on light nuclei in a wide incident energy range. In addition, component-by-component analysis has revealed that the nonelastic breakup reactions make the most dominant contribution to neutron production.
 reactions on beryllium
reactions on berylliumKono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.165 - 170, 2016/09
For engineering design of deuteron accelerator neutron sources, accurate nuclear data of deuteron-induced reactions on neutron converter (Li, Be, C, etc.) and accelerator structure material (Fe, Cr, Ni, etc.) are indispensable. Therefore we have developed a computational code system based on physics models dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation. In the present study, we have analyzed the  reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV. Since there is a lot of experimental Thick Target Neutron Yields (TTNYs), double-differential
reactions on beryllium at incident deuteron energies up to 65 MeV. Since there is a lot of experimental Thick Target Neutron Yields (TTNYs), double-differential  cross sections are calculated by the code system and then are converted to TTNYs. It is found that the calculated TTNYs reproduce the experimental ones fairly well except in the low neutron energy region.
cross sections are calculated by the code system and then are converted to TTNYs. It is found that the calculated TTNYs reproduce the experimental ones fairly well except in the low neutron energy region.
 reactions on
reactions on  Be and
Be and  C at incident energies up to 50 MeV
C at incident energies up to 50 MeVNakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.014618_1 - 014618_9, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:90.01(Physics, Nuclear)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) from deuteron bombardment on thick Be and C targets are analyzed using the DEURACS (DEUteron-induced Reaction Analysis Code System). The calculated TTNYs reproduced the experimental ones quantitatively well in the incident energy range up to 50 MeV. In addition, it was found that the proton stripping reaction makes the most dominant contribution to neutron production. From the analysis, we conclude that the DEURACS is applicable to  reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
reactions and modeling of the stripping reaction is essential to predict neutron production yields accurately.
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Kono, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 122, p.04004_1 - 04004_9, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:88.78(Physics, Nuclear)In recent years, accelerator neutron sources using deuteron-induced reactions on  Li,
Li,  Be,
Be,  C, etc., are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires deuteron nuclear data in a broad incident energy range. We have developed a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation in combination with some theoretical models. The code system has been applied to analyses of double-differential
C, etc., are proposed for applications in various fields. Engineering design of such facilities requires deuteron nuclear data in a broad incident energy range. We have developed a computational code system dedicated for deuteron nuclear data evaluation in combination with some theoretical models. The code system has been applied to analyses of double-differential 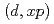 cross sections for
cross sections for  C,
C,  Al, and
Al, and  Ni at incident energies up to 100 MeV. On the other hand, there is few experimental double-differential
Ni at incident energies up to 100 MeV. On the other hand, there is few experimental double-differential  cross sections. Therefore, double-differential thick target neutron yields for light nuclei such as
cross sections. Therefore, double-differential thick target neutron yields for light nuclei such as  Be and
Be and  C are calculated and compared with experimental data. The presentation will show the validation result of the present modelling for nucleon emissions from deuteron-induced reactions through comparison with available experimental data.
C are calculated and compared with experimental data. The presentation will show the validation result of the present modelling for nucleon emissions from deuteron-induced reactions through comparison with available experimental data.
Kai, Takeshi; Tokuhisa, Atsushi*; Moribayashi, Kengo; Fukuda, Yuji; Kono, Hidetoshi; Go, Nobuhiro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(9), p.094301_1 - 094301_5, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tokuhisa, Atsushi*; Taka, Junichiro*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Go, Nobuhiro*
Acta Crystallographica Section A, 68(3), p.366 - 381, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:81.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) have an anomalous endohedral structure? Synthesis and single crystal X-ray structure of the carbene adduct
have an anomalous endohedral structure? Synthesis and single crystal X-ray structure of the carbene adductAkasaka, Takeshi*; Kono, Takayoshi*; Takematsu, Yuji*; Nikawa, Hidefumi*; Nakahodo, Tsukasa*; Wakahara, Takatsugu*; Ishitsuka, Midori*; Tsuchiya, Takahiro*; Maeda, Yutaka*; Liu, M. T. H.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 130(39), p.12840 - 12841, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:76 Percentile:84.42(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report here the results on single crystal X-ray crystallographic analysis of the Gd@C carbene adduct (Gd@C
carbene adduct (Gd@C (ad), Ad=adamantylidene). The Gd atom in Gd@C
(ad), Ad=adamantylidene). The Gd atom in Gd@C (Ad) is located at an off-centered position near a hexagonal ring in the C2v-C
(Ad) is located at an off-centered position near a hexagonal ring in the C2v-C cage, as found for M@C
cage, as found for M@C (M = Sc and La) and La@C
(M = Sc and La) and La@C (Ad). Theoretical calculation also confirms the position of the Gd atom in the X-ray crystal structure.
(Ad). Theoretical calculation also confirms the position of the Gd atom in the X-ray crystal structure.
Fujii, Satoshi*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Takenaka, Shigeori*; Go, Nobuhiro; Sarai, Akinori*
Nucleic Acids Research, 35(18), p.6063 - 6074, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:98 Percentile:86.53(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Proteins recognize specific DNA sequences not only through direct contact between amino acids and bases, but also indirectly based on the sequence-dependent conformation and deformability of the DNA (indirect readout). We used molecular dynamics simulations to analyze the sequence-dependent DNA conformations of all 136 possible tetrameric sequences sandwiched between CGCG sequences. The deformability of dimeric steps obtained by the simulations is consistent with that by the crystal structures. The simulation results further showed that the conformation and deformability of the tetramers can highly depend on the flanking base-pairs. The conformations of xATx tetramers show the most rigidity and are not affected by the flanking base-pairs and the xYRx show by contrast the greatest flexibility and change their conformations depending on the base-pairs at both ends, suggesting tetramers with the same central dimer can show different deformabilities. These results suggest that analysis of dimeric steps alone may overlook some conformational features of DNA and provide insight into the mechanism of indirect readout during protein-DNA recognition. Moreover, the sequence dependence of DNA conformation and deformability may be used to estimate the contribution of indirect readout to the specificity of protein-DNA recognition as well as nucleosome positioning and large-scale behavior of nucleic acids.
Tochio, Daisuke; Watanabe, Shuji; Motegi, Toshihiro; Kawano, Shuichi; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Sekita, Kenji; Kawasaki, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2007-014, 62 Pages, 2007/03
The rise-to-power test of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) was begun in April 2000. The reactor thermal power of 30 MW, which is the maximum thermal power of the HTTR, and the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 850 C in normal operation was achieved in middle of December 2001. After that reactor thermal power of 30 MW a reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950
C in normal operation was achieved in middle of December 2001. After that reactor thermal power of 30 MW a reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950 C was achieved in the final rise-to-power test at April 2004. After receiving the operation permit, the safety demonstration tests were conducted to demonstrate inherent safety features of the HTGRs. This paper summarizes the HTTR operating experiences for five years since rise-to-power test that were catalogued into three categories, (1) Operating experience pertaining to new gas cooled reactor design, (2) Operating experience for improvement of the performance, (3) Operating experience due to fail of system and components.
C was achieved in the final rise-to-power test at April 2004. After receiving the operation permit, the safety demonstration tests were conducted to demonstrate inherent safety features of the HTGRs. This paper summarizes the HTTR operating experiences for five years since rise-to-power test that were catalogued into three categories, (1) Operating experience pertaining to new gas cooled reactor design, (2) Operating experience for improvement of the performance, (3) Operating experience due to fail of system and components.
Yonetani, Yoshiteru*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Fujii, Satoshi*; Sarai, Akinori*; Go, Nobuhiro
Molecular Simulation, 33(1-2), p.103 - 107, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.62(Chemistry, Physical)DNA tetramer sequences AATT and TTAA are known to be conformationally more rigid and flexible, respectively. In this study, we carry out molecular dynamics simulations of these two sequences, and investigate the characteristic hydration pattern. The rigid AATT is found to be more likely to construct the hydration spine in the minor groove than the flexible TTAA. The result suggests that the hydration water molecules play a critical role for determining the sequence dependent deformability of DNA conformation.
Kawano, Yasunori; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Isayama, Akihiko; Kondoh, Takashi; Hatae, Takaki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(10), p.743 - 744, 2005/10
Electron density of post-disruption runaway plasmas in JT-60U has been measured by the tangential CO laser interferometer. Increases in electron density after the first drop of runaway plasma current have been observed during a fast termination phase of the runaway plasma. At the second current drop, an increase in electron density with multiple spikes or oscillation with the period of 1 ms has been found. It is suggested that the increased electron density seems to take part in the shorter current decay time after the second current drop.
laser interferometer. Increases in electron density after the first drop of runaway plasma current have been observed during a fast termination phase of the runaway plasma. At the second current drop, an increase in electron density with multiple spikes or oscillation with the period of 1 ms has been found. It is suggested that the increased electron density seems to take part in the shorter current decay time after the second current drop.
Kawano, Yasunori; Nakano, Tomohide; Isayama, Akihiko; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Bakhtiari, M.; Ide, Shunsuke; Kondoh, Takashi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(8), p.593 - 601, 2005/08
An experiment to investigate mitigation effects of impurity pellet injection on disruption generated runaway electrons was carried out in the JT-60U tokamak device. Deposition of impurity neon pellets into a post-disruption runaway plasma was observed with increment of bulk electron density. At the impurity pellet injection, decay time of runaway current became shorter as factor of  2. There was an approximately linear relationship between changes in decay rate of runaway current and a photo-neutron signal which indicated loss of runaway electrons from the plasma. Consequently, enhanced loss of runaway electrons from a tokamak plasma, hence mitigation effect on them, by injection of impurity neon pellets was found.
2. There was an approximately linear relationship between changes in decay rate of runaway current and a photo-neutron signal which indicated loss of runaway electrons from the plasma. Consequently, enhanced loss of runaway electrons from a tokamak plasma, hence mitigation effect on them, by injection of impurity neon pellets was found.
Metsugi. Shoichi; Uenoyama, Atsuko*; Kubo, Jun*; Miyata, Makoto*; Yura, Kei; Kono, Hidetoshi; Go, Nobuhiro
Biophysics, 1, p.33 - 43, 2005/05
The motile mechanism of Mycoplasma mobile remains unknown but is believed to differ from any previously identified mechanism in bacteria. Gli349 of M. mobile is known to be responsible for both adhesion to glass surfaces and mobility. We therefore carried out sequence analyses of Gli349 and its homolog MYPU2110 from M. pulmonis to decipher their structures. We found that the motif "YxxxxxGF" appears 11 times in Gli349 and 16 times in MYPU2110. Further analysis of the sequences revealed that Gli349 contains 18 repeats of about 100 amino acid residues each, and MYPU2110 contains 22. No sequence homologous to any of the repeats was found in the NCBI RefSeq non-redundant sequence database, and no compatible fold structure was found among known protein structures, suggesting that the repeat found in Gli349 and MYPU2110 is novel and takes a new fold structure. Proteolysis of Gli349 using chymotrypsin revealed that cleavage positions were often located between the repeats, implying that regions connecting repeats are unstructured, flexible and exposed to the solvent.
Bakhtiari, M.; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Kramer, G. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Nakano, Tomohide; Kamiya, Kensaku; Yoshino, Ryuji; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(5), p.318 - 325, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:78.65(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the previous works we had shown that injecting a mixture of large amounts of hydrogen and small amounts of argon can terminate a tokamak discharge quickly with avoiding runaway electron generation. In this work we have done the same experiments but with different gases in addition to argon. In fact we compared the effect of the puffing of argon, krypton, and xenon gases with and without simultaneous hydrogen gas puffing on disruption mitigation. We observed that injecting all impurities in the form of an admixture in hydrogen lead to faster plasma shutdowns with less runaway electron generation. We also found that injecting krypton gas (with or without hydrogen) seems to be a good candidate for plasma shutdown purposes since it induces low heat flux to divertor plates and avoids runaway electron generation more effectively.
Metsugi, Shoichi*; Uenoyama, Atsuko*; Adan, J.*; Miyata, Makoto*; Yura, Kei; Kono, Hidetoshi; Go, Nobuhiro
Biophysics, 1, p.33 - 43, 2005/00
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Nakano, Tomohide; Isayama, Akihiko; Hatae, Takaki; Konoshima, Shigeru; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kondoh, Takashi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Kubo, Hirotaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 29C, 4 Pages, 2005/00
In order to mitigate the post-disruption runaway electrons, experiments has been carried out with impurity pellet injection. As a result, we have observed the prompt exhaust of the runaway electrons and the reduction of runaway plasma. We have presented one possible explanation for basic behavior of the runaway plasma current that it follows the balance of the avalanche generation of runaway electrons and their slowing down predicted by the model, including effects by synchrotron radiation. On the other hand, standing on the fact that the current quench time is extended by runaway electrons, the experiment for avoiding the current quench by runaway electrons has been carried out. The runaway electrons reinforced the discharge to survive against the low Te of less than several tens eV and an additional impurity pellet injection, and thus the plasma current was maintained and terminated as programmed. To study the dynamics of runaway electrons precisely, a new active and direct diagnostic concept using the laser inverse Compton scattering has been proposed.
Takei, Nahoko; Nakamura, Yukiharu; Tsutsui, Hiroaki*; Yoshino, Ryuji; Kawano, Yasunori; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji; Iio, Shunji*; Shimada, Ryuichi*; Jardin, S. C.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(12), p.1815 - 1830, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.99(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 Al conductor developed for JT-60SC
Al conductor developed for JT-60SCKizu, Kaname; Miura, Yushi; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Ando, Toshinari*; Hamada, Kazuya; Hara, Eiji*; Imahashi, Koichi*; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 14(2), p.1535 - 1538, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.57(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Sakasai, Akira; Ishida, Shinichi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Akino, Noboru; Ando, Toshinari*; Arai, Takashi; Ezato, Koichiro; Hamada, Kazuya; Ichige, Hisashi; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 44(2), p.329 - 334, 2004/02
no abstracts in English