Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Asano, Norikazu; Nishimura, Arashi; Takabe, Yugo; Araki, Daisuke; Yanai, Tomohiro; Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Ogasawara, Yasushi; Oto, Tsutomu; Otsuka, Kaoru; Otsuka, Noriaki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-045, 137 Pages, 2022/06
A collapse event of a cooling tower for secondary cooling system in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) was caused by the strong winds of Typhoon No.15 on September 9, 2019. As measures against the event, the working group for the renewal of the UCL (Utility Cooling Loop) cooling tower was established in the department of JMTR, and the integrity of the UCL cooling tower, which is the same type of wooden cooling tower as the secondary cooling tower in the JMTR, was investigated. As a result of this investigation, we have decided to replace the existing UCL cooling tower with a new cooling system. After investigations, in order to reduce the risk of collapse due to wood decay, the new cooling system was installed as a component of the air system to be managed as a performance maintenance facility after decommissioning. This report describes the design of and the evaluation results of the facility.
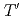 -type La
-type La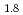 Eu
Eu CuO
CuO and Nd
and Nd CuO
CuO
Asano, Shun*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Kudo, Kota*; Taniguchi, Takanori*; Saito, Shin*; Sunohara, Toshiki*; Kawamata, Takayuki*; Koike, Yoji*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(21), p.214504_1 - 214504_7, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Asano, Masaharu*; Terai, Takayuki*
Journal of Membrane Science, 587, p.117171_1 - 117171_9, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.64(Engineering, Chemical)Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI component in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity (
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity ( ) and transport number (
) and transport number ( ) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H
) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H and I
and I content and the diffusion coefficients of H
content and the diffusion coefficients of H and I
and I in the evaluated membranes on
in the evaluated membranes on  and
and  were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of
were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of  and t
and t , which indicates that the dominant factors for
, which indicates that the dominant factors for  and
and  would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For
would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For  of Nafion 212, H
of Nafion 212, H diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I
diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I
was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I diffusion should be considered. I
diffusion should be considered. I diffusion could more strongly affect
diffusion could more strongly affect  for the evaluated membranes rather than H
for the evaluated membranes rather than H diffusion, which indicates that H
diffusion, which indicates that H selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I
selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I behavior in the membranes.
behavior in the membranes.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shirato, Atsuhiko*; Sato, Takashi*; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Nomi, Takayoshi; Kawakubo, Yoko; Nagatani, Taketeru; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi; Menlove, H. O.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Browne, M. C.*
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Watanabe, Kazuhito; Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji; Someya, Yoji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Uto, Hiroyasu; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Araki, Takao*; Asano, Shiro*; Asano, Kazuhito*
Proceedings of 26th IEEE Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE 2015), 6 Pages, 2016/06
Safety studies of a water-cooled fusion DEMO reactor have been performed. In the event of the blanket cooling pipe break outside the vacuum vessel, i.e. ex-vacuum vessel loss of coolant accident (ex-VV LOCA), the pressurized steam and air may lead to damage reactor building walls which have confinement function, and to release the radioactive materials to the environment. In response to this accident, we proposed three cases of confinement strategies. In each case, the pressure and thermal loads to the confinement boundaries and total mass of tritium released to outside the boundaries were analyzed by accident analysis code MELCOR modified for fusion reactor. These analyses developed design parameters to maintain the integrity of the confinement boundaries.
 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Shirato, Atsuhiko*; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Sato, Takashi*; Kawakubo, Yoko; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2015/07
As one of the candidate material accountancy technologies for the fuel debris at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F), we propose the application of a passive neutron technique. The applicability of the new concept to the fuel debris at 1F was evaluated by simulation and the results were presented at the last INMM annual meeting. As the next phase, we conducted experimental tests to confirm the validity of the simulation results. Because actual fuel debris or irradiated fuel cannot be handled at our facility due to a licensing limitation, un-irradiated MOX samples, neutron absorbers and Cf-252 sources were utilized as the best available material to imitate the property of the fuel debris and various configurations were measured using an Epithermal Neutron Multiplicity Counter. The fissile mass in the samples, neutron absorber mass surrounding the samples and intensity of Cf-252 source were varied to confirm the correlation between DDSI response and the leakage multiplication. Test results agreed well with the trend of the simulation results. This indicates that DDSI has sufficient capability to evaluate the leakage multiplication of a sample which includes an unknown amount of fissile material and neutron absorber such as the fuel debris at 1F. This paper provides experimental studies of passive neutron measurement based on the combination of DDSI technique and coincidence counting for fuel debris at 1F.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Nakajima, Shinji; Kawakubo, Yoko; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H.*; Rael, C.*; Kawasue, Akane*; et al.
Book of Abstracts, Presentations and Papers of Symposium on International Safeguards; Linking Strategy, Implementation and People (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/03
Tamura, Jun; Ao, Hiroyuki; Nemoto, Yasuo; Asano, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Takahiro*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 66(3), p.399 - 404, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)ACSs are going to increase the beam energy of the J-PARC linac from 181 to 400 MeV. The 2011 Tohoku earthquake damaged the J-PARC facilities and the cavity conditioning was interrupted for two years. After the restoration of the facility, the two ACS cavities (M01 and M11) were conditioned. They achieved to 15-20% above the designed accelerating field of 4.2 MV/m. Since M01 was conditioned six years ago, the conditioning time required for M01 was drastically reduced from that for the first time. During the high-power operation for M11, which is an unique cavity equipped with a capacitive iris in a waveguide, no significant increase of the temperature and the discharge rate around the capacitive iris was observed. The vacuum pressure was sufficiently low (4 10
10 Pa) even from the view point of beam loss due to residual gas scattering. The more stable operation can be expected through one-month conditioning before beam commissioning.
Pa) even from the view point of beam loss due to residual gas scattering. The more stable operation can be expected through one-month conditioning before beam commissioning.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Nakajima, Shinji; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
Meltdown of the reactor cores of Units 1-3 occurred at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F). Fuel debris at 1F contains minor actinides and fission products and neutron absorber. These materials make it difficult to quantify fertile nuclear materials in fuel debris by the conventional passive neutron technique. We consider that DDSI and PNAR which focused on fissile material are promising techniques to quantify the nuclear materials in the fuel debris. A concept of application of these techniques to fuel debris measurement was investigated and presented at the last INMM annual meeting. In order to evaluate the applicability of these techniques to fuel debris measurement, we investigated the neutron behavior in the fuel debris by using MCNPX simulation code. Because property of fuel debris is not clear, source term data used were prepared by referring TMI data. This paper provides results of MCNPX simulation for fuel debris measurement at 1F with passive neutron techniques.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Shiromo, Hideo; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Rael, C. D.*; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 55th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2014/07
The Advanced Fuel Assembly Assay System (AFAS) is an unattended non-destructive assay (NDA) system by neutron measurement to verify the plutonium amount in an LWR plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel assembly. The assembly will be fabricated in the MOX fuel fabrication plant under construction by the Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited. The AFAS has been developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory under the auspices of the Secretariat of Nuclear Regulation Authority in Japan. The AFAS is the first NDA system which will verify the active length of the assembly without inspector attendance. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted the performance test for the AFAS under the contract with Nuclear Material Control Center to demonstrate this active length verification technology by using MOX fuel assemblies owned by JAEA. As the results, it was confirmed that measurement error of the active length for the MOX fuel assembly was less than 0.1% and it was satisfied with requirement by IAEA. This paper provides the performance test results for the active length verification of the AFAS.
Tamura, Jun; Ao, Hiroyuki; Nemoto, Yasuo; Asano, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Takahiro*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.437 - 439, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
 -H
-H O mixture
O mixtureTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Journal of Membrane Science, 456, p.31 - 41, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.89(Engineering, Chemical)Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI uptake from a HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, the constitution of the HIx solution absorbed in grafted membranes and in Nafion 212 is evaluated. The affinity of the membranes for the HIx solution is discussed based on the measurement results. The behavior of each component in the membrane was as follows: The strong affinity of the ETFE-St membrane for I
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, the constitution of the HIx solution absorbed in grafted membranes and in Nafion 212 is evaluated. The affinity of the membranes for the HIx solution is discussed based on the measurement results. The behavior of each component in the membrane was as follows: The strong affinity of the ETFE-St membrane for I was shown because of the formation of a charge-transfer complex with electron-donating aromatic groups, whereas I
was shown because of the formation of a charge-transfer complex with electron-donating aromatic groups, whereas I absorption by Nafion 212 was minimal. The difference of affinity for the ions can be attributed to the formation of the I
absorption by Nafion 212 was minimal. The difference of affinity for the ions can be attributed to the formation of the I - complex from I- and I
- complex from I- and I absorbed in the grafted membranes, which was precluded in Nafion 212.
absorbed in the grafted membranes, which was precluded in Nafion 212.
Shibama, Yusuke; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira; Onawa, Toshio*; Araki, Takao*; Asano, Shiro*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(9-10), p.1916 - 1919, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)This presentation focuses on the welding technology R&D between the JT-60SA vacuum vessel and the ports. The vacuum vessel is designed to allow port bore penetration to access the vessel inside for plasma diagnostics, and so on. There are various types of 73 ports and these are categorized by their locations; the upper/lower vertical, the upper/lower oblique, and the horizontal. Ports are onsite-welded onto the VV port stub after the assembly of the VV. This assembly sequence involves the out-vessel components such as VV thermal shield and toroidal field magnets, so that these ports welding are accessed from the inside of the vessel and limited by the internal port wall. The one of the most difficult ports are the upper vertical port with corner radius of 50 mm under narrow space, and it is necessary to clarify mobility of the weld torch head. The port weldability is discussed with the mock-up trial, which consists of the partial test pieces of the product size. The TIG welding manipulator, optimized for this R&D, is prepared by its operational simulation and examined not to interfere with the internal port wall.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Asano, Takashi; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; Watanabe, Takehito*; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; et al.
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
The Advanced Verification for Inventory Sample System (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system in order to verify the plutonium mass in the small MOX samples at Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) MOX fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX) under construction. The AVIS is required the high measurement performance because the AVIS will be used as a verification tool to substitute destructive analysis for a part of the samples which needs the bias defect verification. Therefore, the AVIS will fulfill an important role in the safeguards approach for J-MOX. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) conducted the performance test of the AVIS under the contract with NMCC. As the results of these tests, we confirmed that the AVIS could almost satisfy the required performance by IAEA.
Tamura, Jun; Ao, Hiroyuki; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Masanori*; Maruta, Tomofumi; Miura, Akihiko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ouchi, Nobuo; Sawabe, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.377 - 380, 2013/08
In the J-PARC linac, almost all the cavities and magnets have been precisely aligned because the accelerator tunnel has been deformed by the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake. In the beam transport line called MEBT2 and A0BT at the downstream of the drift tube linac, the beam duct has been roughly aligned after the precise alignment of the quadruple doublets. During the first beam operation after the earthquake, remarkable beam loss and residual radiation have been recognized at the MEBT2 and A0BT. As the result of the duct position measurement, the misalignement including over 10 mm shift from the beam axis was found. By conducting the beam duct realignment, the beam loss and the residual radiation were successfully decreased. In this paper, the procedure of the beam duct alignment and the beam loss due to the misalignment are described.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Nakajima, Shinji; Asano, Takashi
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (1F) were struck by the earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011 and meltdown of the reactor cores of Units 1-3 occurred. Japan decided decommissioning of them. For decommissioning of 1F, Japan plans to recover fuel debris safely and to account nuclear material in it adequately. Survey of applicable technologies for nuclear material quantification of fuel debris, currently, is being conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and United States Department of Energy (DOE) under the collaborative agreement. This survey will identify technologies with the most promising capability to meet IAEA safeguards needs. As one of candidate technologies of plutonium quantification in fuel debris, we, Plutonium Fuel Development Center of JAEA, consider the application of the passive neutron technique which is wildly applied to the field of material accountancy and safeguards in plutonium handing facilities. Fuel debris contains minor actinides and fission products which are intense neutron and  ray emitter due to burn-up of fuel in the reactor. It also contains neutron absorber such as gadolinium included in fuel to moderate burn-up and boron added after accident to avoid re-criticality. These materials make it difficult to quantify plutonium by the current passive neutron technique. Therefore, R&D activities regarding selective counting for neutron derived from plutonium, reduction of
ray emitter due to burn-up of fuel in the reactor. It also contains neutron absorber such as gadolinium included in fuel to moderate burn-up and boron added after accident to avoid re-criticality. These materials make it difficult to quantify plutonium by the current passive neutron technique. Therefore, R&D activities regarding selective counting for neutron derived from plutonium, reduction of  ray influence and estimation of neutron absorber influence are required in order to overcome above difficulties. This paper provides a concept for application of passive neutron technique to fuel debris measurement.
ray influence and estimation of neutron absorber influence are required in order to overcome above difficulties. This paper provides a concept for application of passive neutron technique to fuel debris measurement.
Nakajima, Shinji; Nagatani, Taketeru; Asano, Takashi; Marlow, J. B.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Rael, C. D.*; Kawasue, Akane*; Iso, Shoko*; Kumakura, Shinichi*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/07
The advanced verification inventory system (AVIS) is a nondestructive assay (NDA) system developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) to measure small samples of bulk plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) powder and pellets at the Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL) mixed oxide fuel fabrication plant (J-MOX). In order to mitigate the workload on the Rokkasho On-Site Laboratory (OSL), it is intended that the AVIS measurement will be substituted for a part of the Destructive Assay (DA) for J-MOX. Based on the commission from Office for Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Safeguards (JSGO) of Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and Nuclear Material Control Center (NMCC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted the performance test of the AVIS in order to confirm the system performance before installation at the J-MOX site. The performance test consists of two phases. In the phase 1 test, detector parameters such as detector efficiency and die-away time were evaluated by using a californium-252 neutron source. These results agreed well with design value and were reported at the 53rd INMM annual meeting. JAEA conducted the phase 2 test by using MOX materials in order to evaluate the total measurement uncertainty (TMU). In the test, influence of sample density, plutonium concentration and organic additives in samples were also evaluated. Consequently, it is expected that AVIS can achieve the target TMU of 0.5% required in user requirement of IAEA by optimizing measurement condition and by using well-characterized standards. This paper provides a summary of the results of comprehensive performance test of AVIS.
 -H
-H O mixture for IS process
O mixture for IS processTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
Research and development of a water-splitting hydrogen-production method, called iodine-sulfur (IS) process, has been conducting as one of the heat applications of high temperature gas-cooled reactor. Among the unit operations in this IS process, we have investigated electro-electrodialysis (EED) using an ion-exchange membrane to concentrate HI in an HI-I -H
-H O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I
O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I ) concentrations in the HI-I
) concentrations in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I
O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I
molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I .
.