Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Sekita, Kenji; Watanabe, Shuji; Furusawa, Takayuki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 388, p.111642_1 - 111642_11, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency adapted High-Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to meet the new regulatory requirements that began in December 2013. The safety and seismic classifications of the existing structures, systems, and components were discussed to reflect insights regarding High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) that were acquired through various HTTR safety tests. Structures, systems, and components that are subject to protection have been defined, and countermeasures to manage internal and external hazards that affect safety functions have been strengthened. Additionally, measures are in place to control accidents that may cause large amounts of radioactive material to be released, as a beyond design based accident. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission rigorously and appropriately reviewed this approach for compliance with the new regulatory requirements. After nine amendments, the application to modify the HTTR's installation license that was submitted in November 2014 was approved in June 2020. This response shows that facilities can reasonably be designed to meet the enhanced regulatory requirements, if they reflect the characteristics of HTGRs. We believe that we have established a reference for future development of HTGR.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Uchiyama, Yusuke*; Azuma, Kohei*; Odani, Sachika*; Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Kamidaira, Yuki; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Onda, Yuichi*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, B2 (Kaigan Kogaku) (Internet), 73(2), p.I_685 - I_690, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Ono, Masato; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 2(4), p.044502_1 - 044502_4, 2016/10
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to verify safety evaluation codes to investigate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. The VCS passively removes the retained residual heat and the decay heat from the core via the reactor pressure vessel by natural convection and thermal radiation. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. Through a cold test, which was carried out by non-nuclear heat input from gas circulators with stopping water flow in the VCS, the local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Ono, Masato; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Tochio, Daisuke; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 24th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-24) (DVD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2016/06
On March 11th, 2011, the Great East Japan Earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred. When the great earthquake occurred, the HTTR had been stopped under the periodic inspection and maintenance of equipment and instrument. In the great earthquake, the maximum seismic acceleration observed at the HTTR exceeded the maximum value in seismic design. The visual inspection of HTTR facility was carried out for the seismic integrity conformation of HTTR. The seismic analysis was also carried out using the observed earthquake motion at HTTR site to confirm the integrity of HTTR. The concept of comprehensive integrity evaluation for the HTTR facility is divided into two parts. One is the inspection of equipment and instrument. The other is the seismic response analysis using the observed earthquake. For the basic inspections of equipment and instrument were performed for all them related to the operation of reactor. The integrity of the facilities is confirmed by comparing the inspection results or the numerical results with their evaluation criteria. As the result of inspection of equipment and instrument and seismic response analysis, it was judged that there was no problem to operate the reactor, because there was no damage and performance deterioration, which affects the reactor operation. The integrity of HTTR was also supported by the several operations without reactor power in cold conditions of HTTR in 2011, 2013 and 2015.
Ono, Masato; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Tochio, Daisuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of International Topical Meeting on Research Reactor Fuel Management and Meeting of the International Group on Reactor Research (RRFM/IGORR 2016) (Internet), p.363 - 371, 2016/03
HTTR is graphite moderated and helium gas-cooled reactor with prismatic fuel elements and hexagonal blocks. Here, the graphite block is brittle materials and might be damaged by collision of neighboring blocks by the large earthquake. A seismic observation system is installed in the HTTR site to confirm a behavior of a seismic event. On March 11th, 2011, off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake of magnitude 9.0 occurred. After the accident at the TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the safety of nuclear reactors is the highest importance. To confirm the seismic integrity of HTTR core components, the seismic analysis was carried out using the evaluation waves based on the relationship between the observed earthquake motion at HTTR site and frequency transfer function. In parallel, confirmation tests of primary cooling system on cold state and integrity confirmation of reactor buildings and component support structures were also carried out. As a result, it was found that a stress value of the graphite blocks satisfied an allowable value, and the integrity of the HTTR core components was ensured. The integrity of HTTR core components was also supported by the operation without reactor power in cold conditions of HTTR. The obtained data was compared with the normal plant data before the earthquake. As the result, the integrity of the HTTR facilities was confirmed.
 Nb
Nb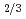 )
) Ti
Ti ]O
]O crystal near the morphotropic phase boundary
crystal near the morphotropic phase boundaryShimizu, Daisuke*; Tsukada, Shinya*; Matsuura, Masato*; Sakamoto, Junya*; Kojima, Seiji*; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owada, Kenji
Physical Review B, 92(17), p.174121_1 - 174121_5, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The phase diagram and the relationship between the crystal coherence length and electrical response of Pb[(Mg Nb
Nb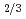 )
) Ti
Ti ]O
]O (PMN-xPT) near the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) have been precisely investigated using a single crystal with a Ti composition gradient by synchrotron X-ray diffraction and inelastic light scattering at room temperature. The crystal has two boundaries at Ti compositions of 29.0 mol% and 34.7 mol% which correspond to the phase boundaries between the monoclinic B (MB) and C (MC) phases and between the MC and tetragonal (T) phases, respectively. It is shown that there is a strong negative correlation between the electrical response and the crystal coherence length at the sub-
(PMN-xPT) near the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) have been precisely investigated using a single crystal with a Ti composition gradient by synchrotron X-ray diffraction and inelastic light scattering at room temperature. The crystal has two boundaries at Ti compositions of 29.0 mol% and 34.7 mol% which correspond to the phase boundaries between the monoclinic B (MB) and C (MC) phases and between the MC and tetragonal (T) phases, respectively. It is shown that there is a strong negative correlation between the electrical response and the crystal coherence length at the sub- m scale. The results are explained by the size effects of domains near the MPB.
m scale. The results are explained by the size effects of domains near the MPB.
Takada, Shoji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Seki, Tomokazu; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to demonstrate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. The local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Tochio, Daisuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Sakaba, Nariaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(11-12), p.1407 - 1412, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed and developed High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) hydrogen cogeneration system named GTHTR300C. The helium gas is used as the primary coolant in HTGR. The helium gas is easy to leak, and the primary helium leakage should be controlled tightly from the viewpoint of preventing the release of radioactive materials to the environment. Moreover from the viewpoint of preventing the oxidization of graphite and metallic material, the helium coolant chemistry should be controlled tightly. The primary helium leakage and the helium coolant chemistry during the operation is the major factor in the HTGR for commercialization of HTGR system. This paper shows the design concept and the obtained operational experience on the primary helium leakage control and primary helium impurity control in the HTTR. Moreover the future plan to obtain the operational experience on these controls for commercialization of HTGR system is shown.
Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Ono, Masato; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Tochio, Daisuke; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 1(4), p.TEP0021_1 - TEP0021_13, 2014/08
On March 11th, 2011, the Great East Japan Earthquake which is one of the largest earthquakes in Japan occurred and the maximum acceleration in observed seismic wave in the HTTR exceeded the design value in a part of input seismic motions. Therefore, a visual inspection, a seismic analysis and a performance confirmation test of facilities were carried out in order to confirm the integrity of facility after the earthquake. The seismic analysis was carried out for the reactor core structures by using the response magnification factor method. As the results of the evaluation, the generated stress in the graphite blocks in the reactor core at the earthquake were well below the allowable values of safety criteria, and thus the structural integrity of the reactor core was confirmed. The integrity of reactor core was also supported by the visual inspections of facilities and the operation without reactor power in cold conditions of HTTR.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Tochio, Daisuke; Saito, Kenji; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Homma, Fumitaka; Furusawa, Takayuki; Saikusa, Akio; Takada, Shoji; Shinozaki, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 271, p.499 - 504, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The long term high temperature operation using HTTR was carried out to establish the technical basis of HTGR in the high temperature test operation mode during 50-day since January till March, 2010. It is necessary to demonstrate the stability of plant during long-term operation in order to attain the stable supply of the high temperature heat to the planned heat utilization system of HTTR. Test data obtained in the operation were evaluated for the technical issues which were extracted before the operation. As the results, Stability and reliability of the components and facility was demonstrated by evaluating the heat transfer performance of high temperature components, the performance of pressure control to compensate helium gas leak, the reliability of the dynamic components such as helium gas circulators, the performance of heat-up protection of radiation shielding. Through the operation, the technical basis for the operation and maintenance technology of HTGRs was established.
Yamada, Katsunori; Fujii, Katsutoshi; Kanda, Hiroshi; Higashi, Daisuke; Kobayashi, Toshiaki; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Fukami, Tomoyo; Yoshida, Keisuke; Ueno, Yumi; Nakajima, Junya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-033, 51 Pages, 2013/12
After the accident at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, various numerical criteria relevant to radiation protection were defined. We surveyed these criteria through internet. As a result of survey, the following 13 items were identified: (1) criteria for taking stable iodine tablets, (2) criteria for the screening of surface contamination, (3) evacuation area, sheltering area, etc., (4) activity concentrations in food, drinking water, etc., (5) dose limit for radiation workers engaged in emergency work, (6) guideline levels of radioactive substances in bathing areas, (7) criteria for use of school buildings and schoolyards, (8) restriction on planting rice, (9) acceptable activity concentrations in feedstuff, (10) acceptable activity concentrations in compost, (11) criteria for export containers and ships, (12) criteria for contaminated waste, (13) standards for radiation workers engaged in decontamination work. In this report, the basis of and issues on these criteria are summarized.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Tochio, Daisuke; Saito, Kenji; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Homma, Fumitaka; Furusawa, Takayuki; Saikusa, Akio; Shinozaki, Masayuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/10
To establish the technical basis of HTGR, the long term high temperature operation using HTTR was carried out during 50-day in 2010. It is necessary to demonstrate the stability of plant during long-term operation and the reliability of components and facilities special to HTGRs, in order to attain the stable supply of the high temperature heat to the planned hydrogen production system of HTTR. Test data obtained in the operation were evaluated for the technical issues which were extracted before the operation. As the results, stability and reliability of the components and facility special to HTGRs was demonstrated by evaluating the heat transfer performance of high temperature components, the helium gas leak tightness, the reliability of the dynamic components such as helium gas circulators, the performance of heat-up protection of radiation shielding. Through the operation, the technical basis for the operation and maintenance technology of HTGRs were established.
 states in
states in 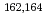 Gd populated by the
Gd populated by the  decay of
decay of 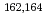 Eu
EuNagae, Daisuke*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Asai, Masato; Makii, Hiroyuki; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Shimizu, Yoshifumi*; Shoji, Takuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1224, p.156 - 160, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.17(Physics, Nuclear)Koizumi, Satoshi; Iwase, Hiroki; Suzuki, Junichi; Oku, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sasao, Hajime*; Tanaka, Hirokazu; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Shimizu, Hirohiko; Hashimoto, Takeji
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1000 - 1006, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:80.68(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Tochio, Daisuke; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Shimizu, Atsushi; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Yamazaki, Kazunori; Shimizu, Yasunori; Aragaki, Etsushi; Ota, Yukimaru; Fujimoto, Nozomu
JAEA-Technology 2006-045, 43 Pages, 2006/09
The auxiliary component cooling water system (ACCWS) is one of the cooling system in High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) The ACCWS has the features not only many facilities cooling but also heat sink of the vessel cooling system which is one of the engineering safety features. Therefore, the ACCWS is required to satisfy the design criteria of heat removal performance. In this report, heat exchange performance data of the rise-to-power-up test and the in-service operation for the ACCWS cooling tower was evaluated. Moreover, the evaluated values were compared with the design values, and it is confirmed that ACCWS cooling tower has the required heat exchange performance in the design.
Takayama, Katsumi*; Hirose, Naoki*; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Shimizu, Daisuke*; Watanabe, Tatsuro*
no journal, ,
An ocean general circulation model in the Japan Sea has been being developed to reproduce and forecast movement of pollutants at JAEA. It was demonstrated that an assimilation of sea level variation at tide stations along the Japanese coast is effective to reproduce oceanic condition in the nearshore region. In this study, an effect of assimilation of satellite altimeter data, CTD data and tide data is quantitatively surveyed. As a result, it was demonstrated that this assimilation scheme improves the oceanic condition.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Furusawa, Takayuki
no journal, ,
For the long term high temperature operation with HTTR, issues for systems and components, which were extracted based on result of long term rated operation, were solved. As the result, the followings were confirmed; deviation of temperature, flow rate and pressure of the primary and secondary coolant were sufficiently restricted against the disturbance of temperature of atmosphere during day and night. The whole plant was operated stable. It was confirmed that the secondary coolant was stably supplied. New findings were acquired for the operation and maintenance of systems and components for future HTGR development.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Tochio, Daisuke; Homma, Fumitaka; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Furusawa, Takayuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishino, Masahiko; Namikawa, Kazumichi; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Owada, Kenji; Shimizu, Daisuke*; Sakamoto, Junya*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English