Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 binding site of a
binding site of a  -lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffraction
-lactamase from the halophile by anomalous X-ray diffractionArai, Shigeki; Shibazaki, Chie; Shimizu, Rumi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Tokunaga, Hiroko*; Ishibashi, Matsujiro*; Tokunaga, Masao*; Kuroki, Ryota
Kyushu Shinkurotoronko Kenkyu Senta Nempo, 2014, p.17 - 19, 2016/03
no abstracts in English
 -lactamase from the moderate halophile
-lactamase from the moderate halophile 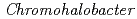 sp.560 and the discovery of a Cs
sp.560 and the discovery of a Cs -selective binding site
-selective binding siteArai, Shigeki; Yonezawa, Yasushi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Matsumoto, Fumiko*; Shibazaki, Chie; Shimizu, Rumi; Yamada, Mitsugu*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Kawamoto, Masahide*; et al.
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 71(3), p.541 - 554, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:50.54(Biochemical Research Methods)The crystal structure of halophilic  -lactamase from
-lactamase from 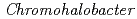 sp.560 (HaBLA) was determined using X-ray crystallography. Moreover, the locations of bound Sr
sp.560 (HaBLA) was determined using X-ray crystallography. Moreover, the locations of bound Sr and Cs
and Cs ions were identified by anomalous X-ray diffraction. The location of one Cs
ions were identified by anomalous X-ray diffraction. The location of one Cs specific binding site was identified on HaBLA even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na
specific binding site was identified on HaBLA even in the presence of 9-fold molar excess of Na (90 mM Na
(90 mM Na /10 mM Cs
/10 mM Cs ). This Cs
). This Cs binding site is formed by two main-chain O atoms and an aromatic ring of a side chain of Trp. An aromatic ring of Trp interacts with Cs
binding site is formed by two main-chain O atoms and an aromatic ring of a side chain of Trp. An aromatic ring of Trp interacts with Cs by the cation-
by the cation- interaction. The observation of a selective and high-affinity Cs
interaction. The observation of a selective and high-affinity Cs binding site provides important information that is useful for designing artificial Cs
binding site provides important information that is useful for designing artificial Cs binding sites useful in bioremediation of radioactive isotopes.
binding sites useful in bioremediation of radioactive isotopes.

Adachi, Motoyasu; Hirayama, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Rumi; Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issey*; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Science, 23(10), p.1349 - 1358, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:25.32(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair A (PprA) is a key protein that facilitates the extreme radioresistance of  . To clarify the role of PprA in the radioresistance mechanism, the interaction between recombinant PprA expressed in Escherichia coli with several double-stranded DNAs was investigated. In a gel-shift assay, the band shift of supercoiled pUC19 DNA caused by the binding of PprA showed a bimodal distribution, which was promoted by the addition of 1 mM Mg, Ca, or Sr ions. The dissociation constant of the PprA-supercoiled pUC19 DNA complex, calculated from the relative portions of shifted bands, was 0.6
. To clarify the role of PprA in the radioresistance mechanism, the interaction between recombinant PprA expressed in Escherichia coli with several double-stranded DNAs was investigated. In a gel-shift assay, the band shift of supercoiled pUC19 DNA caused by the binding of PprA showed a bimodal distribution, which was promoted by the addition of 1 mM Mg, Ca, or Sr ions. The dissociation constant of the PprA-supercoiled pUC19 DNA complex, calculated from the relative portions of shifted bands, was 0.6  M with a Hill coefficient of 3.3 in the presence of 1 mM Mg acetate. This indicates that at least 281 PprA molecules are required to saturate a supercoiled pUC19 DNA, which is consistent with the number of bound PprA molecules estimated by the UV absorption of the PprA-pUC19 complex purified by gel filtration. This saturation also suggests linear polymerization of PprA along the dsDNA. On the other hand, the bands of linear dsDNA and nicked circular dsDNA that eventually formed PprA complexes did not saturate, but created larger molecular complexes when the PprA concentration was greater than 1.3
M with a Hill coefficient of 3.3 in the presence of 1 mM Mg acetate. This indicates that at least 281 PprA molecules are required to saturate a supercoiled pUC19 DNA, which is consistent with the number of bound PprA molecules estimated by the UV absorption of the PprA-pUC19 complex purified by gel filtration. This saturation also suggests linear polymerization of PprA along the dsDNA. On the other hand, the bands of linear dsDNA and nicked circular dsDNA that eventually formed PprA complexes did not saturate, but created larger molecular complexes when the PprA concentration was greater than 1.3  M. This result implies that DNA-bound PprA aids association of the termini of damaged DNAs, which is regulated by the concentration of PprA.
M. This result implies that DNA-bound PprA aids association of the termini of damaged DNAs, which is regulated by the concentration of PprA.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota; Blaber, M.
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.953 - 957, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.13(Instruments & Instrumentation)Symfoil-4P is a 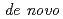 protein exhibiting the threefold symmetrical beta-trefoil fold designed based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. First three asparagine-glycine sequences of Symfoil-4P are replaced with glutamine-glycine (Symfoil-QG) or serine-glycine (Symfoil-SG) sequences protecting from deamidation, and His-Symfoil-II was prepared by introducing a protease digestion site into Symfoil-QG so that Symfoil-II has three complete repeats after removal of the N-terminal histidine tag. The Symfoil-QG and SG and His-Symfoil-II proteins were expressed in
protein exhibiting the threefold symmetrical beta-trefoil fold designed based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. First three asparagine-glycine sequences of Symfoil-4P are replaced with glutamine-glycine (Symfoil-QG) or serine-glycine (Symfoil-SG) sequences protecting from deamidation, and His-Symfoil-II was prepared by introducing a protease digestion site into Symfoil-QG so that Symfoil-II has three complete repeats after removal of the N-terminal histidine tag. The Symfoil-QG and SG and His-Symfoil-II proteins were expressed in 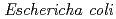 as soluble protein, and purified by nickel affinity chromatography. Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-QG and II crystals gave 1.5 and 1.1
as soluble protein, and purified by nickel affinity chromatography. Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-QG and II crystals gave 1.5 and 1.1 , resolution, respectively. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed pseudo-threefold symmetry as expected from other Symfoils.
, resolution, respectively. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed pseudo-threefold symmetry as expected from other Symfoils.
Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Watanabe, Yoko; Shimizu, Rumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Nishimiya, Yoshiyuki*; Kondo, Hidemasa*; Tsuda, Sakae*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ohara, Takashi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Nishimiya, Yoshiyuki*; Kondo, Hidemasa*; Tsuda, Sakae*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Fumiko; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Meguro, Mizue; Tamada, Taro; Kato, Takashi; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Thrombopoietin (TPO) is a glycoprotein hormone produced mainly by the liver and the kidney that regulates the production of platelets by the bone marrow. It stimulates the production and differentiation of megakaryocytes, the bone marrow cells that fragment into large numbers of platelets. The extracellular domain consists of 450 amino acid residues of thrombopoietin receptor (soluble TPO-R) contains two repeat of cytokine receptor homologous region, CRH-1 and CRH-2. In this work, we prepare CRH-1domein of TPO-R, and we discover that CRH-1 has binding site of TPO.
Shimizu, Rumi; Matsumoto, Fumiko; Arai, Shigeki; Ohara, Takashi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Nishimiya, Yoshiyuki*; Kondo, Hidemasa*; Tsuda, Sakae*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Fumiko; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Meguro, Mizue; Arai, Shigeki; Tamada, Taro; Kato, Takashi; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Shimizu, Rumi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Kuroki, Ryota; Yamashita, Michi*; Morimoto, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Fumiko; Hatanaka, Takaaki*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Tamada, Taro; Ito, Yuji*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota; Moriya, Keisuke*; Kidokoro, Shunichi*; Hidaka, Koshi*; Tsuda, Yuko*; Kiso, Yoshiaki*
no journal, ,
Human immune deficiency virus protease-I (HIV-PR) is one of the important drug target proteins for the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. In this study, we designed the two single chain derivatives of wild-type and A17 type HIV-PRs in which the catalytic residue of Asp25 was placed with Asn25 to inactivate the enzyme. The tertiary structure of sc-HIV-PR of wild-type and A17 type were determined by X-ray crystallography to 1.1 and 1.5  resolution, respectively. The both complex structures showed that Asn25 forms hydrogen bond with carbonyl group of inhibitor.
resolution, respectively. The both complex structures showed that Asn25 forms hydrogen bond with carbonyl group of inhibitor.
Shimizu, Rumi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Kuroki, Ryota; Blaber, M.
no journal, ,
We have already succeeded in creation of the de novo designed protein (Symfoil) exhibiting the threefold symmetrical  -trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20
-trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20 C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9
C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9  resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.
resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota; Blaber, M.
no journal, ,
We have already succeeded in creation of the de novo designed protein (Symfoil) exhibiting the threefold symmetrical  -trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20
-trefoil fold based on the human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Based on the Symfoil protein, we created Symfoil-II having the three repeats. The Symfoil-II protein was expressed in Eschericha coli as soluble protein, and purified by metal affinity chromatography using nickel-chelated agarose. The Symfoil-II was further purified by anion-exchange column chromatography after removing the HisTag by proteolysis. Symfoil-II was crystallized in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.0) containing 1.8 M ammonium sulfate as precipitant at 20 C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9
C. The X-ray diffraction data was collected to 1.9 resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.
resolution using a Rigaku R-AXIS VII diffractometer. The crystal belongs to a monoclinic space group C2. The refined crystal structure of Symfoil-II showed three fold symmetry as is observed in other Symfoils.
Shibazaki, Chie; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Casein kinase 2(CK2) is one of the ubiquitous Ser/Thr kinases and is involved in the cell cycle and the survival and proliferation of cells. CK2 is a heterotetrameric structure comprising two  - or
- or  -subunits. In order to understand the biological function of the alpha catalytic subunit of CK2 (CK2
-subunits. In order to understand the biological function of the alpha catalytic subunit of CK2 (CK2 ), we aim to analyze the structure of CK2
), we aim to analyze the structure of CK2 including information of the hydrogen and hydrating water molecule by neutron crystallography. The gene coding CK2
including information of the hydrogen and hydrating water molecule by neutron crystallography. The gene coding CK2 was inserted into pET24a and expressed in
was inserted into pET24a and expressed in 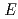 . coli strain BL21DE3, in which the mobile region (330-335) and chemically reactive thiols (Cys147 and Cys220) were removed by amino acid mutation. A total of 150 mg protein was obtained from a 6 L culture, and was used for crystallization trials. The preparation of large crystals was performed using a macro seeding method. Finally, a large crystal with a volume of approximately 2 mm
. coli strain BL21DE3, in which the mobile region (330-335) and chemically reactive thiols (Cys147 and Cys220) were removed by amino acid mutation. A total of 150 mg protein was obtained from a 6 L culture, and was used for crystallization trials. The preparation of large crystals was performed using a macro seeding method. Finally, a large crystal with a volume of approximately 2 mm was reproducibly obtained. The crystal was dialyzed in the deuterated reagent and deuterium water, and the preliminary neutron diffraction experiments were carried out at neutron beam line BioDIFF in research reactor FRM-II in Technical University of Munich. The diffraction was successfully observed greater than 1.9
was reproducibly obtained. The crystal was dialyzed in the deuterated reagent and deuterium water, and the preliminary neutron diffraction experiments were carried out at neutron beam line BioDIFF in research reactor FRM-II in Technical University of Munich. The diffraction was successfully observed greater than 1.9  resolution.
resolution.
Shimizu, Rumi; Hiromoto, Takeshi; Adachi, Motoyasu; Kuroki, Ryota; Kataoka, Misumi*; Ishikawa, Kazuhiko*
no journal, ,
For neutron crystal structure analysis of proteins, it is necessary to prepare large crystals in volume (several mm ) compared to that required for X-ray crystal structure analysis. To prepare the large volume crystal, we inevitably need much amount of purified protein. As a development in preparation of samples for neutron crystal structure analysis of proteins, we have tried to develop expression system for many kinds of protein using Eschericha coli, Brevibacillus, Pichia pastoris, cultivation cell and so on. Recently, we have succeeded in high level expression of cellulose (EGPf) derived from Archaea
) compared to that required for X-ray crystal structure analysis. To prepare the large volume crystal, we inevitably need much amount of purified protein. As a development in preparation of samples for neutron crystal structure analysis of proteins, we have tried to develop expression system for many kinds of protein using Eschericha coli, Brevibacillus, Pichia pastoris, cultivation cell and so on. Recently, we have succeeded in high level expression of cellulose (EGPf) derived from Archaea 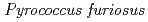 using Brevibacillus system.
using Brevibacillus system.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Shibazaki, Chie; Arai, Shigeki; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
HIV protease-I (HIV-PR) is an important drug target protein for AIDS. Since HIV-PR has a homo dimeric structure, the contribution of each monomer on its structure and function is indistinguishable. To solve this problem, a single chain derivative of HIV-PR (sc-HIV-PR) was designed. The gene coding sc-HIV-PR, in which a linker comprising glycyl-analine was placed between the C-terminal and N-terminal of each HIV-PR, was expressed in E. coli. The inactive form in inclusion bodies was successfully refolded to its active form as reported previously. The tertiary structure of sc-HIV-PR with KNI272 was determined to 1.3  resolution by X-ray crystallography. The structure of scHIV-PR was confirmed to be essentially equivalent to the original dimer form of HIV-PR with a RMSD of less than 0.3
resolution by X-ray crystallography. The structure of scHIV-PR was confirmed to be essentially equivalent to the original dimer form of HIV-PR with a RMSD of less than 0.3  including the structure of active site. This result indicates that the single chain derivatization of HIV-PR was successful and the inserted linker did not affect the overall structure of HIV-PR.
including the structure of active site. This result indicates that the single chain derivatization of HIV-PR was successful and the inserted linker did not affect the overall structure of HIV-PR.
Shibazaki, Chie; Adachi, Motoyasu; Hiromoto, Takeshi; Shimizu, Rumi; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Casein kinase 2 (CK2) is one of the ubiquitous Ser/Thr kinases and is involved in the cell cycle and the survival and proliferation of cells. CK2 is a heterotetrameric structure comprising two  - or
- or  -subunits and two regulatory
-subunits and two regulatory  -subunits. In order to understand the biological function of the alpha catalytic subunit of CK2
-subunits. In order to understand the biological function of the alpha catalytic subunit of CK2 , we aim to analyze the structure of CK2
, we aim to analyze the structure of CK2 including information of the hydrogen and hydrating water molecule by neutron crystallography. The gene coding CK2
including information of the hydrogen and hydrating water molecule by neutron crystallography. The gene coding CK2 was inserted into pET24a and expressed in E. coli strain BL21DE3, in which the mobile region and chemically reactive thiols were removed by amino acid mutation. A total of 150 mg protein was obtained from a 6 L culture, and was used for crystallization trials. The preparation of large crystals was performed using a macro seeding method specially developed for CK2
was inserted into pET24a and expressed in E. coli strain BL21DE3, in which the mobile region and chemically reactive thiols were removed by amino acid mutation. A total of 150 mg protein was obtained from a 6 L culture, and was used for crystallization trials. The preparation of large crystals was performed using a macro seeding method specially developed for CK2 . Finally, a large crystal with a volume of approximately 2 mm
. Finally, a large crystal with a volume of approximately 2 mm was reproducibly obtained. From the X-ray diffraction study, we confirmed that the crystals obtained diffracted to approx. 1
was reproducibly obtained. From the X-ray diffraction study, we confirmed that the crystals obtained diffracted to approx. 1  resolution at 100 K after soaking the crystal into the deuterated cryo protectant. The neutron diffraction data collection is planned to obtain a high resolution neutron structure of CK2
resolution at 100 K after soaking the crystal into the deuterated cryo protectant. The neutron diffraction data collection is planned to obtain a high resolution neutron structure of CK2 .
.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Nishimiya, Yoshiyuki*; Kondo, Hidemasa*; Shimizu, Rumi; Tamada, Taro; Tsuda, Sakae*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Antifreeze proteins can interfere with growing of ice and are focused from the viewpoint of the basic principles and practical applications in science and technology. Previously, it was found that most of the mutant nfeAFP6s showed similar activity to that of the wild type nfeAFP6 whereas A20V-mutant nfeAFP6 showed strong anti-freezing activity. In this study, crystal structures of the wild type and the A20V-mutant AFPs were determined to 1.2 and 1.8 resolution, respectively, by X-ray crystallography to investigate the difference of hydration structure around the essential area. The side chain of Val20 in A20V-mutant faces to the side chain Gln9, and make van der Waals interactions with Gln9 and Thr18. We found the locations of some bound water molecules at the mutated region in A20V-mutant were different from those in wild type. These observations may illustrate the complexity of what hydration structure constitutes to an ice-binding and anti-freezing activity.
resolution, respectively, by X-ray crystallography to investigate the difference of hydration structure around the essential area. The side chain of Val20 in A20V-mutant faces to the side chain Gln9, and make van der Waals interactions with Gln9 and Thr18. We found the locations of some bound water molecules at the mutated region in A20V-mutant were different from those in wild type. These observations may illustrate the complexity of what hydration structure constitutes to an ice-binding and anti-freezing activity.