Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugawara, Takanori; Watanabe, Nao; Ono, Ayako; Nishihara, Kenji; Ichihara, Kyoko*; Hanzawa, Kohei*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has investigated an accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides (MAs) included in high level wastes discharged from nuclear power plants. The ADS is a lead-bismuth cooled tank-type reactor with 800 MW thermal power. It is supposed that the ADS is safer than conventional critical reactors because it is operated in a subcritical state. The previous study performed the transient analyses for the typical ADS accidents such as unprotected loss of flow or beam overpower. It was shown that all calculation cases except loss of heat sink (LOHS) satisfied the no-damage criteria. To avoid the damage by LOHS, the ADS equips Direct Reactor Auxiliary Cooling System (DRACS) to remove the decay heat. The most important points of a DRACS operation are its reliability and to ensure the flowrate in a natural circulation state. This study aims to perform the CFD analysis of the natural circulation to clarify the flowrate in the ADS reactor vessel.
Watanabe, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Okubo, Nariaki; Nishihara, Kenji
JAEA-Technology 2020-026, 59 Pages, 2021/03
As a part of partitioning and transmutation technology development to reduce the burden of radioactive disposal, an investigation of Accelerator-Driven System (ADS) has been performed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. A beam window, which is an inherent structure of the ADS, is planned to be made from T91 steel and its shape is a thin hemisphere shell. However, it had never been tried to manufacture it out of T91 steel. In this investigation, we tried to manufacture miniature beam windows by cutting T91 steel, and to discuss the process, manufacturing accuracy and geometry measurement methods. As a result, considering a real scale ADS beam window, a figure error between designing and machining ones is estimated to be about 5%. Its effect would be very small to the structural strength.
Saito, Shigeru; Wan, T.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Obayashi, Hironari; Watanabe, Nao; Ohdaira, Naoya*; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Yamaki, Kenichi*; Kita, Satoshi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011041_1 - 011041_6, 2021/03
An Accelerator Driven System (ADS) for waste transmutation investigated in JAEA employs lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) as a neutron production target material and coolant. The neutrons are to be produced via the spallation with 1.5 GeV proton beam injection. As materials irradiation data are important for ADS development, JAEA plans to construct an irradiation facility with LBE neutron production target in J-PARC. There are many technical issues on LBE for practical use. In JAEA, various R&Ds are being carried out. Concerning corrosion study, conditioning operation and functional tests of OLLOCHI started. Oxygen concentration control technology has also developing. In the large scale LBE loop experiment, the operation for steady state and transient experiments was performed by using IMMORTAL. In the area of instrument, development of ultrasonic flow meter and freeze seal valve are progressing as a key technology for the LBE loop system. Investigation of behavior of impurities in LBE, which is important for design of the irradiation facility, started. In this paper, the status of the LBE studies and experimental plan will be presented.
Watanabe, Nao; Obayashi, Hironari; Sugawara, Takanori; Sasa, Toshinobu; Nishihara, Kenji; Castelliti, D.*
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.248 - 261, 2019/08
For the R&D for lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) cooled Accelerator Driven System (ADS), installation of experimental facility using LBE spallation target dedicated for ADS materials irradiation under flowing high temperature LBE environment is planned within the J-PARC project. JAEA has recently finalized the construction of "IMMORTAL", a demonstrative test loop representing a 1:1 model of the above LBE spallation target system. Such facility pursues several different objectives such as studies on the thermal-hydraulic behavior of the target, and validation of the LBE physical properties, the pressure drops and the heat transfer correlations. These results will be useful for design of the facility and LBE target/cooled ADS. In the frame of a bi-lateral collaboration between JAEA and SCK-CEN, a benchmark exercise on the experimental results from IMMORTAL has been carried out. The calculations have been performed with RELAP5-3D System Thermal-Hydraulic code. To assess and predict the thermal-hydraulic behavior of its primary loop, RELAP5-3D calculation models have been configured. The calculated results from these models represented that a valid contribution towards the validation of the LBE properties and empirical correlations present in RELAP5-3D code.
Watanabe, Nao; Obayashi, Hironari; Nishihara, Kenji
no journal, ,
JAEA investigates lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) as a candidate of coolant and spallation target of Accelerator Driven System (ADS). Construction of an experimental facility for LBE spallation target is planned within the J-PARC project for feasibility study of ADS's beam window, which is exposed to high temperature LBE flow and strong proton and neutron irradiation environment. As a demonstration, an LBE target mock-up loop "IMMORTAL" was constructed to confirm the operation of a primary cooling system and to implement integration tests of developing components of LBE technologies. One of important subjects is the thermal-hydraulic characteristic of LBE, however, studies about it are still limited compared with that of light water. In this study, numerical thermal-hydraulic simulation of IMMORTAL was implemented by using RELAP5-3D code, and the calculation results were evaluated. A calculation model of the primary LBE loop of IMMORTAL was configurated. In terms of heat balance, except for a module heater (MH) and two heat exchangers (HXs), the adiabatic assumption is considered. The MH have 18 heater rods, but in this model the heat source was simulated as if a rod having the same heat transfer area as the actual. In addition, since RELAP5-3D code is unable to describe directly a configuration of the HXs, positive and negative virtual power source terms were installed to the model. Comparing to the measured values, it overestimated the temperatures in the primary loop by around 20 K. It seems to be caused by the uncertainties in the LBE-side Nusselt correlation and by a possible underestimation of the fin efficiency.
Watanabe, Nao; Obayashi, Hironari; Nishihara, Kenji
no journal, ,
JAEA investigates lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) as a candidate of coolant and spallation target of Accelerator Driven System (ADS). Construction of an experimental facility for LBE spallation target is planned within the J-PARC project for feasibility study of ADS's beam window, which is exposed to high temperature LBE flow and strong proton and neutron irradiation environment. As a demonstration, an LBE target mock-up loop "IMMORTAL" was constructed to confirm the operation of a primary cooling system and to implement integration tests of developing components of LBE technologies. The thermal-hydraulic characteristic of LBE is very important, however, studies about it are still limited compared with that of light water. Therefore, in this research, a calculation model of IMMORTAL's primary loop was made and the thermal-hydraulic behavior was numerically simulated by using the RELAP5-3D code. Then, simulation results and experimental data are compared to validate heat transfer coefficient correlations and properties of LBE.
Sugawara, Takanori; Watanabe, Nao; Nishihara, Kenji
no journal, ,
There are many inherent issues in R&Ds of LBE cooled ADS. To address these issues effectively, we have launched a 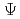 (PSi, Proton accelerator-driven Subcritical virtual system) project which construct a virtual ADS on computer. This presentation will introduce an overview and part of details for the plant design part. One of the most important issues for the ADS is a design of a beam window (BW) which is a boundary of an accelerator and a subcritical core. The BW will be used in the severe condition. In the project, a design system for the BW is developed to achieve an efficient design. The design system consists of the FLUENT and ANSYS codes and performs a coupled analysis of thermal hydraulics and structural ones although the irradiation effect is not considered in the analysis. LBE flow in the reactor vessel is also important for a design of coolant system. For the design of coolant system such as PRACS, LBE flow in the reactor vessel has been simulated by the FLUENT code in three-dimensional calculation model.
(PSi, Proton accelerator-driven Subcritical virtual system) project which construct a virtual ADS on computer. This presentation will introduce an overview and part of details for the plant design part. One of the most important issues for the ADS is a design of a beam window (BW) which is a boundary of an accelerator and a subcritical core. The BW will be used in the severe condition. In the project, a design system for the BW is developed to achieve an efficient design. The design system consists of the FLUENT and ANSYS codes and performs a coupled analysis of thermal hydraulics and structural ones although the irradiation effect is not considered in the analysis. LBE flow in the reactor vessel is also important for a design of coolant system. For the design of coolant system such as PRACS, LBE flow in the reactor vessel has been simulated by the FLUENT code in three-dimensional calculation model.
Watanabe, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji
no journal, ,
In order to design an accelerator driven system (ADS), a beam window, which divides between areas of an accelerator and a subcritical core, is one of important structures. JAEA made a 3D model of a beam window and surrounding lead bismuth thermal flow field and developed a coupled analysis system of thermal hydraulics and structure in ANSYS Workbench. In the system a heat generation distribution from PHITS code is read, and steady thermal hydraulic of LBE coolant and stress of the beam window are calculated by Fluent code. Then its eigenvalue buckling is evaluated. In 3D analyses, non-axisymmetric evaluations are considered and radial deformations are found in low buckling modes.
Watanabe, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Okubo, Nariaki; Nishihara, Kenji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 wt.% oxygen at 803K
wt.% oxygen at 803KWatanabe, Nao; Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki
no journal, ,
Oxide layers form at a surface of 316L stainless steel (SS) in lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) with sufficient oxygen concentration. The oxide layers are known to suppress dissolution corrosion of SS in LBE under constant conditions. However, it was unclear how well the corrosion suppression effect of the oxide layers formed in LBE would be maintained when it exposed to a reducing atmosphere. In order to evaluate it, a reduction test of pre-oxidized 316L SS in stagnant LBE at 803K and low oxygen concentration from 10 wt.% to 10
wt.% to 10 wt.% for 1976h was performed. After pre-oxidation, an outer Fe
wt.% for 1976h was performed. After pre-oxidation, an outer Fe O
O layer and an inner Fe-Cr oxide layer formed at the surface of 316L SS. After the reduction test, most of Fe
layer and an inner Fe-Cr oxide layer formed at the surface of 316L SS. After the reduction test, most of Fe O
O layer was dissolved. On the other hand, Fe-Cr oxide layer was not, and the Fe-Cr oxide layer without Ni prevented LBE penetration. However, the Fe-Cr oxide layer cracking in some areas was observed and LBE penetrated through the layer there.
layer was dissolved. On the other hand, Fe-Cr oxide layer was not, and the Fe-Cr oxide layer without Ni prevented LBE penetration. However, the Fe-Cr oxide layer cracking in some areas was observed and LBE penetrated through the layer there.
Watanabe, Nao; Nishihara, Kenji; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
In the design of a reactor using lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) as a coolant, estimating corrosion rate of structural materials is an important issue in considering safety and the life of the entire structure. Oxide layers formed on the surface of T91 steel have corrosion inhibition effect, however, if they dissolve, corrosion can progress rapidly. Growth and dissolution rates of oxide layers depend on temperature and oxygen concentration, especially under static LBE, a semi-mechanical model of these rates has been developed. However, knowledge of them in flow filed is limited. This study aims to estimate them in flowing LBE by CFD. In this report, results of analysis by ANSYS Fluent code implementing the existing these rates model are described.
Watanabe, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
In the design of Accelerator-Driven System (ADS), a beam window is one of the structures used under severe conditions. Since the maximum temperature of the beam window at rated operation will be more than 500 C, a creep damage evaluation has been required. Therefore, we have developed a coupled analysis system on ANSYS Workbench to evaluate the creep strain quantitatively. In this system, temperature distribution of the beam window is calculated by the coupled analysis of particle transport and thermal hydraulics analyses, and then is used as an input data for a creep analysis. Calculation result by this analysis system showed that the creep strain after the rated operation was less than 0.1%.
C, a creep damage evaluation has been required. Therefore, we have developed a coupled analysis system on ANSYS Workbench to evaluate the creep strain quantitatively. In this system, temperature distribution of the beam window is calculated by the coupled analysis of particle transport and thermal hydraulics analyses, and then is used as an input data for a creep analysis. Calculation result by this analysis system showed that the creep strain after the rated operation was less than 0.1%.