Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kunieda, Satoshi; Furutachi, Naoya; Minato, Futoshi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Ebata, Shuichiro*; Yoshida, Toru*; Nishihara, Kenji; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(12), p.1073 - 1091, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:65.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new nuclear data library, JENDL/ImPACT-2018, is developed for an innovative study on the transmutation of long-lived fission products. Nuclear reaction cross- sections are newly evaluated for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV for 163 nuclides including long-lived nuclei such as  Se,
Se,  Zr,
Zr,  Pd and
Pd and  Cs. Our challenge is an evaluation of cross-sections for a number of unstable nuclei over a wide energy range where the experimental data are very scarce. We estimated cross- sections based on a nuclear model code CCONE that incorporates an advanced knowledge on the nuclear structure theory and a model-parameterization based on a new experimental cross-sections measured by the inverse kinematics. Through comparisons with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data give predictions of cross-sections better than those in the existing libraries.
Cs. Our challenge is an evaluation of cross-sections for a number of unstable nuclei over a wide energy range where the experimental data are very scarce. We estimated cross- sections based on a nuclear model code CCONE that incorporates an advanced knowledge on the nuclear structure theory and a model-parameterization based on a new experimental cross-sections measured by the inverse kinematics. Through comparisons with available experimental data on the stable isotopes, it is found that the present data give predictions of cross-sections better than those in the existing libraries.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Fujita, Reiko*; Niita, Koji*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (122), p.33 - 43, 2019/02
A program related to the transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) entitled "Reduction and Resource Recycling of High-level Radioactive Wastes through Nuclear Transmutation" has been conducted under the Impulsing Paradigm Change through Disruptive Technologies Program (ImPACT) organized by the Cabinet Office since 2014 and it will be finished in FY 2018. Various activities from acquisition of basic data to examination of transmutation scenario are being carried out as the five separated projects. R&Ds related to nuclear data are also conducted and many outcomes are being produced. This article describes results of the two projects related nuclear data with a short introduction of the whole project.
Kunieda, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Minato, Futoshi; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Kitatani, Fumito; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.41 - 46, 2016/09
Neutron- and proton-induced cross-section data are required in a wide energy range beyond 20 MeV, for the design of accelerator applications. New evaluations are performed with recent knowledge in the optical and pre-equilibrium model calculations. We also evaluated cross-sections for p+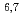 Li and p+
Li and p+ Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Be which have been highly requested from a medical field. The present high-energy nuclear data library, JENDL-4.0/HE, includes evaluated cross-sections for incident neutrons and protons up to 200 MeV (for about 130 nuclei). We overview substantial features of the library, i.e., (1) systematic evaluation with CCONE code, (2) challenges for evaluations of light nuclei and (3) inheritance of JENDL-4.0 and JENDL/HE-2007. In this talk, we also focus on the results of benchmark calculation for neutronics to show performance of the present library.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Maeda, Shota; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)High intensity laser-plasma interaction has attracted considerable interest for a number of years. The laser-plasma interaction is accompanied by generation of various charged particle beams. Results of simultaneous novel measurements of electron-induced photonuclear neutrons (photoneutron), which are a diagnostic of the laser-plasma interaction, are proposed to use for optimization of the laser-plasma ion generation. The proposed method is demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity os 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Sihver, L.*; Niita, Koji*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 88(1-2), p.143 - 150, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:80.57(Biology)The microdosimetric function of PHITS has been applied to the biological dose estimation for charged-particle therapy and the risk estimation for astronauts. The former application was performed in combination with the microdosimetric kinetic model, while the latter was done with the radiation quality factor expressed as a function of lineal energy. Owing to the unique features of the microdosimetric function, the improved PHITS has a potential to establish more sophisticated systems for the radiological protection in space as well as the treatment planning of charged-particle therapy.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Kase, Yuki*; Tsuruoka, Chizuru*; Suzuki, Masao*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Niita, Koji*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 143(2-4), p.491 - 496, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:91.34(Environmental Sciences)We reanalyzed the survival fraction data, using the microdosimetric-kinetic (MK) model implemented in the PHITS code. It is found from the analysis that the MK model successfully accounts for the cell survival-fractions under a variety of irradiation conditions, using only y* parameter.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kase, Yuki*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Niita, Koji*; Sihver, L.*
Hoshasen Kagaku, 52(2), p.47 - 53, 2009/02
We improved the particle transport simulation code PHITS to be capable of estimating the microdosimetric PDs in macroscopic area, by means of incorporating a mathematical function that can instantaneously calculate the PDs around the trajectory of HZE particles with precision equivalent to a microscopic track-structure simulation. A new method for estimating biological dose, a product of physical dose and RBE, from charged-particle therapy was established, using the improved PHITS coupled with a microdosimetric kinetic model.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kase, Yuki*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Niita, Koji*; Sihver, L.*
Radiation Research, 171(1), p.107 - 117, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:91.05(Biology)A new method for estimating biological dose from charged-particle therapy was established, using the improved PHITS coupled with a microdosimetric kinetic model. In the method, the biological dose can be determined by multiplying the physical dose by the RBE for a surviving fraction of tumor cells, which is estimated from the saturation-corrected dose-mean lineal energy y* calculated by the improved PHITS. The accuracy of the biological dose estimated by this method was reliably verified by comparing the calculated physical doses and RBE values with the corresponding experimental data obtained by irradiating a slab phantom with the spread-out Bragg peak beams as well as several types of mono-energetic HZE particles. The simulation technique established in this study will help to optimize the treatment planning of charged-particle therapy for maximizing the therapeutic effect on tumor while minimizing unintended harmful effects on surrounding normal tissues.
 Li(
Li( , n)
, n) B reaction
B reactionIshiyama, Hironobu*; Hashimoto, Takashi; Ishikawa, Tomoko*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Das, S. K.*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 640(3), p.82 - 85, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:84.88(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The excitation function of the  Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction was measured while identifying the final state event by event in the region of E
B reaction was measured while identifying the final state event by event in the region of E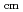 = 0.7 - 2.6 MeV using a highly efficient detector system and a low-energy
= 0.7 - 2.6 MeV using a highly efficient detector system and a low-energy  Li beam. The results are much improved both in statistics and precisions, and show smaller cross sections than those of previous measurements by a factor of more than 2 in the low-energy region of E
Li beam. The results are much improved both in statistics and precisions, and show smaller cross sections than those of previous measurements by a factor of more than 2 in the low-energy region of E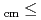 1.5 MeV. A resonance-like structure is found at around E
1.5 MeV. A resonance-like structure is found at around E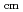 = 0.85 MeV.
= 0.85 MeV.
 Li(
Li( ,n)
,n) B reaction for astrophysical interest
B reaction for astrophysical interestDas, S. K.*; Fukuda, Tomokazu*; Mizoi, Yutaka*; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 847, p.374 - 376, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Takashi; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Ishikawa, Tomoko*; Kawamura, Takashi*; Nakai, Koji*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Miyatake, Hiroari; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 556(1), p.339 - 349, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new type of three dimensional tracking and proportional gas counter has been developed. Adopting a gating-grid system, performance of the detector becomes stable under the injection rate of charged particles less than 4 10
10 pps. It is a useful detection system for astrophysical experiments using radioactive nuclear beams, since the efficiency is so high as 100 %.
pps. It is a useful detection system for astrophysical experiments using radioactive nuclear beams, since the efficiency is so high as 100 %.
Harada, Masahide; Watanabe, Noboru; Konno, Chikara; Meigo, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Yujiro; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.197 - 204, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)For a construction of maintenance and storage scenarios for JSNS, lives of structure material need to be estimated. DPA (Displacement per Atom) was a major index of radiation damage. So we evaluated DPA value of each component. Function of the DPA calculation was equipped to the PHITS code, which was particle and heavy ion transport code. For DPA calculation, displacement cross section was necessary. Displacement cross sections of neutron below 150 MeV were processed by the NJOY code from LA150 library and those of neutron above 150MeV and proton in the all energy region were obtained from energies of fragments calculated in the PHITS. By using the PHITS, we calculated DPA values and DPA mapping. We obtained that the peak DPA values at end of 5000MWh operation were 4.1 for target vessel, 2.8 for reflector and moderator vessels, and 0.4 for proton beam windows, respectively. We estimated the target life at 1 year and the moderator life at 6 year.
Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Takada, Hiroshi; Ino, Takashi*; Sato, Setsuo*; Jerde, E.*; Glasgow, D.*; Niita, Koji*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 150(1), p.99 - 108, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)A neutronic benchmark experiment on a simulated spallation neutron target assembly with 1.94, 12 and 24 GeV proton beams conducted by using the AGS accelerator at BNL/US was analyzed to investigate validity of neutronics calculations on proton accelerator driven spallation neutron sources. Monte Carlo particle transport calculation codes NMTC/JAM, MCNPX and MCNP-4A with associated cross section data in JENDL and LA-150 were used for the analysis. As a result, although the overall energy range was encompassed from GeV to meV, i.e., more than 12 orders of magnitude, calculated fast and thermal neutron fluxes agreed approximately within  40 % with the experiments. Accordingly, it was concluded that neutronics calculations with these codes and cross section data were adequate for estimating nuclear properties in spallation neutron sources.
40 % with the experiments. Accordingly, it was concluded that neutronics calculations with these codes and cross section data were adequate for estimating nuclear properties in spallation neutron sources.
Watanabe, Tadashi; Ito, Goichi*; Nakamura, J.*; Kono, Koji*; Ohashi, H.*
Proceedings of 3rd Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-3), p.146 - 151, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Tadashi; Kono, Koji*; Ohashi, H.*
Application of High-Performance Computing in Engineering VII, p.115 - 124, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Tadashi; Ebihara, Kenichi; Ito, Goichi*; Kono, Koji*
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-029, 61 Pages, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Nishio, Gunji; Koike, Tadao; Miyata, Teijiro; Takada, Junichi; *
JAERI-Tech 95-029, 59 Pages, 1995/03
no abstracts in English
; ; *
JAERI-M 86-101, 205 Pages, 1986/07
no abstracts in English
 ,n) reactions on light neutron-rich nuclei using low-energy radioactive nuclear beams
,n) reactions on light neutron-rich nuclei using low-energy radioactive nuclear beamsHashimoto, Takashi; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Miyatake, Hiroari; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English