Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Chiera, N. M.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Eichler, R.*; Tomitsuka, Tomohiro; Asai, Masato; Adachi, Sadia*; Dressler, R.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Inoue, Hiroki*; Ito, Yuta; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 60(33), p.17871 - 17874, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.88(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The formation and the chemical characterization of single atoms of dubnium (Db, element 105), in the form of its volatile oxychloride, was investigated using the on-line gas phase chromatography technique, in the temperature range 350 - 600  C. Under the exact same chemical conditions, comparative studies with the lighter homologs of group-5 in the Periodic Table clearly indicate the volatility sequence being NbOCl
C. Under the exact same chemical conditions, comparative studies with the lighter homologs of group-5 in the Periodic Table clearly indicate the volatility sequence being NbOCl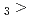 TaOCl
TaOCl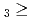 DbOCl
DbOCl . From the obtained experimental results, thermochemical data for DbOCl
. From the obtained experimental results, thermochemical data for DbOCl were derived. The present study delivers reliable experimental information for theoretical calculations on the chemical properties of transactinides.
were derived. The present study delivers reliable experimental information for theoretical calculations on the chemical properties of transactinides.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA07_1 - 06KA07_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.01(Physics, Applied)Thermal oxidation of AlGaN surface and its impact on the electrical properties of AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were investigated by means of synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-PES), atomic force microscopy (AFM) and C-V measurements. SR-PES analysis revealed that the AlGaN surface is oxidized even at low temperature of 400 C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800
C, in contrast to no oxide formation on GaN surface. However, since no noticeable change in the surface morphology was observed at temperatures up to 800 C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850
C, it can be concluded that an ultrathin oxide overlayer is formed on the AlGaN surface. On the other hand, for the oxidation treatments above 850 C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800
C, the formation of small oxide grains was observed over the entire area of the AlGaN surface, and the growth of oxide grains significantly degraded the surface morphology. Therefore, the AlGaN/GaN MOS capacitors were fabricated on the AlGaN surface oxidized at moderate temperatures up to 800 C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400
C. While we have confirmed that relatively good interface properties are obtained for direct AlON deposition without oxidation treatment, it was found that the oxidation treatment at 400 C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
C leads to further improvement of interface properties and reduction of C-V hysteresis.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistors
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS heterojunction field-effect transistorsWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA03_1 - 06KA03_6, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.99(Physics, Applied)The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Shih, H.-A.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(6S3), p.06KA02_1 - 06KA02_7, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:65.6(Physics, Applied)We fabricated AlON dielectric films by repeating thin AlN deposition and in situ O oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
 /GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliability
/GaN stacks for high-quality GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor devices with improved gate dielectric reliabilityYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Hisashi*; Takahashi, Tokio*; Shimizu, Mitsuaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Express, 11(1), p.015701_1 - 015701_4, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:84.89(Physics, Applied)A simple and feasible method for fabricating high-quality and highly reliable GaN-based metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices was developed on the basis of systematic physical and electrical characterizations. Chemical vapor deposition of SiO films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO
films directly onto GaN substrates forming Ga-oxide interlayers was used to fabricate SiO /GaO
/GaO /GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10
/GaN stacked structures. Although well-behaved hysteresis-free GaN-MOS capacitors with extremely low interface state density below 10 cm
cm eV
eV were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO
were obtained by post-deposition annealing, Ga diffusion into overlying SiO layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
layers severely degraded the insulating property and dielectric breakdown characteristics of the MOS devices. However, this problem was found to be solved by employing rapid thermal processing, leading to superior performance of the GaN-MOS devices in terms of interface quality, insulating property and gate dielectric reliability.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 111(4), p.042102_1 - 042102_5, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:60.44(Physics, Applied)AlGaN/GaN HFET (hetero-junction field-effect transitor) has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
Yamaguchi, Mika; Hidaka, Akihide; Ikuta, Yuko; Murakami, Kenta*; Tomita, Akira*; Hirose, Hiroya*; Watanebe, Masanori*; Ueda, Kinichi*; Namaizawa, Ken*; Onose, Takatoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-002, 60 Pages, 2017/03
Since 2010, IAEA has held the NEM School to develop future leaders who plan and manage nuclear energy utilization in their county. Since 2012, JAEA together with Japan Nuclear HRD Network, University of Tokyo, Japan Atomic Industrial Forum and JAIF International Cooperation Center have cohosted the school in Japan in cooperation with IAEA. Since then, the school has been held in Japan every year. In 2006, Japanese nuclear technology and experience, such as lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, were provided to offer a unique opportunity for the participants to learn about particular cases in Japan. Through the school, we contributed to the internationalization of Japanese young nuclear professionals, development of nuclear human resource of other countries including nuclear newcomers, and enhanced cooperative relationship with IAEA. Additionally, collaborative relationship within the network was strengthened by organizing the school in Japan.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 121(3), p.035303_1 - 035303_9, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:91.84(Physics, Applied)Initial oxidation of GaN(0001) epilayers and subsequent growth of thermal oxides in dry oxygen ambient were investigated by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, spectroscopic ellipsometry, atomic force microscopy and X-ray diffraction measurements. It was found that, whereas initial oxide formation tends to saturate at temperatures below 800 C, selective growth of small oxide grains proceeds at dislocations in the epilayers, followed by noticeable grain growth leading to rough surface morphology at higher oxidation temperatures. This indicates that oxide growth and its morphology are crucially dependent on the defect density in the GaN epilayers. Structural characterizations also revealed that polycrystalline
C, selective growth of small oxide grains proceeds at dislocations in the epilayers, followed by noticeable grain growth leading to rough surface morphology at higher oxidation temperatures. This indicates that oxide growth and its morphology are crucially dependent on the defect density in the GaN epilayers. Structural characterizations also revealed that polycrystalline  - and
- and  -phase Ga
-phase Ga O
O grains in an epitaxial relation with the GaN substrate are formed from the initial stage of the oxide growth. On the basis of these experimental findings, we also developed a comprehensive model for GaN oxidation mediated by nitrogen removal and mass transport.
grains in an epitaxial relation with the GaN substrate are formed from the initial stage of the oxide growth. On the basis of these experimental findings, we also developed a comprehensive model for GaN oxidation mediated by nitrogen removal and mass transport.
 adsorption
adsorption  lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water molecules
lattice defect sites of Prussian blue filled with coordination and crystallization water moleculesIshizaki, Manabu*; Akiba, Sae*; Otani, Asako*; Hoshi, Yuji*; Ono, Kenta*; Matsuba, Mayu*; Togashi, Takanari*; Kanaizuka, Katsuhiko*; Sakamoto, Masatomi*; Takahashi, Akira*; et al.
Dalton Transactions, 42(45), p.16049 - 16055, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:178 Percentile:99.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We have revealed the fundamental mechanism of specific Cs adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs
adsorption into Prussian blue (PB) in order to develop high-performance PB-based Cs adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe
adsorbents in the wake of the Fukushima nuclear accident. We compared two types of PB nanoparticles with formulae of Fe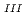
 [Fe
[Fe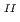 (CN)
(CN) ]3
]3 xH
xH O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH
O (x = 10-15) (PB-1) and (NH )0.70Fe
)0.70Fe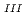 1.10[Fe
1.10[Fe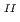 (CN)
(CN) ]
] 1.7H
1.7H O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs
O (PB-2) with respect to the Cs adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe
adsorption ability. The synthesised PB-1, by a common stoichiometric aqueous reaction between 4Fe and 3[Fe
and 3[Fe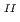 (CN)
(CN) ]
]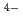 , showed much more efficient Cs
, showed much more efficient Cs adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
adsorption ability than did the commercially available PB-2.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Tsunogai, Shizuo*; Kawada, Kentaro*; Watanabe, Shuichi*; Aramaki, Takafumi
Journal of Oceanography, 59(5), p.685 - 693, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:48.21(Oceanography)The water column distributions of CFC (chlorofluorocarbon) were determined twice in 2000 and 2001 in the northwestern Japan Sea. In 2000, the CFC-11 concentration decreased almost exponentially with depth from 6 pmol/kg at a few hundred m deep to 0.3 pmol/kg or less at the bottom of about 3400 m depth at 3 stations about 300 km off Vladivostok. In 2001, the CFC-11 concentration increased extremely up to 2 pmol/kg in the bottom water, while it did not increase at a station about 450 km away to the northeast. This is due to the renewal of the bottom water replaced by the surface water flowing down along the continental slope. The increase in the CFC-11 concentration was observed even in the whole water column above 3000 m depth. The increase in inventory is almost four times larger than that in the bottom water below 3000 m depth and equals about 1/6 of the total inventory found in 2000. The increase also means that 3 % of the deep water was replaced by the recent surface water or the turnover time of the deep water to be about 30 years, if the turnover occurs every year.
Yamada, Takahiro*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ito, Joyo*; Asahara, Ryohei*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; et al.
no journal, ,
Thermal oxidation process of self-standing GaN (ss-GaN) substrates with low-defect density were investigated by atomic force microscopy and synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. ss-GaN sample showed a flat surface morphology without pits which are ascribed to dislocation defects in the measured area (1  mx1
mx1  m). Therefore, the preferential formation of Ga-oxides at the pits was not observed by thermal oxidation, and the flat surface morphology was kept in the sample oxidized at 800
m). Therefore, the preferential formation of Ga-oxides at the pits was not observed by thermal oxidation, and the flat surface morphology was kept in the sample oxidized at 800 C (the root-mean-square (RMS) roughness of 0.14 nm). However, the ss-GaN sample oxidized at 900
C (the root-mean-square (RMS) roughness of 0.14 nm). However, the ss-GaN sample oxidized at 900 C showed rough surface morphology due to the formation of small Ga-oxide grains (RMS roughness of 0.62 nm). The grains drastically grew at 1000
C showed rough surface morphology due to the formation of small Ga-oxide grains (RMS roughness of 0.62 nm). The grains drastically grew at 1000 C, resulted in the surface morphology consisting of
C, resulted in the surface morphology consisting of  -Ga
-Ga O
O crystal.
crystal.
 /GaN MOS capacitor by interfacial GaOx formation with post-oxidation treatment
/GaN MOS capacitor by interfacial GaOx formation with post-oxidation treatmentYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Interface properties of SiO /GaN structure with post-oxidation treatment were investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and C-V measurements. High-resolution Ga 2p
/GaN structure with post-oxidation treatment were investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and C-V measurements. High-resolution Ga 2p core-level spectra for SiO
core-level spectra for SiO /GaN structure oxidized at 800 degrees showed asymmetric feature with a shoulder at higher binding energies compared to that for wet-cleaned GaN surface. From peak deconvolution of the Ga2p
/GaN structure oxidized at 800 degrees showed asymmetric feature with a shoulder at higher binding energies compared to that for wet-cleaned GaN surface. From peak deconvolution of the Ga2p spectrum, formation of GaOx layer at the SiO
spectrum, formation of GaOx layer at the SiO /GaN interface was revealed. C-V measurements of the SiO
/GaN interface was revealed. C-V measurements of the SiO /GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor exhibited apparently low frequency dispersion and a small hysteresis of below 50 mV. Moreover, the C-V curves well agreed with an ideal C-V curve. These results indicate that good interface properties were achieved by the interfacial GaOx formation.
/GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor exhibited apparently low frequency dispersion and a small hysteresis of below 50 mV. Moreover, the C-V curves well agreed with an ideal C-V curve. These results indicate that good interface properties were achieved by the interfacial GaOx formation.
 /GaN and its effect on electrical properties
/GaN and its effect on electrical propertiesYamada, Takahiro*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
no journal, ,
Formation of thin GaOx interlayer by thermal oxidation of SiO /GaN structure was investigated by spectroscopic ellipsometry and synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. In the SiO
/GaN structure was investigated by spectroscopic ellipsometry and synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. In the SiO /GaN structure before thermal oxidation, GaOx interlayer (about 4 nm) was already formed. This is considered to be attributable to O
/GaN structure before thermal oxidation, GaOx interlayer (about 4 nm) was already formed. This is considered to be attributable to O plasma exposure to GaN surface during SiO
plasma exposure to GaN surface during SiO deposition by plasma CVD. Thickness of the GaOx interlayer slightly increased about 1 nm by thermal oxidation up to 1000 degrees. This behavior indicates that the oxidation of GaN surface was markedly suppressed by the SiO
deposition by plasma CVD. Thickness of the GaOx interlayer slightly increased about 1 nm by thermal oxidation up to 1000 degrees. This behavior indicates that the oxidation of GaN surface was markedly suppressed by the SiO capping layer. C-V characteristics of SiO
capping layer. C-V characteristics of SiO /GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor with the thin GaOx layer, except that prepared at 1000 degrees, exhibited low frequency dispersion and hysteresis of below 10 mV. The measured C-V curves also well agreed with ideal C-V curves. These results demonstrate that the excellent GaN MOS interface properties were realized by the insertion of thin GaOx interlayer.
/GaOx/GaN MOS capacitor with the thin GaOx layer, except that prepared at 1000 degrees, exhibited low frequency dispersion and hysteresis of below 10 mV. The measured C-V curves also well agreed with ideal C-V curves. These results demonstrate that the excellent GaN MOS interface properties were realized by the insertion of thin GaOx interlayer.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
AlGaN/GaN HFET (hetero-junction field-effect transitor) has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. Since AlGaN/GaN HFET with Schottky gate is restricted in device application due to large gate leakage current and normally-on operation, MOS gate stack with deposited gate insulator has been widely investigated to overcome these limitations. Among various insulating materials, Al O
O is one of the potential candidates because of its wide bandgap and high thermal stability. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al
is one of the potential candidates because of its wide bandgap and high thermal stability. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Shih, H.*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Initial oxidation process of AlGaN surface during thermal oxidation was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy. Thermal oxidation of AlGaN/GaN/Si(111) substrates was carried out for 30 min in the temperature range from 200 to 1000 degrees in O ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
ambient. The obtained Ga 2p spectra exhibited peak shift toward the higher binding energy with increasing oxidation temperature, suggesting the growth of Ga oxides on AlGaN surface. The peak deconvolution of Ga 2p spectra into Ga-O and Ga-N components revealed that the formation of Ga oxides was formed on AlGaN surface at above 400 degrees while GaN surface was stable below 600 degrees. These results indicate that AlGaN surface is easy to be oxidized compared to GaN surface.
Watanabe, Kenta*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
AlGaN/GaN HFET has gained much attention as next-generation high frequency and high power devices. Among various insulating materials, Al O
O is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al
is one of the potential candidates. However, large amount of electrical defects at MOS interfaces severely degrade both drive current and threshold voltage stability. Positive Vth shift due to electron trapping in Al O
O layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al
layer by applying positive gate bias is often observed for Al O
O /AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al
/AlGaN/GaN MOS structures. We have recently reported that N incorporation into Al O
O significantly reduces electron traps in Al
significantly reduces electron traps in Al O
O layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al
layer for Si and SiC MOS devices. In this study, we systematically investigated the interface reaction between Al-based dielectrics (Al O
O and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
and AlON) and AlGaN layer during deposition and post-deposition annealing (PDA), and revealed high thermal stability of AlON/AlGaN interface.
 /AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVD
/AlGaN interface property deposited by PECVDTerashima, Daiki*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Shih, H.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Impact of input power and substrate temperature of SiO deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO
deposition by plasma-enhanced CVD on SiO /AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO
/AlGaN interface was investigated by means of electrical characterization of MOS capacitors. Synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy revealed that Ga oxide component on AlGaN surface increases with increasing input power of PECVD. MOS capacitors with SiO gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO
gate insulator deposited at low input power shows relatively better SiO /AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO
/AlGaN interface quality, despite degraded interface quality for the sample with SiO deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
deposited at high input power. These results suggest that AlGaN surface oxidation during oxide deposition should be controlled to obtain good interface property.
 /AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFET
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETWatanabe, Kenta*; Terashima, Daiki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Ishida, Masahiro*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; et al.
no journal, ,
The advantage of SiO /AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO
/AlON stacked gate dielectrics over SiO , AlON and Al
, AlON and Al O
O single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
single dielectric layers was demonstrated. Our systematic research revealed that the optimized stacked structure with 3.3-nm-thick AlON interlayer is beneficial in terms of superior interface quality, reduced gate leakage current and C-V hysteresis for next-generation high frequency and high power AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
Nozaki, Mikito*; Watanabe, Kenta*; Yamada, Takahiro*; Shih, H.*; Nakazawa, Satoshi*; Anda, Yoshiharu*; Ueda, Tetsuzo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
We fabricated AlON dielectric films by repeating thin AlN deposition and in situ O oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.
oxidation for AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs. Uniform nitrogen distribution is achievable by the proposed ALD-based process and that nitrogen concentration can be precisely controlled by changing AlN thickness (ALD cycle number) in each step. It was found that AlON films grown by ALD system offers significant advantages in terms of practical application while keeping superior Vth stability and electrical properties at the insulator/AlGaN interface in AlGaN/GaN MOS-HFETs.