Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.1(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Naoe, Takashi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Watanabe, Akihiko*
Journal of Neutron Research, 22(2-3), p.337 - 343, 2020/10
For operating a spallation neutron source and a muon target safely and efficiently, a general control system (GCS) operates within Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF). GCS administers operation and interlock processes of many instruments under various operation status. Since the first beam injection in 2008, it has operated stably without any serious troubles for more than ten years. GCS has a data storage server storing operational data on status around target stations. It has functioned well to detect and investigate unusual situations by checking data in this server. For continuing stable operation of MLF in future, however, introduction of abnormality sign determination system (ASDS) will be necessary for picking up potential abnormalities of target stations caused by radiation damages, time-related deterioration and so on. It will judge abnormalities from slight state transitions of target stations based on analysis with various operational data throughout proton beams, target stations, and secondary beams during long-term operations. This report mentions present status of GCS, conceptual design of ASDS, and installation of an integral data storage server which can deal with various data for ASDS integrally.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:262 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Arai, Takehiko*; Arai, Tomoko*; Hirata, Naru*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Honda, Chikatoshi*; Imae, Naoya*; et al.
Space Science Reviews, 208(1-4), p.317 - 337, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:71.62(Astronomy & Astrophysics)NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer is installed on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to observe the target C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu at near infrared wavelengths of 1.8 to 3.2 micrometer. It aims to obtain reflectance spectra in order to detect absorption bands of hydrated and hydroxide minerals in the 3 micrometer-band. We adopted a linear-image sensor with indium arsenide (InAs) photo diodes and a cooling system with a passive radiator to achieve an optics temperature of 188 K, which enables to retaining sufficient sensitivity and noise level in the 3 micrometer wavelength region. We conducted ground performance tests for the NIRS3 flight model (FM) to confirm its baseline specifications. The results imply that the properties such as the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conform to scientific requirements to determine the degree of aqueous alteration, such as CM or CI chondrite, and the stage of thermal metamorphism on the asteroid surface.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Hirota, Akinari*; Watanabe, Katsuaki*; Togo, Yoko*; Morikawa, Noritoshi*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Aosai, Daisuke*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(12), p.e113063_1 - e113063_20, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:36.57(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We present multi-isotopic evidence of microbially mediated sulfate reduction in a granitic aquifer, a representative of the terrestrial crust habitat. Deep groundwater of meteoric origin was collected from underground boreholes drilled into the Cretaceous Toki granite, central Japan. A large sulfur isotopic fractionation of 20-60 permil diagnostic to microbial sulfate reduction is associated with the investigated groundwater containing sulfate below 0.2 mM. In contrast, a small carbon isotopic fractionation ( 30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
Shibata, Takanori; Terasaki, Ryo*; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Inoue, Takashi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1515, p.177 - 186, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:92.9(Physics, Applied)In the neutral beam injector in JT-60SA, one of issues is that negative ion beam is partially intercepted at acceleration grids due to a spatial non-uniformity of negative ion production on large extraction area (0.9 0.45m
0.45m ). Previous experiments showed that fast electrons emitted from filament cathodes are transported in a longitudinal direction by
). Previous experiments showed that fast electrons emitted from filament cathodes are transported in a longitudinal direction by 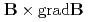 drift and the spatial distribution of electron temperature (
drift and the spatial distribution of electron temperature (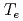 ) strongly relates with the non-uniformity. In this study, a three-dimensional electron transport analysis has been developed. Electron temperature in the analysis agreed well with measurements in JAEA 10A ion source. This study clarified that the bias of
) strongly relates with the non-uniformity. In this study, a three-dimensional electron transport analysis has been developed. Electron temperature in the analysis agreed well with measurements in JAEA 10A ion source. This study clarified that the bias of 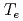 distribution are caused by the following reasons; (1) fast electrons drifted in the longitudinal direction survives near the end wall with energy up to
distribution are caused by the following reasons; (1) fast electrons drifted in the longitudinal direction survives near the end wall with energy up to  = 25-60 eV and (2) they produces thermal electrons by collision with plasma particles there.
= 25-60 eV and (2) they produces thermal electrons by collision with plasma particles there.
 -irradiated ultra high molecular weight polyethylene
-irradiated ultra high molecular weight polyethyleneKobayashi, Yoshinori*; Yamawaki, Masato*; Oka, Toshitaka; Saiki, Seiichi; Mohamed, H.*; Hattori, Kanehisa*; Watanabe, Yoshihiro*
Materials Science Forum, 733, p.147 - 150, 2013/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:80.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) has widely been used for probing open volume defects in various materials. PALS is in principle non-destructive, yet conventional PALS is not strictly non-destructive because cutting out of two specimens from the material is required. Recently we developed a novel method of PALS, which is potentially applicable to non-destructive, onsite material inspection. In order to explore the possibility of onsite monitoring of polymer degradation by this novel method of PALS, we studied variations of positron lifetime and mechanical properties of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) subjected to  -irradiation. Correlations were found between the mechanical properties and o-Ps lifetimes, suggesting the feasibility of non-destructive, onsite monitoring of polymer degradation by PALS. The effect of
-irradiation. Correlations were found between the mechanical properties and o-Ps lifetimes, suggesting the feasibility of non-destructive, onsite monitoring of polymer degradation by PALS. The effect of  -irradiation on positronium formation is discussed.
-irradiation on positronium formation is discussed.
Shibata, Takanori; Koga, Shojiro*; Terasaki, Ryo*; Inoue, Takashi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Tsuchida, Kazuki; Umeda, Naotaka; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(2), p.02A719_1 - 02A719_3, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)In the NBI for large fusion devices, production of uniform negative ion beam is one of important issues. A physical model is proposed to understand the non-uniformity. It has been qualitatively shown that the non-uniform beam intensity is due to the following process; (1) formation of non-uniform EEDF, (2) localized production of hydrogen atoms/ions (H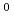 /H
/H ) due to (1), (3) non-uniform flux of H
) due to (1), (3) non-uniform flux of H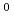 /H
/H to the PG and (4) localized surface production of negative ions. However, in the past studies, the EEDF was assumed as two temperature Maxwellian distribution from measurements. Thus effects of high energy electrons are not taken into account precisely. In the present research, local EEDF is calculated by the 3D Monte-Carlo kinetic model which takes into account the spatial and magnetic configurations of the real negative ion source. The numerical result show that high energy component of the EEDF enhances the spatial non-uniformity in the production rate of H
to the PG and (4) localized surface production of negative ions. However, in the past studies, the EEDF was assumed as two temperature Maxwellian distribution from measurements. Thus effects of high energy electrons are not taken into account precisely. In the present research, local EEDF is calculated by the 3D Monte-Carlo kinetic model which takes into account the spatial and magnetic configurations of the real negative ion source. The numerical result show that high energy component of the EEDF enhances the spatial non-uniformity in the production rate of H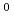 /H
/H .
.
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Saito, Koki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; et al.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(2), p.278 - 280, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.75(Chemistry, Physical)The chemical structures of various ion-beam irradiated isotactic-polypropylene samples were studied. Results of micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy suggest not only the linear energy transfer, but also the fluence is effective in local transformation of the isotactic-polypropylene.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Hanada, Masaya; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Shimizu, Takashi; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(8), p.665 - 669, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:46.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Morishita, Takatoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Iga, Takashi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Shimizu, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Hanada, Masaya; Imai, Tsuyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-007, 16 Pages, 2003/03
Recently the ion source for IFMIF (International Fusion Material Irradiation facility) achieved positive ion beams of 120 mA with the proton ratio of 90% by applying magnetic filter even in a small ion source. The mechanism of a high proton ration plasma production in such a small ion source has not been studied. Molecular ions are destroyed and the proton is produced from the dissociation of molecular ions in the filter region. Thus the proton yield is enhanced even in the small volume discharge. Using the same numerical method, the plasma production was calculated for the large ion source. The high proton ratio can be easily obtained, where the contribution of proton production by the ionization of H becomes high. From the negative ion production point of view, the negative ion beam current was numerically evaluated. The high atom flux to the plasma grid generates the large amount of negative ions rather than that by the positive ions in Cs-seeded large ion sources.
Shimizu, Takashi; Morishita, Takatoshi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Hanada, Masaya; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Imai, Tsuyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2003-006, 26 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Morishita, Takatoshi; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Shimizu, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro
Dai-1-Kai 21-Seiki Rengo Shimpojiumu; Kagaku Gijutsu To Ningen Rombunshu, p.221 - 224, 2002/11
A high proton ratio ( 90%) and a high current density proton beam is demanded in the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF). In the development of the beam source for nuclear fusion, it was indicated that the enhancement of the ion confinement using the large ion source is suitable for the increase in the proton ratio. In the beam source for accelerators, a single beamlet is enough to obtain a certain beam current, therefore, a small ion source is suitable from the aspect of efficiency and simplification of the system. To obtain the high proton ratio beam from the small ion source, it is necessary to grasp the production mechanism of proton. Then, the production process of the proton in the small ion source was investigated using rate equations. Obtained results were compared with experimental results. Consequently, although the proton is mainly produced from the molecular positive ions as considered conventionally, the production of the high proton ratio beam is also possible in the small ion source due to the effects of the magnetic filter.
90%) and a high current density proton beam is demanded in the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (IFMIF). In the development of the beam source for nuclear fusion, it was indicated that the enhancement of the ion confinement using the large ion source is suitable for the increase in the proton ratio. In the beam source for accelerators, a single beamlet is enough to obtain a certain beam current, therefore, a small ion source is suitable from the aspect of efficiency and simplification of the system. To obtain the high proton ratio beam from the small ion source, it is necessary to grasp the production mechanism of proton. Then, the production process of the proton in the small ion source was investigated using rate equations. Obtained results were compared with experimental results. Consequently, although the proton is mainly produced from the molecular positive ions as considered conventionally, the production of the high proton ratio beam is also possible in the small ion source due to the effects of the magnetic filter.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Hanada, Masaya; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Morishita, Takatoshi; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Shimizu, Takashi*; Takayanagi, Tomohiro*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 19th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2002) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2002/10
A high power neutral beam injector (NBI) has been designed for ITER. A key component of the NBI system is a high power beam source which produces a 40A D ion beams at the energy of 1 MeV. JAERI has developed a vacuum insulated beam source (VIBS). The VIBS insulates the high voltage of 1 MV by immersing the ion source and accelerator in vacuum. So far the VIBS succeeded in acceleration of 37 mA (power supply drain current) beam up to 970 keV for 1 s. The achieved beam energy is nearly equal to the required value for the ITER NBI system. The negative ion source for the ITER beam source has been also developed. One of the key issues for the negative ion source is reduction of the operating pressure. By optimizing the filter magnetic field for negative ion production even at low pressure, a H
ion beams at the energy of 1 MeV. JAERI has developed a vacuum insulated beam source (VIBS). The VIBS insulates the high voltage of 1 MV by immersing the ion source and accelerator in vacuum. So far the VIBS succeeded in acceleration of 37 mA (power supply drain current) beam up to 970 keV for 1 s. The achieved beam energy is nearly equal to the required value for the ITER NBI system. The negative ion source for the ITER beam source has been also developed. One of the key issues for the negative ion source is reduction of the operating pressure. By optimizing the filter magnetic field for negative ion production even at low pressure, a H ion beam of 31 mA/cm
ion beam of 31 mA/cm was extracted at 0.1 Pa. Although the pulse length was very short (0.1 s) the ITER requirement on the current density was demonstrated at 1/3 of the ITER design pressure (0.3 Pa), which could reduce the heat loading on the accelerator grids.
was extracted at 0.1 Pa. Although the pulse length was very short (0.1 s) the ITER requirement on the current density was demonstrated at 1/3 of the ITER design pressure (0.3 Pa), which could reduce the heat loading on the accelerator grids.
Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Seki, Masahiro; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Kato, Takashi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Hanada, Masaya; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.75 - 93, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.13(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japanese contributions to ITER Engineering Design Activity are presented, together with an introduction of the objectives and design of the ITER whose program have been carried out through the international collaboration by EU, Japan, Russian Federation and the USA. New technologies have been produced through the development, fabrication and testing of scalable models in the fields of superconducting magnet, reactor structure with vacuum vessel, high-heat-flux plasma facing component, neutral beam injector, high-power mm-wave generator and so on. As major contributions from Japan, development and testing results of a 13-T, 640-MJ, Nb Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m
Sn pulsed magnet, a 18-degree sector of vacuum vessel with a height of 15 m and a width of 9 m, CFC armors to CuCrZr cooling tube that withstood 20 MW/m , a 31 mA/cm
, a 31 mA/cm negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
negative ion beam source, a 1-MeV beam-accelerator, a 1-MW 170-GHz gyrotron were described.
Mori, Masahiro; Shoji, Teruaki; Araki, Masanori; Saito, Keiji*; Senda, Ikuo; Omori, Junji*; Sato, Shinichi*; Inoue, Takashi; Ono, Isamu*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(1), p.16 - 89, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Takashi; Wada, Motoi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Hanada, Masaya; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Morishita, Takatoshi; Amemiya, Toru*; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Dai-12-Kai Ryushisen No Sentanteki Oyo Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu (BEAMS 2001) Hobunshu, p.25 - 28, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Hanada, Masaya; Morishita, Takatoshi; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Orita, Yoshitaka*; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Ido, Shuji*
JAERI-Tech 2001-046, 19 Pages, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; Hama, Yoshimasa*
no journal, ,
Yamamoto, Yuhei; Aosai, Daisuke; Mizuno, Takashi; Watanabe, Katsuaki*; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Suzuki, Yohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English