Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Kimura, Kenji; Shimada, Akiomi; et al.
Dai-35-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.17 - 19, 2024/03
The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has three accelerator mass spectrometers. We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Yamamoto, Yusuke*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2023-003, 67 Pages, 2024/02
A long-term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios ( D,
D, 
 O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for
O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for  D and
D and 
 O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of
O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of  D and
D and 
 O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the
O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the  D and
D and 
 O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Ogawa, Hiroki; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2023-005, 78 Pages, 2023/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Watanabe, Takahiro; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Niwa, Masakazu
Chigaku Zasshi, 132(4), p.353 - 361, 2023/08
U-Pb dating of detrital zircons in paleotsunami deposits from the 1662 CE Kanbun-Hyuganada sea earthquake, Miyazaki plain on the Pacific coast of southwest Japan, was performed by a laser ablation multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS) system at Tono Geoscience Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Twenty-five zircon grains were separated from the paleotsunami deposits by chemical abrasion and analyzed by the LA-ICPMS. U-Pb ages of the detrital zircons showed from ca. 14 Ma to 2405 Ma, and the age spectrum revealed high relative probability values around ca. 100 Ma and 2000 Ma. Detrital zircons with the age of ca. 100 Ma in the 1662 CE paleotsunami deposits could be partly originated from the Shimanto supergroup in southwest Japan. Moreover, the age spectrum of detrital zircons with Precambrian grains from the paleotsunami deposits was similar with those of fore-arc sandstones from central Kyushu Island.
Kokubu, Yoko; Fujita, Natsuko; Watanabe, Takahiro; Matsubara, Akihiro; Ishizaka, Chika; Miyake, Masayasu*; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Kato, Motohisa*; Ogawa, Yumi*; Ishii, Masahiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 539, p.68 - 72, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has an accelerator mass spectrometer (JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV). The spectrometer enabled us to use a multi-nuclide AMS of carbon-14 ( C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for
C), beryllium-10, aluminium-26 and iodine-129, and we have recently been proceeding test measurement of chlorine-36. In response to an increase of samples, we installed a state-of-the-art multi-nuclide AMS with a 300 kV Tandetron accelerator in 2020. Recently, we are driving the development of techniques of isobar separation in AMS and of sample preparation. Ion channeling is applied to remove isobaric interference and we are building a prototype AMS based on this technique for downsizing of AMS. The small sample graphitization for  C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
C has been attempted using an automated graphitization equipment equipped with an elemental analyzer.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Ukai, Masatoshi*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Watanabe, Ritsuko*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 158(16), p.164103_1 - 164103_8, 2023/04
New insight into water radiolysis and photolysis is indispensable in the dramatic progress of sciences and technologies in various research areas. In the radiation field, reactive hydrated electrons are considerably produced along radiation tracks. Although the formation results from a transient dynamic correlation between ejected electrons and water, the individual mechanisms of electron thermalization, delocalization, and polarization are unknown. Using a dynamic Monte Carlo code, we show herein that the ejected electrons are immediately delocalized by molecular excitations in parallel with phonon polarization and gradually thermalized by momentum transfer with an orientation polarization in a simultaneous manner. Our results show that these mechanisms heavily depend on the intermolecular vibration and rotation modes peculiar to water. We expect our approach to be a powerful technique for connecting physical and chemical processes in various solvents.
Matsubara, Akihiro*; Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Kimura, Kenji; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2022-002, p.55 - 62, 2023/03
We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO. Particularly, the destructions of varistors used in the beamline equipment will be presented. The cause of the destruction as well as implementation of the safety measures are mentioned.
Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Yamamoto, Yusuke; Kimura, Kenji; et al.
Dai-23-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.1 - 4, 2022/12
The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has three accelerator mass spectrometers. We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO.
Sasao, Eiji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-022, 29 Pages, 2022/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2022. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2022 are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques
Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Miyake, Masayasu*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi*; Kato, Motohisa*; Shimada, Akiomi; Ogata, Nobuhisa
Dai-33-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, P. 48, 2022/04
no abstracts in English
Tsuru, Tomohito; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Watanabe, Chihiro*; Miura, Hiromi*
Computational Materials Science, 203, p.111081_1 - 111081_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The deformation mode of some titanium (Ti) alloys differs from that of pure Ti due to the presence of alloying elements in  -phase. Herein, we investigated all possible slip modes in pure Ti and the effects of Al and V solutes as typical additive elements on the dislocation motion in
-phase. Herein, we investigated all possible slip modes in pure Ti and the effects of Al and V solutes as typical additive elements on the dislocation motion in  -Ti alloys using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The stacking fault (SF) energies in possible slip planes indicated that both Al and V solutes reduce the SF energy in the basal plane and, in contrast, the Al solute increases the SF energy particularly in the prismatic plane. DFT calculations were subsequently performed to simulate dislocation core structures. The energy landscape of the transition between all possible dislocation core structures and the barriers for dislocation glide in various slip planes clarified the nature of dislocation motion in pure Ti. (i) the energy of prismatic core is higher than most stable pyramidal core, and thereby dislocations need to overcome the energy barrier of the cross-slip (22.8 meV/b) when they move in the prismatic plane, (ii) the energy difference between the prismatic and basal cores is larger (127 meV/b), that indicates the basal slip does not activate, (iii) however, the Peierls barrier for motion in the basal plane is not as high (16 meV/b). Direct calculations for the dislocation core around solutes revealed that both Al and V solutes facilitate dislocation motion in the basal plane by reducing the energy difference between the prismatic and basal cores. The effect of solutes characterizes the difference in the deformation mode of pure Ti and
-Ti alloys using density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The stacking fault (SF) energies in possible slip planes indicated that both Al and V solutes reduce the SF energy in the basal plane and, in contrast, the Al solute increases the SF energy particularly in the prismatic plane. DFT calculations were subsequently performed to simulate dislocation core structures. The energy landscape of the transition between all possible dislocation core structures and the barriers for dislocation glide in various slip planes clarified the nature of dislocation motion in pure Ti. (i) the energy of prismatic core is higher than most stable pyramidal core, and thereby dislocations need to overcome the energy barrier of the cross-slip (22.8 meV/b) when they move in the prismatic plane, (ii) the energy difference between the prismatic and basal cores is larger (127 meV/b), that indicates the basal slip does not activate, (iii) however, the Peierls barrier for motion in the basal plane is not as high (16 meV/b). Direct calculations for the dislocation core around solutes revealed that both Al and V solutes facilitate dislocation motion in the basal plane by reducing the energy difference between the prismatic and basal cores. The effect of solutes characterizes the difference in the deformation mode of pure Ti and  -Ti alloys.
-Ti alloys.
Watanabe, Takahiro; Kagami, Saya; Niwa, Masakazu
Marine Geology, 444, p.106704_1 - 106704_13, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.35(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Miyazaki plain on the Pacific coast of southwest Japan along the Nankai-Suruga trough was also affected by marine incursion by the past interplate earthquakes and tsunami. Notably, paleotsunami deposits were found on the area and important clues to reconstruct the past marine incursion by earthquakes and tsunami. However, geochemical and heavy mineral analyses on the area were not enough to characterize the deposits. Therefore, quantification analyses with high-time resolution by portable energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (portable XRF), scanning by X-ray analytical microscope (XGT), statistical analyses for chemical components, and heavy mineral analyses were performed for the paleotsunami deposits of the Kanbun Hyuganada earthquake with the age of 1662 CE from the south Miyazaki plain in this study. Based on our research, we summarized as follows: (1) increases in the titanium normalized values of S, Ca, Fe and Sr, and depletions of Si, K, and Rb were observed in the deposits, (2) Zr accumulations and heavy minerals such as zircon were found in the deposits caused by possible high energy tsunami, and (3) cluster analyses of the geochemical data from the core by portable XRF distinguished the paleotsunami deposits on the Miyazaki plain.
 and SrLaCuNbO
and SrLaCuNbO ; Spin-
; Spin- quasi-square-lattice
quasi-square-lattice 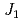 -
-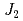 Heisenberg antiferromagnets
Heisenberg antiferromagnetsWatanabe, Masari*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Ueno, Wataru*; Matsui, Kazuki*; Goto, Takayuki*; Hagihara, Masato
Physical Review B, 105(5), p.054414_1 - 054414_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:59.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) kagome-lattice antiferromagnets Cs
kagome-lattice antiferromagnets Cs Cu
Cu SnF
SnF and Rb
and Rb Cu
Cu SnF
SnF
Saito, Mutsuki*; Takagishi, Ryunosuke*; Kurita, Nubuyuki*; Watanabe, Masari*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Nomura, Ryuji*; Fukumoto, Yoshiyuki*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi
Physical Review B, 105(6), p.064424_1 - 064424_15, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:73.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamamoto, Yusuke; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2021-003, 58 Pages, 2022/01
A long term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Whole-rock geochemical compositions in rocks and sediments are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for rapid and simple whole-rock geochemical analyses (original specification; 8 mm-diameter analysis). In particular, the 3 mm-diameter small spot analysis using the portable XRF was performed for quantitative analyses of small-weight geological samples. In this study, we reported a quantitative method for major and trace elements using calibration curves by standard reference materials, as well as evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards measured by the portable XRF (3 mm-diameter small spot analysis). Furthermore, the small spot quantitative analyses by the portable XRF were also applied to fault rock samples that have been analyzed in previous studies.
Miura, Hiromi*; Watanabe, Chihiro*; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru*; Oba, Yojiro; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Yoshinaga, Naoki*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 833, p.142531_1 - 142531_12, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:45.58(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2021-007, 65 Pages, 2021/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 6th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimada, Kazumasa; Iijima, Masashi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Takahara, Shogo
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2021 (ASRAM 2021) (Internet), 17 Pages, 2021/10
The radiation doses received by the off-site responders in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident were assessed. Atmospheric dispersion simulation was conducted with the source term of the previous research to calculate the atmospheric concentration and ground surface deposition in the municipalities where off-site responders actives. The external exposure dose from cloudshine and groundshine, the internal exposure dose due to inhalation of radioactive plume and resuspended radio nuclei, and the temporal and spatial distribution within each municipality were assessed. As a result of comparing the assessed values of the external exposure dose with the measured values of the personal dosimeter, the measured values were within the assessed range. As a result of our assessment with internal dose exposure, if the exposures occurred without protective measures, the potential daily effective dose in the period between 12 and 31 March 2011 were several tens mSv per day or more in the relatively high dose area. Therefore, to keep the doses received by the responders below the reference level of 20 mSv recommended by the ICRP, it is necessary to ensure that the protective measures for internal exposures such as masks are taken, and to manage the time spent for their activity at least daily.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-012, 48 Pages, 2021/08
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2021. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2021 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.