Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Nobuyuki
Maku, 47(4), p.197 - 201, 2022/07
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process enables us to provide the Carbon-free hydrogen (H ) at high-efficiency levels, and it uses high-temperature heat sources, including high-temperature gas-cooled reactors, solar heat, and more. The cation exchange membranes (CEMs) for the HI mediated electro electrodialysis (EED) were developed using a radiation grafted polymerization method in order to improve the process efficiency of the IS process. High proton (H
) at high-efficiency levels, and it uses high-temperature heat sources, including high-temperature gas-cooled reactors, solar heat, and more. The cation exchange membranes (CEMs) for the HI mediated electro electrodialysis (EED) were developed using a radiation grafted polymerization method in order to improve the process efficiency of the IS process. High proton (H ) conductivity and selectivity are required for the performance of CEMs to reduce the consumption energy for EED. The H
) conductivity and selectivity are required for the performance of CEMs to reduce the consumption energy for EED. The H conductivity of the radiation grafted CEMs were successfully improved by controlling the grafting amount, comparing with that of Nafion. Moreover, the H
conductivity of the radiation grafted CEMs were successfully improved by controlling the grafting amount, comparing with that of Nafion. Moreover, the H selectivity and water transport of the developed CEMs was improved by introducing the crosslinker. Currently, the further improvement of the membrane performance is underway by using the ion-track grafting technic.
selectivity and water transport of the developed CEMs was improved by introducing the crosslinker. Currently, the further improvement of the membrane performance is underway by using the ion-track grafting technic.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Sawada, Shinichi*; Sugimoto, Chihiro; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
QST-M-33; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2020, P. 37, 2022/03
We have been developing the ion exchange membranes by a radiation grafted polymerization method to improve HI concentration performance for Electro-electrodialysis (EED) in the thermochemical water-splitting hydrogen production iodine-sulfur process. We verify to adopt the cation exchange membrane prepared by ion-track grafted technique. In this membrane preparation technique, one-dimensional cylindrical ion-channel can be formed in the base polymer film by the radiation of the heavy ion beam. And, the excess swelling of the ion-channel could be prevented, expecting that the HI concentration performance could be improved. In our works, The HI concentration experiment was conducted by the electric cell assembled the membrane prepared by the ion-track grafting technique. The HI composition of the tested solution increased, indicating that the tested membrane can operate HI concentration by EED.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Myagmarjav, O.; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(55), p.27891 - 27904, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.37(Chemistry, Physical)The thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur (IS) process enables producing hydrogen. In a previous operation procedure, after the components of the unit operations were individually started, they were connected at the same time. However, it was challenging to stably interconnect the components. This study introduces a new loop operation, subdividing the process configuration into four sections before transferring the continuous operation. The proposed loop operation was validated analyzing the material and heat balances of each section. The calculated results showed that the material balances of respective loop sections were closed. The loop operation mode would transfer to the continuous operation by connect all sections. Regarding the switching of operation modes, the material and heat balance showed no or little difference, indicating that two operation modes could only be changed by switching the pipelines. Consequently, the loop sections could be individually operated to stabilize the IS process system, and the loop operation could be smoothly transferred to the continuous operation.
Myagmarjav, O.; Shibata, Ai*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Takegami, Hiroaki
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(56), p.28435 - 28449, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.63(Chemistry, Physical)Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Noguchi, Hiroki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kamiji, Yu; Kubo, Shinji; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 137, p.103772_1 - 103772_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Kimura, Takehiro*; Nomura, Mikihiro*
Chemical Engineering Science, 237, p.116575_1 - 116575_11, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.08(Engineering, Chemical)We have been developing the ion exchange membranes by a radiation grafted polymerization method to improve HI concentration performance for Electro-electrodialysis (EED) in the thermochemical water-splitting hydrogen production iodine-sulfur process. In this work, the crosslinking structures were introduced to the ion exchange membranes. The proton conductivity ( ), transport number (t
), transport number (t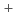 ), and water permeation factor (
), and water permeation factor ( ) of these crosslinked ion exchange membranes were measured and the effect of crosslinks to these performance indexes were investigated. The introduction of crosslinks was found to improve the selectivity of H
) of these crosslinked ion exchange membranes were measured and the effect of crosslinks to these performance indexes were investigated. The introduction of crosslinks was found to improve the selectivity of H and water transport (increase of t
and water transport (increase of t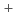 and decrease of
and decrease of  ), although the
), although the  somewhat decreased. The EED model that we established to discuss the permeation mechanism of EED system was used to theoretically analyze the effect of crosslink on the performance indexes. Based on this analysis of measurement results, the introduction of the crosslink was found to little affect the absorbed amount of HIx solution and H
somewhat decreased. The EED model that we established to discuss the permeation mechanism of EED system was used to theoretically analyze the effect of crosslink on the performance indexes. Based on this analysis of measurement results, the introduction of the crosslink was found to little affect the absorbed amount of HIx solution and H diffusion coefficient in the tested membranes, whereas it could lead to decrease I
diffusion coefficient in the tested membranes, whereas it could lead to decrease I diffusion coefficient. The results of
diffusion coefficient. The results of  and t
and t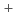 could reflect these effects. In addition, we found the fact that crosslink can inhibit the swelling due to the absorption of the HIx solution. As a result, the
could reflect these effects. In addition, we found the fact that crosslink can inhibit the swelling due to the absorption of the HIx solution. As a result, the  value decreased owing to the introduction of crosslink.
value decreased owing to the introduction of crosslink.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Myagmarjav, O.; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(43), p.22328 - 22343, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:59.85(Chemistry, Physical)An iodine-sulfur process offers the potential for mass producing hydrogen with high-efficiency, and it uses high-temperature heat sources, including HTGR, solar heat, and waste heat of industries. R&D tasks are essential to confirm the integrity of the components that are made of industrial materials and the stability of hydrogen production in harsh working conditions. A test facility for producing hydrogen was constructed from corrosion-resistant components made of industrial materials. For stable hydrogen production, technical issues for instrumental improvements (i.e., stable pumping of the HIx solution, improving the quality control of glass-lined steel, prevention of I precipitation using a water removal technique in a Bunsen reactor) were solved. The entire process was successfully operated for 150 h at the rate of 30 L/h. The integrity of components and the operational stability of the hydrogen production facility in harsh working conditions were demonstrated.
precipitation using a water removal technique in a Bunsen reactor) were solved. The entire process was successfully operated for 150 h at the rate of 30 L/h. The integrity of components and the operational stability of the hydrogen production facility in harsh working conditions were demonstrated.
Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(35), p.17557 - 17561, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.38(Chemistry, Physical)The thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur (IS) process requires corrosion-resistant materials owing to usage of a mixture of HI-I -H
-H O. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and PFA, are adaptable as lining materials for protecting plant components. However, there has been a concern: PTFE and PFA have the ability to permeate various permeants. From the viewpoint of corrosion, the permeation of HI and I
O. Fluoropolymers, such as PTFE and PFA, are adaptable as lining materials for protecting plant components. However, there has been a concern: PTFE and PFA have the ability to permeate various permeants. From the viewpoint of corrosion, the permeation of HI and I should be evaluated to improve the integrity of the IS process. In this study, permeation tests on PTFE and PFA membranes were performed to measure the permeated fluxes of HI and I
should be evaluated to improve the integrity of the IS process. In this study, permeation tests on PTFE and PFA membranes were performed to measure the permeated fluxes of HI and I , and the effects of the operating conditions on them were investigated. The introduction of a permeability parameter could be successful for normalizing the permeated fluxes for a specific membrane thickness and a vapor pressure. Then, the empirical formula of the permeability was given as an Arrhenius-type equation to use as a plant design.
, and the effects of the operating conditions on them were investigated. The introduction of a permeability parameter could be successful for normalizing the permeated fluxes for a specific membrane thickness and a vapor pressure. Then, the empirical formula of the permeability was given as an Arrhenius-type equation to use as a plant design.
Sawada, Shinichi*; Kimura, Takehiro*; Nishijima, Haruyuki*; Kodaira, Takahide*; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Imabayashi, Shinichiro*; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45(27), p.13814 - 13820, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.8(Chemistry, Physical)An electrochemical membrane Bunsen reaction using a cation exchange membrane (CEM) is a key to achieving an iodine-sulfur (IS) thermochemical water splitting process for mass-production of hydrogen. In this study, we prepared both the radiation-grafted CEM with a high ion exchange capacity (IEC) and the highly-porous Au-electroplated anode, and then used them for the membrane Bunsen reaction to reduce the cell overvoltage. The high-IEC grafted CEM exhibited low resistivity for proton transport, while the porous Au anode had a large effective surface area for anodic SO oxidation reaction. As a result, the cell overvoltage for the membrane Bunsen reaction was significantly reduced to 0.21 V at 200 mA/cm
oxidation reaction. As a result, the cell overvoltage for the membrane Bunsen reaction was significantly reduced to 0.21 V at 200 mA/cm , which was only one-third of that of the previous test using the commercial CEM and non-porous anode. From the analysis of the current-voltage characteristics, employment of the grafted CEM was found to be more effective for the overvoltage reduction compared to the porous Au anode.
, which was only one-third of that of the previous test using the commercial CEM and non-porous anode. From the analysis of the current-voltage characteristics, employment of the grafted CEM was found to be more effective for the overvoltage reduction compared to the porous Au anode.
Kamiji, Yu; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 361, p.110573_1 - 110573_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:66.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has been conducting R&D on the thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process for nuclear-powered hydrogen production. The IS process is one of the promising candidates of heat application of the high-temperature gas-cooled reactors. The glass-lined steel is one of the candidate materials which has both corrosion resistance and structural strength. This paper reveals technical matters to improve reliability of the glass-lined steel equipment. It found that the improved glass-lined steel showed soundness in the process environment from the results of stress analyses for the glass layer by FEM, tests for heat cycle, bending load and corrosion.
Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kamiji, Yu; Kasahara, Seiji; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kubo, Shinji
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 360, p.110498_1 - 110498_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:86.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting R&D on the thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process for nuclear-powered hydrogen production. The IS process is one of the promising candidates of heat application of the high-temperature gas-cooled reactors. JAEA fabricated main chemical reactors made of industrial structural materials and confirmed their integrity in practical corrosive environments in the IS process. Based on the results of these confirmation tests, JAEA have constructed a 100 NL/h-H -scale test facility made of industrial structural materials. In this report, we succeeded in extending the hydrogen production time from 8 hours to 31 hours by developing a stable hydrogen iodide solution transfer technology in a continuous hydrogen production test. In addition, using the fracture test data of the ceramic specimen, an equation for estimating the strength of the ceramic component was developed.
-scale test facility made of industrial structural materials. In this report, we succeeded in extending the hydrogen production time from 8 hours to 31 hours by developing a stable hydrogen iodide solution transfer technology in a continuous hydrogen production test. In addition, using the fracture test data of the ceramic specimen, an equation for estimating the strength of the ceramic component was developed.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(59), p.30832 - 30839, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.23(Chemistry, Physical)Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Asano, Masaharu*; Terai, Takayuki*
Journal of Membrane Science, 587, p.117171_1 - 117171_9, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.64(Engineering, Chemical)Electro-electrodialysis (EED) has been applied to thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production in order to enhance the HI component in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity (
O mixture (HIx solution). In this paper, HIx solution concentration dependence of the conductivity ( ) and transport number (
) and transport number ( ) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H
) as the membrane-performance indexes of Nafion 212 and a styrene-grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane was experimentally investigated. From the theoretical analysis for the measurements based on the new EED model, the effects of the H and I
and I content and the diffusion coefficients of H
content and the diffusion coefficients of H and I
and I in the evaluated membranes on
in the evaluated membranes on  and
and  were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of
were as follows: HIx solution concentration dependence of ion contents exhibited a significantly small or different variation in comparison with that of  and t
and t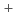 , which indicates that the dominant factors for
, which indicates that the dominant factors for  and
and  would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For
would not be ion contents; thereby, the effect of ion diffusion coefficients should not be ruled out. For  of Nafion 212, H
of Nafion 212, H diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I
diffusion is the dominant factor because the existence of I was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I
was negligible, whereas for the ETFE-St membrane, the effect of I diffusion should be considered. I
diffusion should be considered. I diffusion could more strongly affect
diffusion could more strongly affect  for the evaluated membranes rather than H
for the evaluated membranes rather than H diffusion, which indicates that H
diffusion, which indicates that H selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I
selectivity of the membranes could be relatively determined by the variation of the I behavior in the membranes.
behavior in the membranes.
Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Sawada, Shinichi*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Nihon Kaisui Gakkai-Shi, 73(4), p.194 - 202, 2019/08
The thermochemical IS process is a promising hydrogen production method which can produce hydrogen in a large amount and stably with high efficiency by thermal splitting of water. Research and development on chemical reaction technology with membranes was conducted for the purpose of improving the efficiency of IS process and application of solar heat. The basic technology of ceramic membranes applied to decomposition reactions of hydrogen iodine and sulfuric acid was developed, and it is expected that the conversion rate on decomposition in each reaction can be remarkably improved. The basic technology of a cation exchange membrane applied to Bunsen reaction was developed with radiation-induced grafting technique, it is expected that the amount of iodine can be reduced to about one-fifth compared to the conventional method. These achievements are important technologies for practical use of the IS process.
Myagmarjav, O.; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kamiji, Yu; Ioka, Ikuo; Kubo, Shinji; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Sawada, Shinichi*; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(35), p.19141 - 19152, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:49.6(Chemistry, Physical)Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(25), p.12583 - 12592, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:55.95(Chemistry, Physical)JAEA has been conducting R&D on thermochemical water-splitting hydrogen production IS process to develop one of heat applications of high-temperature gas-cooled reactor. A test facility was constructed using corrosion-resistant industrial materials to verify integrity of the IS process components and to demonstrate continuous and stable hydrogen production. The performance of components installed in each section was confirmed. Subsequently, a trial operation of integration of the processing sections was successfully carried out for 8 hours with hydrogen production rate of approximately 10 NL/h. After that, hydrogen production operation was extended to 31 hours (approximately hydrogen production rate of 20 NL/h) by introducing a corrosion-resistance pump system with a developed shaft seal technology.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Kubo, Shinji
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44(21), p.10207 - 10217, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:47.35(Chemistry, Physical)Takegami, Hiroaki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kamiji, Yu; Kasahara, Seiji; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting R&D on the thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process for nuclear-powered hydrogen production. The IS process is one of the promising candidates of heat application of the high-temperature gas-cooled reactors. JAEA fabricated main chemical reactors made of industrial structural materials and confirmed their integrity in practical corrosive environments in the IS process. Based on the results of these confirmation tests, JAEA have constructed a 100 NL/h-H -scale test facility made of industrial structural materials. This report will present an outline and results of hydrogen production tests and reliability improvements of operation stability and components, such as development of a strength estimation method for heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant ceramics components made of silicon carbide.
-scale test facility made of industrial structural materials. This report will present an outline and results of hydrogen production tests and reliability improvements of operation stability and components, such as development of a strength estimation method for heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant ceramics components made of silicon carbide.
Kamiji, Yu; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting R&D on the thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process for nuclear-powered hydrogen production. The IS process is one of the promising candidates of heat application of the HTGR. JAEA achieved continuous hydrogen production for one week with a hydrogen production rate of 30 NL/h by using a test apparatus made of glass and fluororesin material. Subsequently, JAEA fabricated main chemical reactors made of industrial materials and confirmed their integrity in corrosive environments in the IS process. Based on the results, JAEA has constructed a 100 NL/h-H -scale test facility made of industrial materials; one of the important materials is the glass-lined steel for corrosion resistant components such as vessels, pipes and protective sheaths of sensors. This report will present technical matters to improve reliability of the glass-lined protective sheaths of thermocouple. In addition, results of quality confirmation will be presented, which are stress analyses for the glass layer by FEM, tests for heat cycle, bending load and corrosion.
-scale test facility made of industrial materials; one of the important materials is the glass-lined steel for corrosion resistant components such as vessels, pipes and protective sheaths of sensors. This report will present technical matters to improve reliability of the glass-lined protective sheaths of thermocouple. In addition, results of quality confirmation will be presented, which are stress analyses for the glass layer by FEM, tests for heat cycle, bending load and corrosion.