Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 to extreme environments
to extreme environmentsHorikawa, Daiki*; Yamaguchi, Ayami*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Tanaka, Daisuke*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yukuhiro, Fumiko*; Kuwahara, Hirokazu*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; et al.
Astrobiology, 12(4), p.283 - 289, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.61(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We examined the hatchability of hydrated and anhydrobiotic eggs of the tardigrade  to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
to hatch after ionizing irradiation (helium ions), extremely low and high temperatures, and high vacuum. Anhydrobiotic eggs (50% lethal dose; 1690 Gy) were substantially more radioresistant than hydrated ones (50% lethal dose; 509 Gy). Anhydrobiotic eggs also have a broader temperature resistance compared with hydrated ones. Over 70% of the anhydrobiotic eggs treated at high and low temperatures, but all of the hydrated eggs failed to hatch. After exposure to high vacuum conditions, the hatchability of the anhydrobiotic eggs was comparable to that of untreated control eggs.
 -ray-irradiated tobacco cells; Evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in plant cells
-ray-irradiated tobacco cells; Evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in plant cellsYokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Hase, Yoshihiro; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 691(1-2), p.41 - 46, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:28.36(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)Ionizing radiation-induced genomic instability has been documented in various end points such as chromosomal aberrations and mutations, which arises in the descendants of irradiated mammalian or yeast cells many generations after the initial insult. This study aimed at addressing radiation-induced genomic instability in higher plant tobacco cells. We thus investigated micronucleus (MN) formation and cell proliferation in tobacco cells irradiated with  -rays and their descendants. The descendants that have undergone at least 22 generations after irradiation still showed a two-fold MN frequency compared to sham-irradiated cells. This is the direct evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in tobacco cells.
-rays and their descendants. The descendants that have undergone at least 22 generations after irradiation still showed a two-fold MN frequency compared to sham-irradiated cells. This is the direct evidence for radiation-induced genomic instability in tobacco cells.
 -irradiated tobacco cultured cells
-irradiated tobacco cultured cellsYokota, Yuichiro; Wada, Seiichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Narumi, Issei; Tanaka, Atsushi
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(2), p.171 - 175, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.5(Biology)The rejoining efficiency of double-strand breaks (DSBs) was quantified in tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells following  -ray irradiation in order to compare DNA reparability of higher plants with mammals. The DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts were well represented by a biphasic-exponential equation: half of initial-induced DSBs were rejoined for 1 h and the others were almost rejoined within 4 h. We found that the DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts at 27
-ray irradiation in order to compare DNA reparability of higher plants with mammals. The DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts were well represented by a biphasic-exponential equation: half of initial-induced DSBs were rejoined for 1 h and the others were almost rejoined within 4 h. We found that the DSB rejoining kinetics of tobacco protoplasts at 27 C are the same as those of CHO-K1 cells at 37
C are the same as those of CHO-K1 cells at 37 C. These findings indicate that the DSB rejoining efficiency of tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells are comparable at their respective cell cultivation temperatures, suggesting that DSB rejoining efficiency is little responsible for the higher radiation-tolerance of tobacco protoplasts.
C. These findings indicate that the DSB rejoining efficiency of tobacco protoplasts and CHO-K1 cells are comparable at their respective cell cultivation temperatures, suggesting that DSB rejoining efficiency is little responsible for the higher radiation-tolerance of tobacco protoplasts.
 /M phase after
/M phase after  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationYokota, Yuichiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Inoue, Masayoshi*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 69, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Yuichiro; Inoue, Masayoshi; Narumi, Issei; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Atsushi
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 42(4), p.402 - 415, 2007/12
It has been known that many types of higher plants are several hundred times more radio-tolerant than mammals at an individual level. There was, however, no available information on the detail mechanism of radiation tolerance of higher plants. Thus, we have done the radiobiological studies using tobacco BY-2 cell line as a model plant cell. In their studies, we made clear that tobacco cells are ten times more radio-tolerant than mammalian cells, and that radioresistant tobacco cells can tolerate a large number of DNA double-strand breaks compared with mammalian cells. In this review, we discussed the radiation tolerant mechanism of higher plants by taking together the past findings with our latest data: tobacco cells are tolerant of radiation-induced chromosomal aberration although DNA double-strand break repair abilities of tobacco and mammalian cells are almost the same.
Tanaka, Atsushi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Hase, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Journal of Experimental Botany, 53(369), p.683 - 687, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:59.82(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Atsushi; Shimizu, Takashi*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Yamashita, Takao*; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Conf 97-003, p.323 - 326, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
*; *; *; *; *; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; *; Akashi, Makoto*; *; et al.
J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 43, p.175 - 177, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:37.63(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)no abstracts in English
; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Takashi*; Inoue, Masayoshi*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tano, Shigemitsu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 129(1), p.42 - 48, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Ryuichi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Oyo Butsuri, 65(2), p.168 - 172, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
; ; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; ; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI TIARA Annual Report, Vol. 1, 0, p.159 - 162, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Q.Hu*; *; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; ; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Proc. of Int. Conf. on Radiation Effects and Protection, 0, p.166 - 170, 1992/00
no abstracts in English
Oku, Tatsuo; Kodaira, Tsuneo; Fukaya, Kiyoshi; Suzuki, Masahide; *; *; *; *
Nucl. Eng. Des., 119, p.177 - 186, 1990/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:52.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; ; Araki, Masanori; ; ; ; ; Matsuda, Shinzaburo; ; *; et al.
JAERI-M 8869, 40 Pages, 1980/05
no abstracts in English
*; ; ; Araki, Masanori; ; ; ; ; Matsuda, Shinzaburo; ; et al.
JAERI-M 8740, 56 Pages, 1980/03
no abstracts in English
Saito, Mikio*; Sugihara, Takashi*; Tanaka, Kimio*; Ogiso, Yoichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Hiroo*; Shimizu, Nobuaki*; Oue, Atsushi*; Tanaka, Atsushi*; Saha, M. N.*; Shinagawa, Masahiko*; Otsuki, Takahiro*; Hoque, A.*; Mori, Takahisa*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 C ion-beam in a glioma cell line latently infected with HTLV-I
C ion-beam in a glioma cell line latently infected with HTLV-ITanaka, Atsushi*; Oue, Atsushi*; Shimizu, Nobuaki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Hoshino, Hiroo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Atsuko*; Ichikawa, Kazuki*; Kojima, Kazuaki*; Ono, Yutaka; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Shigeo*; Sakata, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Phytochelatin (PC) has been shown to play an important role in heavy metal detoxification. However, Arabidopsis transgenic plants overexpressing the PC synthase gene failed to show an increase in Cd tolerance. To explore a novel heavy metal detoxification mechanism, we screened for an Arabidopsis Cd-sensitive mutant (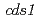 ) by carbon ion beam mutagenesis, which causes large base pair deletions at random loci in the genome. Genetic analyses and GSH synthesis inhibitor studies revealed that the
) by carbon ion beam mutagenesis, which causes large base pair deletions at random loci in the genome. Genetic analyses and GSH synthesis inhibitor studies revealed that the 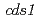 phenotype was different from those of PC synthesis mutants. Moreover, Cd content in shoots of
phenotype was different from those of PC synthesis mutants. Moreover, Cd content in shoots of 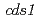 cultured on Cd-containing media was similar to wild type, suggesting that Cd-sensitive phenotype of
cultured on Cd-containing media was similar to wild type, suggesting that Cd-sensitive phenotype of 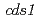 was not attributed to the Cd transport system from roots to shoots. In the rough mapping,
was not attributed to the Cd transport system from roots to shoots. In the rough mapping, 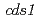 was localized to approximately 300kbp region of chromosome 4. One of the genes was found to have a 2.5 kbp deletion in the promoter region.
was localized to approximately 300kbp region of chromosome 4. One of the genes was found to have a 2.5 kbp deletion in the promoter region.
Yokota, Yuichiro; Hase, Yoshihiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei; Wada, Seiichi*; Inoue, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English