Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takubo, Yusaku*; Takayama, Yusuke; Idiart, A.*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Fujisaki, Kiyoshi*
Proceedings of 2022 International High Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM 2022) (Internet), p.906 - 915, 2022/11
no abstracts in English
Yano, Midori; Ito, Takayuki*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Matsuoka, Daisuke*; Araki, Fumiaki*; Czauderna, T.*; Stephens, K.*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.201 - 208, 2020/10
Visual analysis plays an important role in understanding and evaluating the climate models, their variables, and their outputs because complex processes are required for the tuning of the climate models. Virtual Reality (VR) technologies are effective for 3D visualization and have been recently employed for visual analysis of more various scientific data. However, researchers may have some problematic situations while using VR space depending on user operations and target geometries. Here, we propose an image-based view selection method to solve these situations and understand differences in ocean states between simulations and observations based on shapes of mode water regions. This view selection takes evaluation criteria for shape comparison of mode water regions generated from simulations and observations into account. This paper introduces two example cases applying this view selection and discusses on a degree of shape matching of mode water regions of each case.
Ohashi, Yusuke; Tanaka, Yoshio; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(3), p.382 - 390, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:61.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sludge-like uranium wastes (SUWs) have been generated with neutralization of acidic aqueous solutions used for decontamination of metal wastes containing a large amount of iron. We have examined the method for recovering uranium from such SUWs using 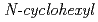 -2-pyrrolidone (NCP) as a precipitate. As a result, it was found that precipitation ratios (PRs) of uranium in the solutions prepared by dissolving SUWs in HNO
-2-pyrrolidone (NCP) as a precipitate. As a result, it was found that precipitation ratios (PRs) of uranium in the solutions prepared by dissolving SUWs in HNO is 97.7% at [NCP]/[U(VI)] = 20, and that the PRs of iron, aluminum, fluorine, and sulfate species are less than 1%. This indicates that uranium species are precipitated selectively. The content ratios of U, Fe, Ca, F, and S in the materials after calcining precipitates obtained at [NCP]/[U(VI)] = 20 were in accordance with the conditions of uranium ore concentrate. From these results, it is expected that highly purified uranium can be efficiently recovered from SUWs by using NCP as the precipitant.
is 97.7% at [NCP]/[U(VI)] = 20, and that the PRs of iron, aluminum, fluorine, and sulfate species are less than 1%. This indicates that uranium species are precipitated selectively. The content ratios of U, Fe, Ca, F, and S in the materials after calcining precipitates obtained at [NCP]/[U(VI)] = 20 were in accordance with the conditions of uranium ore concentrate. From these results, it is expected that highly purified uranium can be efficiently recovered from SUWs by using NCP as the precipitant.
Ohashi, Yusuke; Harada, Masayuki*; Asanuma, Noriko*; Ando, Shion; Tanaka, Yoshio; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 311(1), p.491 - 502, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Chemistry, Analytical)In order to assess the feasibility of method for recovering U from wastes containing uranium (scrap uranium) using polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) adsorbent, we have examined the adsorption and desorption behavior of metal species in HCl aqueous solutions dissolving scrap uranium. It was found that the U(VI) species are selectively adsorbed onto PVPP regardless of the presence of a large amount of Na(I) and Al(III), that the adsorbed U(VI) species are desorbed from PVPP column selectively by water. Pure uranium was efficiently recovered from the eluates. From these results, the PVPP resin is expected to be used as the adsorbent in the treatment process of scrap uranium.
Ohashi, Yusuke; Asanuma, Noriko*; Harada, Masayuki*; Tanaka, Yoshio; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 309(2), p.627 - 636, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.03(Chemistry, Analytical)As one of methods for recovering uranium from the uranium-bearing wastes, we have proposed the electrolytic deposition method using choline chloride-urea (CCU) which is known as an ambient temperature molten salt. More than 92% of uranium components in inactivated alumina and spent sodium fluoride adsorbent was dissolved into CCU solution. Cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of the solutions prepared by dissolving uranium-bearing wastes in CCU were measured in the potential range of -2.0 to 1.1 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). The one reduction peak was observed around -0.7 V for all solutions. Based on the results of CVs, bulk electrolyses of the solutions dissolving uranium-bearing wastes were also carried out at -1.5V at 80  C. The deposits were formed on a carbon electrode as cathode. Consequently, we confirmed that CCU is effective media for recovering uranium selectively from uranium-bearing waste.
C. The deposits were formed on a carbon electrode as cathode. Consequently, we confirmed that CCU is effective media for recovering uranium selectively from uranium-bearing waste.
Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kobayashi, Takuya; Nishikawa, Shiro*; Ishikawa, Yoichi*; Usui, Norihisa*; Kamachi, Masafumi*; Aso, Noriko*; Tanaka, Yusuke*; Awaji, Toshiyuki*
Global Environmental Research (Internet), 18(1), p.81 - 96, 2014/09
A drift simulation of tsunami debris flushed out from the Tohoku district, Japan, into the North Pacific due to the tsunami on March 11, 2011, has been conducted to monitor and forecast the drift path over the North Pacific. Results showed that tsunami debris was first transported eastward by the intense Kuroshio Extension and westerly, spreading in the north and south directions by both an energetic ocean eddy and a storm track over the ocean. Tsunami debris with larger windage was transported over the North Pacific by ocean surface wind rather than ocean current and arrived at the west coast of the North American Continent in the fall of 2011. Tsunami debris located near the North American Continent migrated, associated with the basin-scale seasonal change in the atmospheric pressure pattern. Our forecast run suggested that the tsunami debris belt will be formed from the North American Continent in the east to the Philippines in the west.
Ohashi, Yusuke; Nomura, Mitsuo; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Ando, Shion; Sugitsue, Noritake; Ikeda, Yasuhisa*; Tanaka, Yoshio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(2), p.251 - 265, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sludge-like uranium-bearing wastes generated from uranium refining and conversion R&D facilities are stored at the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center. We have proposed an aqueous process for recovering uranium from spent filter aid and CaF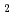 precipitate using hydrochloric acid. The distributions of the dissolved species in the sample solutions at different pH levels were calculated using the chemical equilibrium modeling system. Calculated results of fluorine contents of recovered uranium were compared with the experimental results. The fluorine content in the recovered uranium decreased as the aluminum concentration of the solution increased. On the other hand, uranium of spent filter aid was recovered selectively. The size of the particles of recovered uranium tends to decrease with increasing pH in the precipitation treatments. Also, the uranium concentration of the precipitate generated by the neutralization of the barren solution falls below 1 Bq/g.
precipitate using hydrochloric acid. The distributions of the dissolved species in the sample solutions at different pH levels were calculated using the chemical equilibrium modeling system. Calculated results of fluorine contents of recovered uranium were compared with the experimental results. The fluorine content in the recovered uranium decreased as the aluminum concentration of the solution increased. On the other hand, uranium of spent filter aid was recovered selectively. The size of the particles of recovered uranium tends to decrease with increasing pH in the precipitation treatments. Also, the uranium concentration of the precipitate generated by the neutralization of the barren solution falls below 1 Bq/g.
Ohashi, Yusuke; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 5th International Conference and Exhibition on Decommissioning Challenges; Industrial Reality and Prospects (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/04
Technologies for uranium refining and conversion for production of UF had been developed in Ningyo-Toge environmental engineering center. As a result, a significant sludge like uranium bearing waste and adsorbent was generated. These wastes total 1500 tons. They are dissolved using hydrochloric acid and dissolved uranium is recovered as uranium peroxide. Impurities in uranium peroxide and uranium content were compared with the requirement defined by ASTM. Consequently, highly pure uranium which met the requirement was recovered at low pH. The uranium remaining in the solution was removed using chelating resin in order to decrease uranium radioactivity of the neutralized precipitate that is generated later in the process. It is confirmed that aluminum in the neutralized precipitate is recovered selectively using sodium hydroxide.
had been developed in Ningyo-Toge environmental engineering center. As a result, a significant sludge like uranium bearing waste and adsorbent was generated. These wastes total 1500 tons. They are dissolved using hydrochloric acid and dissolved uranium is recovered as uranium peroxide. Impurities in uranium peroxide and uranium content were compared with the requirement defined by ASTM. Consequently, highly pure uranium which met the requirement was recovered at low pH. The uranium remaining in the solution was removed using chelating resin in order to decrease uranium radioactivity of the neutralized precipitate that is generated later in the process. It is confirmed that aluminum in the neutralized precipitate is recovered selectively using sodium hydroxide.
Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Tanaka, Momoko; Tatsumi, Toshihiro*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi*; Nagashima, Keisuke; Kimura, Toyoaki*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; et al.
Journal of Crystal Growth, 311(3), p.875 - 877, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:86.17(Crystallography)The temperature dependence of scintillation properties of a hydrothermal-method-grown zinc oxide (ZnO) emission is investigated using a nickel-like silver laser emitting at 13.9 nm. A broad peak at 386 nm with a full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of 15 nm at room temperature (298 K) is obtained. The peak position tends to be blue shifted while the FWHM becomes narrower when the crystal temperature is decreased to 25 K. Streak images fitted by a double exponential decay reveal that the measured emission decay at 105 K was 
 = 0.88 ns and
= 0.88 ns and 
 = 2.7 ns. This decay time of a few nanoseconds is suitable for lithographic applications and is sufficiently short for the characterization of laser plasma extreme ultraviolet (EUV) sources with nanosecond durations.
= 2.7 ns. This decay time of a few nanoseconds is suitable for lithographic applications and is sufficiently short for the characterization of laser plasma extreme ultraviolet (EUV) sources with nanosecond durations.
Tanaka, Momoko; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Tatsumi, Toshihiro*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Kagamitani, Yuji*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2008; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.130, p.501 - 505, 2009/00
We measured the time-resolved fluorescence spectra of ZnO and GaN single crystals excited by an X-ray laser operating at 13.9 nm and evaluated their scintillation properties for EUV excitation as compared with UV excitation case. For ZnO, a clear fluorescence peak of excitonic origin was observed at around 380 nm and the decay lifetime of less than 3 ns is found to be almost similar to the UV excitation case. The fluorescence at 380 nm is ideal for scintillator device design in the EUV and further applications. For GaN, the lifetimes are much longer than ZnO and the temporal profile of the EUV-excited fluorescence differs with the UV excitation case. As such, the EUV scintillation properties of ZnO is said to be more favorable than GaN. Finally, it is also demonstrated that an X-ray laser is an excellent tool for spectroscopic characterization of materials intended for next-generation lithography applications.
Furukawa, Yusuke*; Tanaka, Momoko; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Mima, Kunioki*; Kagamitani, Yuji*; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 36(APLS), p.1028 - 1030, 2008/12
Optical technologies in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) region have been receiving strong interests for the next generation lithography. Here we report properties of ZnO as scintillators in the EUV region, and to demonstrate the feasibility of using a Ni-like Ag EUV laser operated at 13.9-nm to evaluate these properties. The ZnO sample was irradiated with EUV laser pulses and the fluorescence was measured using a streak camera fitted with a spectrograph. A clear, excitonic, fluorescence peak was observed at around 380 nm with a decay lifetime of 3 ns. The prominent peak fluorescence is ideal for EUV detection and further applications including imaging.
Furukawa, Yusuke*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Tatsumi, Toshihiro*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; Kimura, Toyoaki; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; et al.
Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 25(7), p.B118 - B121, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:72.65(Optics)Using EUV laser operated at 13.9 nm ZnO and GaN are shown to be excellent scintillators in this wavelength region. Especially ZnO has short response time of 3 ns and prominent peak fluorescence from excitation at 380 nm.
Tanaka, Momoko; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.443 - 445, 2008/07
X-ray laser is a characteristic EUV source with short pulse duration of several pico-seconds, narrow spectral width, and high coherence. As an application of the X-ray laser, the UV emission from the ZnO single crystal excited by the 13.9 nm X-ray laser was observed and evaluated for EUV scintillator. The response time is sufficiently short for characterizing EUV lithography light sources having several nanoseconds duration. It is also shown that the X-ray laser is an excellent tool for time-resolved spectroscopy and characterization of materials intended for next-generation lithography applications.
Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; Kimura, Toyoaki; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 91(23), p.231117_1 - 231117_3, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:84.56(Physics, Applied)The scintillation properties of a hydrothermal method grown zinc oxide (ZnO) crystal are evaluated for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) laser excitation at 13.9 nm wavelength. The exciton emission lifetime at around 380 nm is determined to be 1.1 ns, almost identical to ultraviolet laser excitation cases. This fast response time is sufficiently short for characterizing EUV lithography light sources having a few nanoseconds duration. The availability of large size ZnO crystal up to 3-inch is quite attractive for future lithography and imaging applications.
Kawashima, Yusuke*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Yusuke*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nagashima, Keisuke; Kimura, Toyoaki; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Fukuda, Tsuguo*
no journal, ,
Using Ni-like Ag extreme ultraviolet (EUV) laser operated at 13.9-nm, ZnO is shown to be the excellent scintillator in this wavelength region with sufficiently short response time of less than 3 nsec and prominent peak fluorescence originated form exciton at 380 nm.
Tanaka, Momoko; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nagashima, Keisuke; Kimura, Toyoaki; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Fukuda, Tsuguo*
no journal, ,
Using Ni-like Ag extreme ultraviolet (EUV) laser operated at 13.9-nm, ZnO is shown to be the excellent scintillator in this wavelength region with sufficiently short response time of less than 3 nsec and prominent peak fluorescence originated form exciton at 380 nm.
Furukawa, Yusuke*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Mima, Kunioki*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; et al.
no journal, ,
Zinc oxide (ZnO) has previously been reported to be a potential light-emitting diode materia. We measured the time-resolved emission spectrum of a ZnO crystal for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) laser excitation at 13.9 nm wavelength and compared with UV excitation case. The emission lifetime was determined to be 2.6 ns. This value was not changed even for ultraviolet laser excitation. In the context of the nanosecond regime in the EUV region, ZnO crystal promises to be a feasible scintillation material.
Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Saito, Shigeki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Mima, Kunioki*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; et al.
no journal, ,
Optical technologies in the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) region have been receiving strong interest for the next generation lithography. Here we report properties of ZnO and GaN as scintillators in the EUV region, and to demonstrate the feasibility of using a Ni-like Ag EUV laser operated at 13.9-nm to evaluate these properties. The sample was irradiated with EUV laser pulses and the fluorescence were measured using a streak camera fitted with a spectrograph. In the case of ZnO, a clear, excitonic, fluorescence peak was observed at around 380 nm with a decay lifetime of 3 ns, as shown in Fig. 1. The prominent peak fluorescence is ideal for EUV detection and further applications including imaging. For GaN, a fluorescence peak at 370 nm having slower 5-ns decay time was observed. In this respect, the EUV scintillation properties of ZnO is said to be more favorable than GaN.
Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Shimazaki, Masao; Ohashi, Yusuke; Tanaka, Yoshio; Nomura, Mitsuo
no journal, ,
The operation waste of uranium conversion plant and uranium enrichment plant is called sludge, and contains many fluoride which is deleterious material. For disposal, elution of fluoride is a problem. Moreover, sludge contains many calcium sulfate and we are anxious about expansion of cement solidification object by superfluous generation ofettringite. Therefore, we report solidification and the leaching property of the cement solidification object of the sludge containing many fluoride. Moreover, we report solidification and the leaching property of sludge using magnesium oxide solidification material as a method of controlling elution and expansion of fluoride.