Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Norito; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Fujimura, Yuki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Materials, 17(3), p.547_1 - 547_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Chemistry, Physical)Natural monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite) was irradiated with 340-MeV Au ions, and the irradiation-induced nanostructures (i.e., ion tracks and nanohillocks) were observed using transmission electron microscopy. The diameter of the nanohillocks is approximately 10 nm, which is similar to the maximum molten region size calculated using the analytical thermal spike model. Ion tracks are imaged as strained regions that maintain their crystalline structure. The cross-sections of most of the ion tracks are imaged as parallelopiped or rectangular contrasts as large as 10 nm. These results strongly indicate that the molten region is recrystallized anisotropically, reflecting the lattice structure. Furthermore, low-density track cores are formed in the center of the ion tracks. The formation of low-density track cores can be attributed to the ejection of molten matter toward the surface.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidence
irradiated with swift heavy ions at grazing incidenceIshikawa, Norito; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu; Szabo, G. L.*; Wilhelm, R. A.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Nanotechnology, 33(23), p.235303_1 - 235303_10, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:48.5(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A single crystal of SrTiO doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
doped with niobium (Nb-STO) was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at grazing incidence. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used to study the relation between irradiation-induced change of surface topography and corresponding material property changes. As expected, multiple hillocks as high as 5-6 nm are imaged by AFM observation. It is also found that the region in between the adjacent hillocks is slightly elevated rather than depressed. Line-like contrasts along the ion paths are found in both AFM phase images and SEM images, indicating the formation of continuous ion tracks in addition to multiple hillocks. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation shows that the ion tracks in the near-surface region are found to be relatively large, whereas buried ion tracks in the deeper region are relatively small. The results suggest that recrystallization plays an important role in the formation of small ion tracks in the deep region, whereas formation of large ion tracks in the near-surface region is likely due to the absence of recrystallization.
Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:84.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
Ishikawa, Norito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Ogawa, Hiroaki
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.43_1 - 43_14, 2020/12
Amorphizable ceramics were irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions, and the as-irradiated samples were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ion track diameter and hillock diameter are similar for all the amorphizable ceramics. For SrTiO and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
and niobium-doped STO, 200 MeV Au ion irradiation and TEM observation were also performed. The ion track diameters in these materials are found to be markedly smaller than the hillock diameters. The ion tracks in these materials exhibit inhomogeneity, which is similar to that reported for non-amorphizable ceramics. On the other hand, the hillocks appear to be amorphous, and the amorphous feature is in contrast to the crystalline feature of hillocks observed in non-amorphizable ceramics. No marked difference is recognized between the nanostructures in STO and those in Nb-STO.
Etani, Reo*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Kanzaki, Norie*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Ishimori, Yuu; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Taguchi, Takehito*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Journal of Radiation Research, 58(5), p.614 - 625, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:53.9(Biology)Radon therapy using radon ( Rn) gas is classified into two types of treatment: inhalation of radon gas and drinking water containing radon. Although short- or long-term intake of spa water is effective in increasing gastric mucosal blood flow, and spa water therapy is useful for treating chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer, the underlying mechanisms for and precise effects of radon protection against mucosal injury are unclear. In the present study, we examined the protective effects of hot spring water drinking and radon inhalation on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Mice inhaled radon at a concentration of 2000 Be/m
Rn) gas is classified into two types of treatment: inhalation of radon gas and drinking water containing radon. Although short- or long-term intake of spa water is effective in increasing gastric mucosal blood flow, and spa water therapy is useful for treating chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer, the underlying mechanisms for and precise effects of radon protection against mucosal injury are unclear. In the present study, we examined the protective effects of hot spring water drinking and radon inhalation on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Mice inhaled radon at a concentration of 2000 Be/m for 24 h or were provided with hot spring water for 2 weeks. The activity density of
for 24 h or were provided with hot spring water for 2 weeks. The activity density of  Rn ranged from 663 Bq/l (start point of supplying) to 100 Bq/l (end point of supplying).Mice were then orally administered ethanol at three concentrations. The ulcer index (UI), an indicator of mucosal injury, increased in response to the administration of ethanol; however, treatment with either radon inhalation or hot spring water inhibited the elevation in the UI due to ethanol. Although no significant differences in antioxidative enzymes were observed between the radon-treated groups and the non-treated control groups, lipid peroxide levels were significantly lower in the stomachs of mice pre-treated with radon or hot spring water. These results suggest that hot spring water drinking and radon inhalation inhibit ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury.
Rn ranged from 663 Bq/l (start point of supplying) to 100 Bq/l (end point of supplying).Mice were then orally administered ethanol at three concentrations. The ulcer index (UI), an indicator of mucosal injury, increased in response to the administration of ethanol; however, treatment with either radon inhalation or hot spring water inhibited the elevation in the UI due to ethanol. Although no significant differences in antioxidative enzymes were observed between the radon-treated groups and the non-treated control groups, lipid peroxide levels were significantly lower in the stomachs of mice pre-treated with radon or hot spring water. These results suggest that hot spring water drinking and radon inhalation inhibit ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury.
 -Ti
-Ti O
O and
and  -Ti
-Ti O
O studied by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
studied by hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyKobayashi, Keisuke*; Taguchi, Munetaka*; Kobata, Masaaki; Tanaka, Kenji*; Tokoro, Hiroko*; Daimon, Hiroshi*; Okane, Tetsuo; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Ikenaga, Eiji*; Okoshi, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 95(8), p.085133_1 - 085133_7, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Awual, M. R.; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Suzuki, Shinichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 278, p.227 - 235, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:311 Percentile:99.19(Engineering, Environmental)Awual, M. R.; Suzuki, Shinichi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, p.127 - 135, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:338 Percentile:99.58(Engineering, Environmental)Imai, Suguru*; Taguchi, Kenji*; Kashiwa, Tatsuya*; Kitazawa, Toshihide*; Kato, Yoshiyuki; Segawa, Tomoomi; Suzuki, Masahiro
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, A, 133(5), p.271 - 272, 2013/05
As a part of the nuclear fuel cycle in Japan, the mixed oxide (MOX) fuels are produced through the microwave heating of the Pu/U mixed nitrate solution obtained from spent fuels. In this work, we investigate the effect of a spacer between the bottom of cavity and solution dish in microwave oven cavity to heat unifomly Pu/U mixed nitrate solution for making MOX fuels. As a result, we show the effectiveness of inserting the spacer for a uniform heating of the solution by evaluating the top-to-bottom ratio.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Nishiyama, Yuichi*; Toyota, Teruaki*; Yoshimoto, Masaaki*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishimori, Yuu; Aoyama, Yutaka*; Taguchi, Takehito*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
Inflammation, 34(6), p.559 - 567, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:49.49(Cell Biology)We assessed whether radon inhalation provided protection from carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic and renal damage in mice. Mice were subjected to intraperitoneal injection of CCl after inhaling approximately 18 kBq/m
after inhaling approximately 18 kBq/m radon for 6 h. Radon inhalation significantly increased total glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase activity in the liver and kidney. Injection of CCl
radon for 6 h. Radon inhalation significantly increased total glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase activity in the liver and kidney. Injection of CCl was associated with significantly higher levels of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and alkaline phosphatase activity and creatinine level in serum, and pretreatment with radon significantly decreased the GOT and ALP activity and creatinine level associated with CCl
was associated with significantly higher levels of glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and alkaline phosphatase activity and creatinine level in serum, and pretreatment with radon significantly decreased the GOT and ALP activity and creatinine level associated with CCl injection, suggesting that radon inhalation alleviates CCl
injection, suggesting that radon inhalation alleviates CCl -induced hepatic and renal damage. The t-GSH contents an GPx activity in the liver and kidney of animals pretreated with radon were significantly higher than those of the CCl
-induced hepatic and renal damage. The t-GSH contents an GPx activity in the liver and kidney of animals pretreated with radon were significantly higher than those of the CCl -only group. These findings suggested that radon inhalation activated antioxidative functions and inhibited CCl
-only group. These findings suggested that radon inhalation activated antioxidative functions and inhibited CCl -induced hepatic and renal damage in mice.
-induced hepatic and renal damage in mice.
Imai, Suguru*; Nakajima, Yuki*; Taguchi, Kenji*; Kashiwa, Tatsuya*; Kitazawa, Toshihide*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Segawa, Tomoomi; Fujii, Kanichi
Proceedings of 2011 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP 2011) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2011/10
As a part of the nuclear fuel cycle in Japan, the mixed oxide (MOX) fuels are produced through the microwave heating of the Pu/U mixed nitrate solution obtained from spent fuels. This paper investigated the electric power absorption of the solid Pu/U mixed nitrate medium in a cylindrical oven cavity and the effect of the input polarized waves. The numerical simulations have revealed that the incidence of the circularly polarized wave improves the uniformity of the absorbed power of the medium placed in the cylindrical cavity.
Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sakoda, Akihiro*; Yoshimoto, Masaaki*; Nakagawa, Shinya*; Toyota, Teruaki*; Nishiyama, Yuichi*; Yamato, Keiko*; Ishimori, Yuu; Kawabe, Atsushi*; Hanamoto, Katsumi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.360 - 363, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.28(Environmental Sciences)Our previous studies showed the possibility that activation of the antioxidative function alleviates various oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases. Results showed that, low-dose X-ray irradiation activated superoxide dismutase and inhibits oedema following ischaemia-reperfusion. To alleviate ischaemia-reperfusion injury with transplantation, the changes of the antioxidative function in liver graft using low-dose X-ray irradiation immediately after exenteration were examined. Results showed that liver grafts activate the antioxidative function as a result of irradiation. In addition, radon inhalation enhances the antioxidative function in some organs, and alleviates alcohol-induced oxidative damage of mouse liver. Moreover, in order to determine the most effective condition of radon inhalation, mice inhaled radon before or after carbon tetrachloride (CCl ) administration. Results showed that radon inhalation alleviates CCl
) administration. Results showed that radon inhalation alleviates CCl -induced hepatopathy, especially prior inhalation. It is highly possible that adequate activation of antioxidative functions induced by low-dose irradiation can contribute to preventing or reducing oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases.
-induced hepatopathy, especially prior inhalation. It is highly possible that adequate activation of antioxidative functions induced by low-dose irradiation can contribute to preventing or reducing oxidative damages, which are related to lifestyle diseases.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Araki, Koshi*; Dally, E. B.*; Hirota, Koichi
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49(12), p.5517 - 5522, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.03(Engineering, Chemical)An electron-beam (EB) irradiation/catalytic oxidation system was developed for the purification of a volatile organic compounds (VOC) gas stream under a practical gas flow condition. This system consists of a compact-sized electron accelerator and an ozone decomposition catalyst, which is MnO . The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm
. The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm /h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO
/h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO relative to CO
relative to CO increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi; Nakahira, Masataka; Matsumoto, Yasuhiro; Taguchi, Ko; Kozaka, Hiroshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Tesini, A.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(7-11), p.1813 - 1817, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The maintenance operation of the ITER in-vessel component, such as a blanket and divertor, must be executed by the remote equipment because of the high  -ray environment. During the Engineering Design Activity (EDA), the Japan Atomic Energy Agency had been fabricated the prototype of the vehicle manipulator system for the blanket remote handling and confirmed feasibility of this system including automatic positioning of the blanket and rail deployment procedure of the articulated rail. The JAEA is continuing several R&Ds so that the system can be procured smoothly to ITER. The residual key issues after the EDA are rail connection, cable handling and in-situ replacement of first wall. The last issue is newly raised and currently under the discussion. This presentation concentrates on the former two issues.
-ray environment. During the Engineering Design Activity (EDA), the Japan Atomic Energy Agency had been fabricated the prototype of the vehicle manipulator system for the blanket remote handling and confirmed feasibility of this system including automatic positioning of the blanket and rail deployment procedure of the articulated rail. The JAEA is continuing several R&Ds so that the system can be procured smoothly to ITER. The residual key issues after the EDA are rail connection, cable handling and in-situ replacement of first wall. The last issue is newly raised and currently under the discussion. This presentation concentrates on the former two issues.
Ide, Hiroshi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Kawamata, Kazuo; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu; Onuma, Yuichi; Watanabe, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Shuichi; Izumo, Hironobu; Ishida, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2008-012, 36 Pages, 2008/03
It is known that Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking (IASCC) occurs when austenitic stainless steel components used for light water reactor (LWR) are irradiated for a long period. In order to evaluate the high aging of the nuclear power plant, the study of IASCC becomes the important problem. The specimens irradiated in the reactor were evaluated by post irradiation examination in the past study. For the appropriate evaluation of IASCC, It is necessary to test it under the simulated LWR conditions; temperature, water chemistry and irradiation conditions. In order to perform in-pile SCC test, saturated temperature capsule (SATCAP) was developed. There are crack growth test, crack propagation test and so on for in-pile SCC test. In this report, SATCAP for crack propagation test is reported.
Ide, Hiroshi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Kawamata, Kazuo; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu; Onuma, Yuichi; Watanabe, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Shuichi; Izumo, Hironobu; Ishida, Takuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2008-011, 46 Pages, 2008/03
It is known that Irradiation Assisted Stress Corrosion Cracking (IASCC) occurs when austenitic stainless steel components used for light water reactor (LWR) are irradiated for a long period. In order to evaluate the high aging of the nuclear power plant, the study of IASCC becomes the important problem. The specimens irradiated in the reactor were evaluated by post irradiation examination in the past study. For the appropriate evaluation of IASCC, It is necessary to test it under the simulated LWR conditions; temperature, water chemistry and irradiation conditions. In order to perform in-pile SCC test, saturated temperature capsule (SATCAP) was developed. There are crack growth test, crack propagation test and so on for in-pile SCC test. In this report, SATCAP for crack growth test is reported.
 Co
Co  -ray irradiations
-ray irradiationsKimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Otani, Yoshimi*; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Kojima, Takuji
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 61, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Zennyoji, Yoshihiro*; Takigami, Machiko*; Baldacchino, G.*; Kimura, Atsushi; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki; Kojima, Takuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75(5), p.564 - 571, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.45(Chemistry, Physical)The suspended fine particles formed in aqueous phenol solution under high dose irradiation were studied using the MeV electron beam and  Co
Co  -ray irradiations. The fine particle's size was 100-800 nm in diameter and became bigger at higher dose and lower dose rate. The distributions of the particle size became narrower for irradiation at higher dose rate. The fine particles were regarded to consist of molecules of about 1.9
-ray irradiations. The fine particle's size was 100-800 nm in diameter and became bigger at higher dose and lower dose rate. The distributions of the particle size became narrower for irradiation at higher dose rate. The fine particles were regarded to consist of molecules of about 1.9 10
10 molecular weight.
molecular weight.
 -nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by
-nonylphenols in water and elimination of their estrogen activities by  Co
Co  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Otani, Yoshimi*; Takigami, Machiko; Shimada, Yoshitaka*; Kojima, Takuji; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 75(1), p.61 - 69, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Chemistry, Physical)Decomposition of  -Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1
-Nonylphenols (NPs) in water at 1  mol dm
mol dm was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by
was decreased exponentially with absorbed dose when NPs were irradiated by  Co
Co -rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg
-rays. Two products having molecular weight of 236, presumably OH adducts of NPs, were detected by LC-MS analyses. The elimination of estrogen activity of aqueous NPs solution including such irradiation products at 5000 Gy (J kg ) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
) was confirmed by the yeast two hybrid assay. These results should expand the application of ionizing radiation to the treatment of NPs.
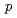 -nonylphenols in water by
-nonylphenols in water by  Co
Co  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji; Hiratsuka, Hiroshi*; Namba, Hideki
JAERI-Research 2004-018, 49 Pages, 2005/01
no abstracts in English