Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C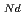 and C
and C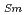 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C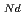 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C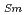 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
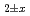 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Tokuyasu, Kayoko; Yasue, Kenichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Tamura, Itoko; Horiuchi, Yasuharu
QST-M-2; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2015, P. 189, 2017/03
Understanding the stage of mountain building is crucial to the stability assessment of geological environments in geological disposal system. In this context, we have carried out the research and development of provenance analysis techniques to elucidate the mountain-building stage. Here we present the results focusing on the R&D using the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) signals from quartz in sediments and their basement rocks.
Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(1), p.120 - 127, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:95.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*; Suzuki, Kiichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Safe Technologies and Sustainable Scenarios (FR-13) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2013/03
As research and development activities for MOX fuel pellet production, oxidation and reduction behaviors of MOX powders were investigated by thermogravimetry and X-ray diffraction measurements. It was observed that the oxidation limit decreased with oxidizing temperature and Pu content. The MOX powders showed a two-step oxidation and kinetic stability under non-stoichiometry. The oxidation rates were evaluated from the isothermal oxidation tests. It was found that the reduction temperature of M O
O + M
+ M O
O was higher than that of M
was higher than that of M O
O . This indicated that the reduction of M
. This indicated that the reduction of M O
O was prevented by the existence of M
was prevented by the existence of M O
O . Activation energy of the reduction was derived from the non-isothermal reduction tests. The data are expected to contribute to establishing a control technique for O/M ratio during MOX powder storage and pellet production.
. Activation energy of the reduction was derived from the non-isothermal reduction tests. The data are expected to contribute to establishing a control technique for O/M ratio during MOX powder storage and pellet production.
Okura, Takehisa; Oishi, Tetsuya; Taki, Mitsumasa; Shibanuma, Yukio; Kikuchi, Masamitsu; Akino, Hitoshi; Kikuta, Yasuaki; Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Saegusa, Jun; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-010, 37 Pages, 2012/05
Due to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant caused by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake occurred at 11th March 2011, the emergency environmental radiation monitoring was conducted at Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). This report provides the monitoring results of ambient  -ray dose rate and atmospheric radioactivity concentration until the beginning of June 2011. Some anthropogenic radionuclides such as Cs-134, Cs-137, I-131, I-132, Te-132, Xe-133 and others were detected from air samples. The atmospheric radioactivity concentrations varied with some peaks corresponded with that of ambient
-ray dose rate and atmospheric radioactivity concentration until the beginning of June 2011. Some anthropogenic radionuclides such as Cs-134, Cs-137, I-131, I-132, Te-132, Xe-133 and others were detected from air samples. The atmospheric radioactivity concentrations varied with some peaks corresponded with that of ambient  -ray dose rate after 15th March 2011. Composition of each peak showed various characteristic. Internal exposure caused by inhalation was estimated from the observed atmospheric radioactivity.
-ray dose rate after 15th March 2011. Composition of each peak showed various characteristic. Internal exposure caused by inhalation was estimated from the observed atmospheric radioactivity.
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 35(4), p.648 - 651, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:52.07(Thermodynamics)Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed homogeneous MOX fuels containing minor actinides (MAs) such as Am and Np elements. In this work, particular attention is paid to the influence of small MA addition on oxygen potential of MOX fuels. Oxygen potentials of (Am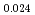 Pu
Pu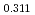 U
U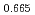 )O
)O and (Am
and (Am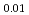 Np
Np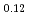 Pu
Pu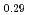 U
U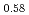 )O
)O in the near stoichiometric region were measured at 1473, 1573 and 1623K by thermogravimetry. (Am
in the near stoichiometric region were measured at 1473, 1573 and 1623K by thermogravimetry. (Am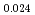 Pu
Pu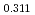 U
U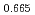 )O
)O and (Am
and (Am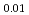 Np
Np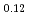 Pu
Pu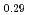 U
U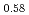 )O
)O were slightly higher than those of (Pu
were slightly higher than those of (Pu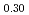 U
U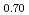 )O
)O . From this work, it was found that oxygen potential of MOX is slightly increased by small Am addition and influence of Np addition on oxygen potential is not significant.
. From this work, it was found that oxygen potential of MOX is slightly increased by small Am addition and influence of Np addition on oxygen potential is not significant.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Konashi, Kenji*; Aono, Shigenori; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 389(3), p.416 - 419, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) has been developed to use as a core fuel of the fast reactor. The oxygen to metal ratio (O/M) of the MOX fuel is an important parameter to control the FCCI. The oxygen potential and the oxygen diffusion coefficient of the MOX are essential data to understand the oxygen behaviour in MOX. The oxygen potentials of the MOX were measured with accuracy as a function of O/M and temperatures in the previous work. In this work the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient in (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O were investigated using thermo gravimetric technique. The kinetics of the reduction processes of (Pu
were investigated using thermo gravimetric technique. The kinetics of the reduction processes of (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O were measured by TG-DTA method. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients have been estimated from the reduction curves. It was concluded that the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient in (Pu
were measured by TG-DTA method. The oxygen chemical diffusion coefficients have been estimated from the reduction curves. It was concluded that the oxygen chemical diffusion coefficient in (Pu U
U )O
)O is a smaller than that of (Pu
is a smaller than that of (Pu U
U )O
)O .
.
Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Konashi, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 385(2), p.419 - 423, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:82.24(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potentials of homogenous (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Np
and (Np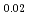 Am
Am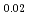 Pu
Pu U
U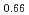 )O
)O which have been developed as a fuel of fast breeder reactors were measured at temperatures of 1473 - 1623 K by gas equilibrium technique using Ar/H
which have been developed as a fuel of fast breeder reactors were measured at temperatures of 1473 - 1623 K by gas equilibrium technique using Ar/H /H
/H O gas mixture. Oxygen potentials of (Pu
O gas mixture. Oxygen potentials of (Pu U
U )O
)O measured in this work were about 25 kJ/mol lower than those of (Pu
measured in this work were about 25 kJ/mol lower than those of (Pu U
U )O
)O and were consistent with the value calculated by Besmenn and Lindemer's model. Those of (Np
and were consistent with the value calculated by Besmenn and Lindemer's model. Those of (Np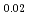 Am
Am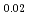 Pu
Pu U
U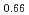 )O
)O were slightly higher than those of MOX without minor actinides.
were slightly higher than those of MOX without minor actinides.
 X-ray reflectometry and LiNi
X-ray reflectometry and LiNi Co
Co O
O epitaxial film electrode synthesized by pulsed laser deposition method
epitaxial film electrode synthesized by pulsed laser deposition methodHirayama, Masaaki*; Sakamoto, Kazuyuki*; Hiraide, Tetsuya*; Mori, Daisuke*; Yamada, Atsuo*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Sonoyama, Noriyuki*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Mizuki, Junichiro
Electrochimica Acta, 53(2), p.871 - 881, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:66.81(Electrochemistry)An  experimental technique was developed for detecting structure changes at the electrode/electrolyte interface of lithium cell using synchrotron X-ray reflectometry and two-dimensional model electrodes with a restricted lattice plane. The electrode was constructed with an epitaxial film of LiNi
experimental technique was developed for detecting structure changes at the electrode/electrolyte interface of lithium cell using synchrotron X-ray reflectometry and two-dimensional model electrodes with a restricted lattice plane. The electrode was constructed with an epitaxial film of LiNi Co
Co O
O synthesized by the pulsed laser deposition method. These films provided an ideal reaction field suitable for detecting structure changes at the electrode/electrolyte interface during the electrochemical reaction. The X-ray reflectometry indicated a formation of a thin-film layer at the LiNi
synthesized by the pulsed laser deposition method. These films provided an ideal reaction field suitable for detecting structure changes at the electrode/electrolyte interface during the electrochemical reaction. The X-ray reflectometry indicated a formation of a thin-film layer at the LiNi Co
Co O
O (1 1 0)/electrolyte interface during the first charge-discharge cycle, while the LiNi
(1 1 0)/electrolyte interface during the first charge-discharge cycle, while the LiNi Co
Co O
O (0 0 3) surface showed an increase in the surface roughness without forming the surface thin-film layer.
(0 0 3) surface showed an increase in the surface roughness without forming the surface thin-film layer.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases
with two fcc phasesSuzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Aono, Shigenori; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 444-445, p.590 - 593, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.91(Chemistry, Physical)It was reported that sintered MOX pellet of hypostoichiometric composition was oxidized at room temperature in an atmosphere of inert gas and air. The region of two fcc phases exist at room temperature in the (U,Pu)O with Pu content of greater than 20%. In this study, the oxidation rate of (U
with Pu content of greater than 20%. In this study, the oxidation rate of (U Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases was investigated to contribute to understanding of the oxidation behavior using thermogravimetric technique. The sintered pellets of (U
with two fcc phases was investigated to contribute to understanding of the oxidation behavior using thermogravimetric technique. The sintered pellets of (U Pu
Pu )O
)O were prepared by mechanical blending method and were sliced into disc-like sample with about 1 mm thick and 85-93% theoretical density. The oxidation rate of the samples were measured at 60, 125 and 150
were prepared by mechanical blending method and were sliced into disc-like sample with about 1 mm thick and 85-93% theoretical density. The oxidation rate of the samples were measured at 60, 125 and 150 C in an atmosphere of Air, N
C in an atmosphere of Air, N and Air/N
and Air/N gas mixture containing moisture of 1 - 700ppm using thermal gravity and differential thermal analysis. The curve of the isothermal oxidation was analyzed by the model of diffusion in a system consisting of two phases. The diffusion model can represent the oxidation curve as a function of time and temperature. In the results of X-ray diffraction measurement, fcc phase with O/M
gas mixture containing moisture of 1 - 700ppm using thermal gravity and differential thermal analysis. The curve of the isothermal oxidation was analyzed by the model of diffusion in a system consisting of two phases. The diffusion model can represent the oxidation curve as a function of time and temperature. In the results of X-ray diffraction measurement, fcc phase with O/M  2.00 was observed to increase by oxidation of sample. These results indicate that the oxidation of the (U
2.00 was observed to increase by oxidation of sample. These results indicate that the oxidation of the (U Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases proceeds by diffusion of the phase with O/M
with two fcc phases proceeds by diffusion of the phase with O/M  2.00 which is formed on the sample surface.
2.00 which is formed on the sample surface.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-049, 32 Pages, 2006/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a fast breeder reactor(FBR), and plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) having low density and 20-30%Pu content has used as a fuel of the FBR, Monju. In plutonium, Americium has been accumulated during long-term storage, and Am content will be increasing up to 2-3% in the MOX. It is essential to evaluate the influence of Am content on physical properties of MOX on the development of FBR in the future. In this study melting points and thermal conductivities which are important data on the fuel design were measured systematically in wide range of composition, and the effects of Am accumulated were evaluated. The solidus temperatures of MOX were measured as a function of Pu content, oxygen to metal ratio(O/M) and Am content using thermal arrest technique. The sample was sealed in a tungsten capsule in vacuum for measuring solidus temperature. In the measurements of MOX with Pu content of more than 30%, a rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction between MOX and tungsten. In the results, it was confirmed that the melting points of MOX decrease with as an increase of Pu content and increase slightly with a decrease of O/M ratio. The effect of Am content on the fuel design was negligible small in the range of Am content up to 3%. Thermal conductivities of MOX were evaluated from thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method and heat capacity calculated by Nuemann- Kopp's law. The thermal conductivity of MOX decreased slightly in the temperature of less than 1173K with increasing Am content. The effect of Am accumulated in long-term storage fuel was evaluated from melting points and thermal conductivities measured in this study. It is concluded that the increase of Am in the fuel barely affect the fuel design in the range of less than 3%Am content.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
JNC TN8400 2004-022, 44 Pages, 2005/03
Japan Nuclear Development Institute has developed homogeneous mixed oxide fuel containing minor actinide as a fuel of an advanced fast reactor. Study on the sintering behavior of the fuel was carried out and the heat treatment technique for preparing homogeneous low O/M fuel had been developed. In this report, oxygen potential was measured and phase relation was evaluated, which are needed essentially for developing the new type fuel.Oxygen potential of (Npsub0.02Amsub0.02Pusub0.3Usub0.66)Osub2-X was measured by gas equilibrium method as a function of temperature and O/M ratio. The MOX with MA has slightly higher oxygen potential as compared with that of MOX without MA. And the model of oxygen potential was derived from the measurement results based on lattice defect theory.In samples with low O/M ratio, two fcc phases were observed at room temperature. The temperature of the phase separation was measured and it is observed that the addition of MA have the effect to be decreased the phase separation temperature. In the MOX containing MA and Nd simulated a low decontaminated fuel, the Pu-Am-Nd oxides were precipitated by decreasing O/M ratio in less than 1.96.
Kato, Masato; Aono, Shigenori; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Konashi, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 344, p.235 - 239, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The oxygen potentials of (Pu U
U )O
)O near stoichiometric region were measured by thermogravimetric technique which was used to establish the equilibrium between the oxide phases and H
near stoichiometric region were measured by thermogravimetric technique which was used to establish the equilibrium between the oxide phases and H /H
/H O system gas. The experimental results of (Pu
O system gas. The experimental results of (Pu U
U )O
)O give a consistent picture variation in Po
give a consistent picture variation in Po with O/M and the temperature with other works. The relationship between the partial oxygen pressure and X in MO
with O/M and the temperature with other works. The relationship between the partial oxygen pressure and X in MO was evaluated by the lattice defect theory. The relation in hypo-stoichiometric region is x
was evaluated by the lattice defect theory. The relation in hypo-stoichiometric region is x Po
Po
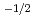 near stoichiometric composition, and changes to x
near stoichiometric composition, and changes to x Po
Po
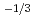 with a decrease in O/M.
with a decrease in O/M.
Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Aono, Shigenori
Proceedings of 11th Symposium on Thermodynamics of Nuclear Materials (STNM-11), P. 81, 2004/00
The oxygen potentials of (Pu U
U )O
)O were measured by thermogravimetric equilibrium measurement in the range of the temperature from 800 to 1350 in Ar/H
were measured by thermogravimetric equilibrium measurement in the range of the temperature from 800 to 1350 in Ar/H /H
/H O or He/H
O or He/H /H
/H O mixture gas flow. The experimental results of (Pu
O mixture gas flow. The experimental results of (Pu U
U )O
)O are in good agree with the other works. The relationship between the partial oxygen pressure (PO
are in good agree with the other works. The relationship between the partial oxygen pressure (PO ) and X in MO
) and X in MO was analized based on lattice defect theory. The oxygen potential of (Pu
was analized based on lattice defect theory. The oxygen potential of (Pu U
U )O
)O was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduces the oxygen potential-temperature data for (Pu
was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduces the oxygen potential-temperature data for (Pu U
U )O
)O .
.
Kato, Masato; ; ; *; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; *
JNC TN8400 2003-014, 151 Pages, 2003/05
JNC has been developing low decontaminated MOX fuel containing Miner Actinide (MA) for advanced FBR. It is very important for the fuel development to investigate sintering properties and physical properties of the fuel. In this paper, the influence of oxygen partial pressure during sintering on sintering behavior and migration of MA and FPs in MOX pellets containing Np/Am and simulated FP have been studied. The results of the examination are as follows. (1)The pellets sintered in atmosphere of high oxygen partial pressure have homogeneous composition and large grain size. Additive Ln elements promote homogenization and restrain grain growth in the pellets. (2)O/M ratio of the sintered pellets could be controlled to 1.95 by heat treatment of appropriate temperature, time and oxygen partial pressure. Phase separation was observed in the pellets with O/M=1.95. (3)Pu-Am-Ln compounds precipitated in the pellets with Ln. The form of precipitation of Pu-Am-Ln compounds changed depending on sintering conditions. (4)Y and Zr were distributed homogeneously in the pellet not depending on the sintering condition and it is considered that Ru, Rh and Pd are precipitated with metallic particle or alloy of this particles.
Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2003-013, 48 Pages, 2003/05
JNC have been manufacturing MOX fuels from Plutonium and Uranium mixed oxide powder (1:1 MOX) that were prepared by microwave direct denitration method. It is well known that MOX raw material oxidize in storage and manufacturing process due to heat generation by self-radiation. The oxidation process and rate of MOX powder were examined for three kinds of powders having different surface area. The examination of isothermal and non-isothermal oxidation was carried out by TG-DTA. The oxidized samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction measurement. The oxidation of MOX powders proceeded in two steps and the oxidation process changed depending on the surface area of the powder as follows. Process 1 (Surface Area : 2.24m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO
 MO
MO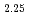 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO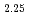
 MO
MO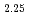 +M
+M O
O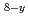 Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m
Process 2 (Surface Area : 5.59, 3.86m /g) First Step : MO
/g) First Step : MO
 MO
MO +MO
+MO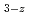
 MO
MO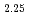 +MO
+MO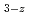 Second Step : MO
Second Step : MO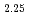 +MO
+MO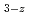
 MO
MO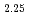 +M
+M O
O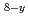 +MO
+MO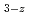 The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.
The kinetic analysis of the oxidation was evaluated by Avrami-Erofeev equation. The equation of O/M change on the MOX powder was obtained as function of temperature, keeping time and the surface area of the powder.
 I -Oxygen potential measurement of UO
I -Oxygen potential measurement of UO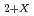 and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O
Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Endo, Hideo
JNC TN8400 2002-020, 76 Pages, 2003/03
The ratio of oxygen to metal is one of important fuel specifications on UO and MOX fuels, because it effect on irradiation behavior. Oxygen potential of oxide fuels have been measured by various methods on the purpose of optimization of irradiation behavior and fabrication condition. In this repot the oxygen potential of UO
and MOX fuels, because it effect on irradiation behavior. Oxygen potential of oxide fuels have been measured by various methods on the purpose of optimization of irradiation behavior and fabrication condition. In this repot the oxygen potential of UO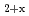 and (Pu
and (Pu U
U )O
)O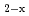 was measured by thermal gravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). Measurements of oxygen potential were carried out at 800
was measured by thermal gravimetry and differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA). Measurements of oxygen potential were carried out at 800 C, 1000
C, 1000 C and 1200
C and 1200 C in Ar/H
C in Ar/H /H
/H O mixture gas flow. Ratio of O/M was obtained from the weight change of the sample according to the partial oxygen pressure that was controlled by H
O mixture gas flow. Ratio of O/M was obtained from the weight change of the sample according to the partial oxygen pressure that was controlled by H /H
/H O ratio in atmosphere. The partial oxygen pressure in atmosphere was measured by stabilized zyrconia oxygen sensor. The experimental results agree approximately to the other works. Thermodynamic data,
O ratio in atmosphere. The partial oxygen pressure in atmosphere was measured by stabilized zyrconia oxygen sensor. The experimental results agree approximately to the other works. Thermodynamic data,  Go
Go ,
,  Ho
Ho ,
,  So
So , were evaluatedfrom the experimental data. The oxygen potential of UO
, were evaluatedfrom the experimental data. The oxygen potential of UO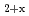 , (Pu,U)O
, (Pu,U)O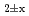 and PuO
and PuO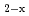 was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduce the large amount of oxygen potential-temperature-composition data for the Pu-U oxide system.
was modeled by lattice defect theory using the data of the literature and this work. The resulting equation well reproduce the large amount of oxygen potential-temperature-composition data for the Pu-U oxide system.

Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Nishiyama, Motokuni; Endo, Hideo; Kono, Shusaku; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*
JNC TN8400 2003-011, 32 Pages, 2003/01
MOX fuel containing Neptunium is being developed as candidate fuel for an advanced nuclear fuel recycle. In this report, influence of Np on the sintering behavior, phase separation behavior of MOX fuel pellets and the homogeneity of MOX fuel pellets were evaluated. It was observed that the high Np containing pellets had a low sintered density and the microstructure changes of the pellets during the sintering were slow compared with MOX without Np. The pellets were also analyzed via Ceramography, X-ray diffraction measurement and an electron probe microanalysis. The phase separation behavior of MOX with Np was similar to that of MOX. The homogeneity of the pellet produced with this experiment was acceptable to the fuel specification.