Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishii, Tetsuya; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Kenya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 9(2), p.207 - 218, 2010/06
In order to develop an innovative fuel fabrication method for americium containing oxide fuels, a feasibility study of metallic U and Mo-doped oxide fuel concept with extruding granulated oxide material was conducted using UO . In the concept, it is expected that doped U should reduce the effective oxygen potential and doped Mo should increase the thermal conductivity of the fuel. In this study, sintering tests of U and Mo-doped UO
. In the concept, it is expected that doped U should reduce the effective oxygen potential and doped Mo should increase the thermal conductivity of the fuel. In this study, sintering tests of U and Mo-doped UO powder were done and thermal conductivities of the sintered material were evaluated. From the results, it can be seen that the doped U and Mo would function as a oxygen potential reducer and thermal conductivity improver, respectively. And it can be seen that the U and Mo doped oxide fuel pellets would be fabricated successfully using hot pressing. Also, from the results of a sintering test of U and Mo-doped extruding granulated UO
powder were done and thermal conductivities of the sintered material were evaluated. From the results, it can be seen that the doped U and Mo would function as a oxygen potential reducer and thermal conductivity improver, respectively. And it can be seen that the U and Mo doped oxide fuel pellets would be fabricated successfully using hot pressing. Also, from the results of a sintering test of U and Mo-doped extruding granulated UO , it can be seen that the extruding granulated substances have a preferable sintering characteristic.
, it can be seen that the extruding granulated substances have a preferable sintering characteristic.
Tanaka, Kenya; Ishii, Tetsuya; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Asaka, Takeo
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle; Sustainable Options & Industrial Perspectives (Global 2009) (CD-ROM), p.2045 - 2050, 2009/09
As a part of the economic evaluation of the MA recycling system, the management cost of high level radioactive waste was estimated quantitatively. The development of an innovative fuel fabrication process has been done by using UO powder, U metal particles and Mo powder. From comparisons of granulated material characteristics, two candidate methods, mixing granulation (MIX/G) and extruding granulation (EXT/G), were considered to have good feasibility as the fuel fabrication process. In the preliminary sintering test of granulated UO
powder, U metal particles and Mo powder. From comparisons of granulated material characteristics, two candidate methods, mixing granulation (MIX/G) and extruding granulation (EXT/G), were considered to have good feasibility as the fuel fabrication process. In the preliminary sintering test of granulated UO obtained by EXT/G, a high density UO
obtained by EXT/G, a high density UO pellet (97% of TD) with 5wt% of U and 5wt% of Mo was successfully sintered. From the results of thermal conductivity measurements, it was confirmed that the dispersion of Mo powder and U metal into the oxide matrix was an effective way to improve the characteristic.
pellet (97% of TD) with 5wt% of U and 5wt% of Mo was successfully sintered. From the results of thermal conductivity measurements, it was confirmed that the dispersion of Mo powder and U metal into the oxide matrix was an effective way to improve the characteristic.
Ishii, Tetsuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 51(5), p.366 - 367, 2009/05
, 51(5), p.366 - 367, 2009/05
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Tetsuya; Nemoto, Junichi*; Asaka, Takeo; Sato, Seichi*; Mayorshin, A.*; Shishalov, O.*; Kryukov, F.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(4), p.263 - 273, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to develop a vibro-packed MOX fuel performance analysis code, thermochemical and mechanical properties of the vibro-packed fuels were incorporated into a pellet type fuel performance analysis code CEDAR. Calculations were made by the developed code on a vibro-packed MOX fuel pin irradiated at BN-600 in Russia. Since the calculated results agreed well with the behaviors obtained from the experimental data, it can be concluded that the code was well modeled and qualitatively validated.
Ishii, Tetsuya; Ukai, Shigeharu
JNC TN9400 2005-030, 86 Pages, 2005/07
U-Pu-Zr alloys are candidate materials for commercial FBR fuel. However, informations about chemical reactions with cladding materials developed by JNC for commercial FBR have not been well obtained. In this work, the reaction zones formed in four diffusion couples U-10wt.%Zr/PNC-FMS, U-10wt.%Zr/9Cr-ODS, U-10wt.%Zr/12Cr-ODS, and U-10wt.%Zr/Fe at about 1013K have been examined and following results were obtained.1)At about 1013K, in the U-10wt.%Zr/Fe couple, the liquid phase zones were obtained. In the other couples U-10wt.%Zr/PNC-FMS, U-10wt.%Zr/9Cr-ODS and U-10wt.%Zr/12Cr-ODS, no liquid phase zones were obtained. The obtained chemical reaction zones in the later 3 couples were similar to the reported ones obtained in U-Zr/Fe couples without liquid phase formation. In comparison with the reaction zones obtained in the U-10wt.%Zr/Fe couple, the reaction zones inside cladding materials obtained in the PNC-FMS, 9Cr-ODS, and 12Cr-ODS couples were thin.2)From the investigations of the mechanisms of chemical reactions between U-Pu-Zr/cladding materials, it was considered that the mechanisms would be similar to those of U-Pu-Zr/Fe. Therefore, it was considered that the threshold temperature of liquid phase formation for U-Pu-Zr/Fe would be conservatively available for U-Pu-Zr/PNC-FMS, U-Pu-Zr/9Cr-ODS, and U-Pu-Zr/12Cr-ODS as the case of U-Zr/cladding materials.3)From the investigations of relationship between the obtained depths of the chemical reaction zones inside cladding materials and composition of the cladding materials, it was considered that the depth of chemical reaction zones would depend on the Cr content of the cladding materials and the depth would decrease with increasing Cr content.
 Compacts with/without Uranium Particles
Compacts with/without Uranium ParticlesIshii, Tetsuya; Yuda, Ryoichi*; Hirai, Mutsumi*; Tsuboi, Yasushi*; Ukai, Shigeharu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1204 - 1210, 2004/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal conductivities of granular UO compacts with and without uranium particles were measured to evaluate the thermal performance of vibro-packed granular MOX fuels containing metallic fine particle oxygen getters. The thermal conductivity of the compact with 10wt.% of the uranium particles was higher than without uranium particles and after heating beyond 1408K, the melting point of the uranium particle, the thermal conductivity further increased..The evaluation model for analyzing such phenomena were developed and it was revealed that once the UO
compacts with and without uranium particles were measured to evaluate the thermal performance of vibro-packed granular MOX fuels containing metallic fine particle oxygen getters. The thermal conductivity of the compact with 10wt.% of the uranium particles was higher than without uranium particles and after heating beyond 1408K, the melting point of the uranium particle, the thermal conductivity further increased..The evaluation model for analyzing such phenomena were developed and it was revealed that once the UO compact with the uranium particles was exposed to the temperature beyond 1408K, the uranium particle should melt and provide interconnect area between the UO
compact with the uranium particles was exposed to the temperature beyond 1408K, the uranium particle should melt and provide interconnect area between the UO granules and uranium particles, and between the uranium particles with each other. The resulting increase of the thermal conductivity was reasonably expressed by the effect of necks in the compact on the heat conduction.
granules and uranium particles, and between the uranium particles with each other. The resulting increase of the thermal conductivity was reasonably expressed by the effect of necks in the compact on the heat conduction.
Ishii, Tetsuya; *;
JNC TN9400 2000-045, 64 Pages, 2000/03
During the irradiation, the Pu redistribution phenomena would occur in the FBR MOX fuel pellets. The phenomena would considerably affect on the thermal properties of the fuels, therefore, it is need to establish the evaluation method for Pu redistribution phenomena. ln JNC, the efforts for development of the evaluation model for the phenomena had been continued and the simple evaluation model was constructed in 1992. In this work, the modification of the simple model developed in JNC has been done and the following results were obtained. (1)Based on the recent data of the MOX fuel irradiation tests, the evaluation model for Pu redistribution phenomena constructed in l992 is modified. And the model is included into the fuel performance analysis code "CEDAR". (2)To calibrate the modified CEDAR code, it is confirmed that the uncertainty in the Pu concentration evaluation for the center of the fuel pellet at EOL is about  3wt.%. (3)Based on the results of the evaluations using the modified CEDAR code, it is found that, in the early stage of the irradiation, the Pu redistribution is controlled by the vapor transportation mechanism via pores, and after that, the Pu redistribution is kept in progress due to the thermal diffusion mechanism with the change of the Pu concentration due to the degradation of U and Pu by fissions. And it is also found that the O/M ratio dependence of the U-Pu inter diffusion coefficients would affect on the Pu redistribution mechanisms, in especial, in the early stage of the irradiation.
3wt.%. (3)Based on the results of the evaluations using the modified CEDAR code, it is found that, in the early stage of the irradiation, the Pu redistribution is controlled by the vapor transportation mechanism via pores, and after that, the Pu redistribution is kept in progress due to the thermal diffusion mechanism with the change of the Pu concentration due to the degradation of U and Pu by fissions. And it is also found that the O/M ratio dependence of the U-Pu inter diffusion coefficients would affect on the Pu redistribution mechanisms, in especial, in the early stage of the irradiation.
Ishii, Tetsuya;
JNC TN9400 2000-031, 15 Pages, 2000/03
For the irradiation performance of metallic fuel, many of the analyses were conducted in USA using EBR-l and EBR-II. ln this study, based on the published data and papers on the above results, the appropriate methods to the evaluation of the irradiation performance of FBR metallic fuel for the design study were considered, as the fbasibility study for FBR. The followings are the targets in this work; (1)deformation of cladding (2)deformation of fuel slug (3)FP gas release (4)fluctuation of the bonding Na level in the fuel pin (5)FCCI
Ishii, Tetsuya;
S3-WED-11:40C, 0 Pages, 2000/00
None
Ishii, Tetsuya; *;
JNC TN9400 99-055, 99 Pages, 1999/06
It is one of the major subjects in the improvement of the design method for determining the thermal conditions of the solid type Mixed - Oxide (MOX) fuels in FBR to evaluate the fuel temperature at BOL as precisely as possible. Therefore, we have planned to modify the fuel temperature evaluation method "FEVER", which was developed by JNC in 1988, as one of the investigation for the establishment of the precise fuel temperature evaluation method. And, we also have planned to use the modified FEVER, named "FEVER-M", for estimation of the irradiation conditions of the PTM test in Joyo, called "B10 test", planning to perform in 2000. In this work, the following results were obtained; (1)As a result of the modification, the uncertainty in the fuel temperature evaluation of "FEVER-M" is reduced to about  60K. (2)Estimating the irradiation conditions of "B10" test using the method "FEVER-M", it is found that the appropriate maximum linear heat rate for the test is 620 W/cm. The detail plan of the "B10" test were also determined based on the results. (3)Based on the results of this work, it is found that one of the effective procedure for the impovement of the accuracy of the fuel temperature evaluation method seems to calculate the fuel temperature taking the pellet relocation phenomena into account. In future, although there are a lot of matters to be discussed in this phenomena, the design method for the thermal conditions of the MOX fuels in FBR should be performed with taking the pellet relocation phenomena into account.
60K. (2)Estimating the irradiation conditions of "B10" test using the method "FEVER-M", it is found that the appropriate maximum linear heat rate for the test is 620 W/cm. The detail plan of the "B10" test were also determined based on the results. (3)Based on the results of this work, it is found that one of the effective procedure for the impovement of the accuracy of the fuel temperature evaluation method seems to calculate the fuel temperature taking the pellet relocation phenomena into account. In future, although there are a lot of matters to be discussed in this phenomena, the design method for the thermal conditions of the MOX fuels in FBR should be performed with taking the pellet relocation phenomena into account.
Ishii, Tetsuya;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 247, p.82 - 85, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:63.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)None
Ishii, Tetsuya; Hirosawa, Takashi
PNC TN9410 97-075, 20 Pages, 1997/08
Fuel melting temperature is one of the major thermodynamical properties that is used for determining the design criteria on fuel temperature during irradiation in FBR. In general, it is necessary to evaluate the correlation of fuel melting temperature to confirm that the fuel temperature must be kept below the fuel melting temperature during irradiation at any conditions. The correlations of the melting temperature of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel, typical FBR fuel, used to be estimated and formulized based on the measured values reported in 1960's and has been applied to the design. At present, some experiments have been accumulated with improved experimental techniques. And it reveals that the recent measured melting temperatures does not agree well to the data reported in 1960's and that some of the 1960's data should be modified by taking into account of the recent measurements. In this study, the experience of melting temperature up to now are summarized and evaluated in order to make the fuel pin design more reliable. The effect of plutonium content, oxygen to metal ratio and burnup on MOX fuel melting was examined based on the recent data under the UO - PuO
- PuO - PuO
- PuO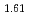 ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T
ideal solution model, and then formulized. The correlation obtained in this work is as-follows; T = T +
+  T
T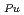 +
+  T
T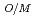 +
+  T
T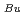 ----(A) T
----(A) T = 3120
= 3120  T
T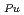 = -5.7537
= -5.7537 PU + 1.3631
PU + 1.3631 10
10
 PU
PU + 1.7952
+ 1.7952 10
10
 PU
PU
 T
T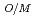 = -1.41
= -1.41  PU
PU  (2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP =
(2.00 - OP)/0.39 OP : OP = 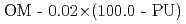 /(0.01
/(0.01 PU)
PU)  T
T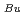 = -5.0
= -5.0 BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO
BU/10000 where T is the melting temperature (degree of K), PU is the weight fraction of PuO in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.
in the mixed oxide fuel, OM is the oxygen to metal ratio, and BU is the burnup in the unit of MWd/MTM. respectively.  T
T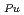 (plutonium content),
(plutonium content),  T
T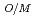 (O/M Ratio),
(O/M Ratio),  ...
...
Ishii, Tetsuya;
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 231, p.242 - 244, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:92.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)None
Nemoto, Junichi*; Ishii, Tetsuya; Ukai, Shigeharu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kenya; Sato, Isamu; Ishii, Tetsuya; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Asaka, Takeo; Kurosaki, Ken*
no journal, ,
In order to reduce the environment burden due to MA origin of LWR in near future, MA recycle concept which has consistency with current fuel cycle technology has been proposed. Also the related core development plan for innovative Am-MOX fuel has been created.
Ishii, Tetsuya; Yuda, Ryoichi*; Matsuyama, Shinichiro*
no journal, ,
For improvement of the physical properties of MOX fuels containing americium, the method that metallic uranium particles are mixed with fuel powders and sintered could be one of the probable techniques. In this work, the feasibility of the method was studied using UO with metallic uranium particles
with metallic uranium particles
Tanaka, Kosuke; Sato, Isamu; Ishii, Tetsuya; Katsuyama, Kozo; Tanaka, Kenya; Nemoto, Junichi*
no journal, ,
The purpose and the things to be focused attention on the post irradiation examinations of Am-1 test are summarized in this presatation.
Ishii, Tetsuya; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Kenya
no journal, ,
To investigate the fabrication method of Am-containing Oxide Fuels with metallic particles, for improvement of fuel thermo chemical properties, fabrication tests of simulated fuels using hot press sintering method were done. It can be concluded from the results that the Am-containing Oxide Fuels with metallic particles would be fabricated well by hot press sintering method.
Tanaka, Kenya; Sato, Isamu; Ishii, Tetsuya; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Asaka, Takeo
no journal, ,
A rational MA recycle concept based on high Am content fuel has been proposed. A design study of an Am-MOX fabrication plant, which is a key facility for the MA recycle concept, has been done and the facility concept was clarified from the viewpoint of basic process viability. Preliminary cost estimation suggested that the total construction cost of the MA recycle facilities including Am-MOX, Np-MOX and MA recovery could be comparable with that of the large scale LWR-MOX fabrication plant required for plutonium in LWR fuel cycle.