Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Norito; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Fujimura, Yuki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Materials, 17(3), p.547_1 - 547_21, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Chemistry, Physical)Natural monoclinic zirconia (baddeleyite) was irradiated with 340-MeV Au ions, and the irradiation-induced nanostructures (i.e., ion tracks and nanohillocks) were observed using transmission electron microscopy. The diameter of the nanohillocks is approximately 10 nm, which is similar to the maximum molten region size calculated using the analytical thermal spike model. Ion tracks are imaged as strained regions that maintain their crystalline structure. The cross-sections of most of the ion tracks are imaged as parallelopiped or rectangular contrasts as large as 10 nm. These results strongly indicate that the molten region is recrystallized anisotropically, reflecting the lattice structure. Furthermore, low-density track cores are formed in the center of the ion tracks. The formation of low-density track cores can be attributed to the ejection of molten matter toward the surface.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 154, p.108100_1 - 108100_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the design of innovative nuclear reactors such as fast reactors, the improvement of the prediction accuracies for neutronics properties is an important task. The nuclear data adjustment is a promising methodology for this issue. The idea of the nuclear data adjustment was first proposed in 1964. Toward its practical application, however, a great deal of study has been conducted over a long time. While it took about 10 years to establish the theoretical formulation, the research and development for its practical application has been conducted for more than half a century. Researches in this field are still active, and the fact suggests that the improvement of the prediction accuracies is indispensable for the development of new types of nuclear reactors. Massimo Salvatores, who passed away in March 2020, was one of the first proposers to develop the nuclear data adjustment technique, as well as one of the great contributors to its practical application. Reviewing his long-time works in this area is almost the same as reviewing the history of the nuclear data adjustment methodology. The authors intend that this review would suggest what should be done in the future toward the next development in this area. The present review consists of two parts: a) the establishment of the nuclear data adjustment methodology and b) the achievements related to practical applications. Furthermore, the former is divided into two aspects: the study on the nuclear data adjustment theory and the numerical solution for sensitivity coefficient that is requisite for the nuclear data adjustment. The latter is separated to three categories: the use of integral experimental data, the uncertainty quantification and design target accuracy evaluation, and the promotion of nuclear data covariance development.
 nanocubes via precise solvothermal crystal growth and their anomalous surface compositional reconstruction
nanocubes via precise solvothermal crystal growth and their anomalous surface compositional reconstructionNakashima, Koichi*; Onagi, Kaito*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yin, S.*; Kakihana, Masato*; Sekino, Toru*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(14), p.9410 - 9425, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:59.91(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in synthesizing barium titanate nanocubes by hydrothermal synthesis. When the nanocubes were examined in detail using a scanning electron microscope, pulsed neutrons, and large synchrotron radiation, it was found that a reconstituted layer of titanium oxide was formed on the surface.
Oba, Takashi*; Ishikawa, Tetsuo*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Tokonami, Shinji*; Hasegawa, Arifumi*; Suzuki, Gen*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.3639_1 - 3639_11, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:83.61(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Internal doses of residents after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident have been reconstructed. In total 896 behaviour records in the Fukushima Health Management Survey were analysed to estimate thyroid doses via inhalation, using a spatiotemporal radionuclides concentration database constructed by atmospheric dispersion simulations. After a decontamination factor for sheltering and a modifying factor for the dose coefficient were applied, estimated thyroid doses were close to those estimated on the basis of direct thyroid measurement. The median and 95th percentile of thyroid doses of 1-year-old children ranged from 1.2 to 15 mSv and from 7.5 to 30 mSv, respectively.
Sugino, Kazuteru; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 130, p.118 - 123, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In MA sample irradiation test data calculations, the neutron fluence during irradiation period is generally scaled by using dosimetry data in order to improve calculation accuracy. In such a case, appropriate correction is required to burnup sensitivity coefficients obtained by the conventional generalized perturbation theory because some cancellations occur in the burnup sensitivity coefficients. Therefore, a new formula for the burnup sensitivity coefficient has been derived with the consideration of the neutron fluence scaling effect (NFS). In addition, the cross-section-induced uncertainty is evaluated by using the obtained burnup sensitivity coefficients and the covariance data based on the JENDL-4.0.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Maruyama, Shuhei; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
We have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section set ADJ2010 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology, which integrates with the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. The ADJ2017 is based on Japan's latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 as in the previous version of ADJ2010, and it incorporates more information on integral experimental data sets related to minor actinides (MAs) and degraded plutonium (Pu). In the creation of ADJ2010, a total of 643 integral experimental data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and 488 of the integral experimental data sets were finally selected to be used for the cross-section adjustment. In contrast, we have evaluated a total of 719 data sets, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets to create ADJ2017. ADJ2017 shows almost the same performance as ADJ2010 for the main neutronic characteristics of conventional sodium-cooled MOX-fuel fast reactors. In addition, for the neutronic characteristics related to MA and degraded Pu, ADJ2017 improves the C/E values of the integral experimental data sets, and reduces the uncertainty induced by the nuclear data. ADJ2017 is expected to be widely used in the analysis and design research of fast reactors. Moreover, it is expected that the integral experimental data sets used for ADJ2017 can be utilized as a standard database of FBR core design.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:98.06(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 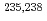 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Palmiotti, G.*; Salvatores, M.*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto
NEA/NSC/R(2016)6 (Internet), 42 Pages, 2017/05
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ikeda, Kazumi*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kan, Taro*; Maruyama, Shuhei; Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Oki, Shigeo
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
Yokoyama, Kenji; Maruyama, Shuhei; Numata, Kazuyuki; Ishikawa, Makoto; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Unifying Theory and Experiments in the 21st Century (PHYSOR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.1906 - 1915, 2016/05
Oizumi, Akito; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kugo, Teruhiko
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 81, p.117 - 124, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)The uncertainty associated with physical quantities, such as nuclear data, needs to be quantitatively analyzed. The present paper illustrates an analysis methodology to investigate the physical mechanisms of burnup actinide composition with nuclear-data sensitivity based on the generalized depletion perturbation theory. The target in this paper is the MOX fuel of the light water reactor. We start with the discussion of the basic physical mechanisms for burnup actinide compositions using the reaction-rate flow chart on the burnup chain. After that, the physical mechanisms of the productions of  Cm and
Cm and  Pu are analyzed in detail with burnup sensitivity calculation. Conclusively, we can identify the source of actinide productions and evaluate the indirect influence of the nuclear reactions if the physical mechanisms of burnup actinide composition are analyzed using the reaction-rate flow chart on the burnup chain and burnup sensitivity calculation. Finally, we demonstrate the usefulness of the burnup sensitivity coefficients in an application to determine the priority of accuracy improvement in nuclear data in combination with the covariance of the nuclear data. In addition, the target actinides and reactions are categorized into patterns according to a sensitivity trend.
Pu are analyzed in detail with burnup sensitivity calculation. Conclusively, we can identify the source of actinide productions and evaluate the indirect influence of the nuclear reactions if the physical mechanisms of burnup actinide composition are analyzed using the reaction-rate flow chart on the burnup chain and burnup sensitivity calculation. Finally, we demonstrate the usefulness of the burnup sensitivity coefficients in an application to determine the priority of accuracy improvement in nuclear data in combination with the covariance of the nuclear data. In addition, the target actinides and reactions are categorized into patterns according to a sensitivity trend.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto
Nuclear Data Sheets, 123, p.97 - 103, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.15(Physics, Nuclear)The current status of covariance applications to fast reactor analysis and design in Japan is summarized. To improve the accuracy of core design values by adopting the integral data such as the critical experiments and the power reactor operation data, the cross-section adjustment based on the Bayesian theorem is used. After the release of JENDL-4.0, a development project of the new adjusted group-constant set ADJ2010 was started and completed in 2013. In the present paper, the final results of ADJ2010 are briefly described. In addition, the adjustment results of ADJ2010 are discussed from the viewpoint of use and impact of nuclear data covariances. For this purpose, three kind of indices, called "degree of mobility", "adjustment motive force", and "adjustment potential", are newly proposed.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 178(3), p.350 - 362, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to provide a reactor physics benchmark problem of burnup reactivity coefficients, experimental data of relationship between excess reactivity and accumulated thermal power acquired during experimental fast reactor JOYO MK-I duty power operation in the late 1970s have been evaluated and analyzed. All possible uncertainty factors were evaluated and quantified by utilizing knowledge obtained after the MK-I duty power operation and calculation results based on the latest reactor physics analysis methods. Meanwhile, the present evaluated data have been registered to the International Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments Project (IRPhEP), with the expectation that this data will be widely used. In the present paper, the evaluation of nominal values and uncertainties is described with a focus on the measurement technique uncertainty which is a dominant uncertainty factor of the burnup reactivity coefficient.
Ishikawa, Makoto; Ikegami, Tetsuo*; Sanda, Toshio*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 178(3), p.335 - 349, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)Under the IRPhEP framework, nine ZPPR critical experimental cores performed as the cooperative JUPITER program between the USA and Japan are established in the benchmarks to study large FBR core physics. These benchmarks cover a wide variety of core concepts including homogeneous and heterogeneous configurations, clean and engineering-mockup cores of 600-1,000 MW(electric)-class sizes, and various kinds of core parameters. Detailed experimental information has recently been dug out from the ANL original documents and scrutinized very carefully to establish the benchmark model and to evaluate the experimental uncertainty quantitatively. The benchmarks supply users with the heterogeneous cell model and three-dimensional core configuration with preserving the important physical features of the ZPPR cores. Further, the benchmark handbook includes the as-built information of the ZPPR cores as a complete set of electrical form, therefore, a user can develop his own benchmark model if necessary. The analysis of the benchmark with the latest method demonstrates the usefulness both for the improvement of analytical methods and for the validation of nuclear data.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Ishikawa, Makoto; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Kugo, Teruhiko
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.405 - 409, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)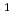 H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 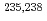 U, and
U, and  Pu
PuChadwick, M. B.*; Dupont, E.*; Bauge, E.*; Blokhin, A.*; Bouland, O.*; Brown, D. A.*; Capote, R.*; Carlson, A. D.*; Danon, Y.*; De Saint Jean, C.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.1 - 25, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:98.48(Physics, Nuclear)CIELO (Collaborative International Evaluated Library Organization) provides a new working paradigm to facilitate evaluated nuclear reaction data advances. It brings together experts from across the international nuclear reaction data community to identify and document discrepancies among existing evaluated data libraries, measured data, and model calculation interpretations, and aims to make progress in reconciling these discrepancies to create more accurate ENDF-formatted files. The focus will initially be on a small number of the highest-priority isotopes, namely  H,
H,  O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 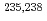 U, and
U, and  Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.
Pu. This paper identifies discrepancies between various evaluations of the highest priority isotopes. The evaluated data for these materials in the existing nuclear data libraries are reviewed, and some integral properties are given. The paper summarizes a program of nuclear science and computational work needed to create the new CIELO nuclear data evaluations.
Kugo, Teruhiko; Ishikawa, Makoto; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Yokoyama, Kenji; Fukaya, Yuji; Maruyama, Hiromi*; Ishii, Yoshihiko*; Fujimura, Koji*; Kondo, Takao*; Minato, Hirokazu*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-046, 53 Pages, 2014/03
The present report summarizes the results of a 2-year cooperative study between JAEA and Hitachi-GE in order to contribute to the settlement of the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants which suffered from the severe accident on March 2011. In the present study, the possible scenarios to reach the recriticality events in Fukushima-Daiichi were investigated first. Then, the analytical methodology to evaluate the time-dependent recriticality events has been developed by modelling the reactivity insertion rate and the possible feedback according to the recriticality scenarios identified in the first step. The methodology developed here has been equipped as a transient simulation tool, PORCAS, which is operated on a multi-purpose platform for reactor analysis, MARBLE. Finally, the radiation exposure rates by the postulated recriticality events in Fukushima-Daiichi were approximately evaluated to estimate the impact to the public environment.
Oizumi, Akito; Jin, Tomoyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kugo, Teruhiko
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-019, 278 Pages, 2014/02
In design work for nuclear fuel cycle plants, decommissioning facilities and light water reactors (LWRs), it has been feasible to quantitatively evaluate the uncertainty of fuel burnup characteristics with identifying error sources arising from the analytical modeling or the related physical property such as nuclear data. Owing to the recent improvement of sensitivity analysis method and enhancement of computer capability, this new evaluation technology would be a promising strategy against the current demand for quality assurance, verification & validation (V&V) and accountability. The present report summarizes nuclear-data sensitivity of atomic number densities after burnup for the LWR fuels of UO and MOX in PWR and BWR. The analysis method is based on the generalized perturbation theory with JENDL-4.0 and a multi-purpose reactor analysis code MARBLE. The present study focuses on 35 fission products and 18 actinides. Sensitivities are calculated with respect to multigroup cross sections, half-lives and fission yields. Electronic files of the sensitivities are stored in a compact disk as a database. Important trends of the sensitivities are presented and their physical mechanisms are discussed. By incorporating the sensitivities with nuclear data covariance and post irradiation examination data, it would be possible to meet the demand for V&V and to break down the uncertainty due to nuclear data into dominant error sources. Thus, the sensitivities can be used to suggest the needs for nuclear data measurements and to extract those for reactor physics experiments in order to make the strategic deliberation of design rationalization.
and MOX in PWR and BWR. The analysis method is based on the generalized perturbation theory with JENDL-4.0 and a multi-purpose reactor analysis code MARBLE. The present study focuses on 35 fission products and 18 actinides. Sensitivities are calculated with respect to multigroup cross sections, half-lives and fission yields. Electronic files of the sensitivities are stored in a compact disk as a database. Important trends of the sensitivities are presented and their physical mechanisms are discussed. By incorporating the sensitivities with nuclear data covariance and post irradiation examination data, it would be possible to meet the demand for V&V and to break down the uncertainty due to nuclear data into dominant error sources. Thus, the sensitivities can be used to suggest the needs for nuclear data measurements and to extract those for reactor physics experiments in order to make the strategic deliberation of design rationalization.
 Cm production in spent fuel of light water reactor by using burnup sensitivity analysis
Cm production in spent fuel of light water reactor by using burnup sensitivity analysisOizumi, Akito; Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kugo, Teruhiko
JAEA-Conf 2013-002, p.59 - 64, 2013/10