Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructuresIeda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The combination of spin-driven thermoelectric (STE) devices based on spin Seebeck effect (SSE), and radioactive isotopes as heat sources, has potential as a next-generation method of power generation in applications such as power supplies for space probes. However, there has been very limited knowledge available indicating the irradiation tolerance of spin thermoelectric devices. Through analysis using a heavy ion-beam accelerator and the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements, we show that a prototypical STE device based on Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to
/Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to 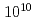 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 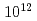 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y
/Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
/Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.49(Physics, Applied)Iwasaki, Yuma*; Sawada, Ryoto*; Stanev, V.*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Omori, Yasutomo*; Someya, Hiroko*; Takeuchi, Ichiro*; Saito, Eiji; Yorozu, Shinichi*
npj Computational Materials (Internet), 5, p.103_1 - 103_6, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:87.87(Chemistry, Physical)Iwasaki, Yuma*; Takeuchi, Ichiro*; Stanev, V.*; Gilad Kusne, A.*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Sawada, Ryoto*; Terashima, Koichi*; Someya, Hiroko*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9, p.2751_1 - 2751_7, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:92.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yagmur, A.*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Ioka, Ikuo; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Ono, Madoka*; Endo, Junichi*; Kashiwagi, Kimiaki*; Nakashima, Tetsuya*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 109(24), p.243902_1 - 243902_4, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.94(Physics, Applied)Thermoelectric devices based on the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) were irradiated with gamma ( ) rays with the total dose of around 3
) rays with the total dose of around 3 10
10 Gy in order to investigate the
Gy in order to investigate the  -radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni
-radiation resistance of the devices. To demonstrate this, Pt/Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O /Glass and Pt/Bi
/Glass and Pt/Bi Y
Y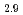 Fe
Fe O
O /Gd
/Gd Ga
Ga O
O SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the
SSE devices were used. We confirmed that the thermoelectric, magnetic, and structural properties of the SSE devices are not affected by the  -ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
-ray irradiation. This result demonstrates that SSE devices are applicable to thermoelectric generation even in high radiation environments.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Hiroto; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Yorozu, Shinichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji*
Proceedings of the IEEE, 104(10), p.1946 - 1973, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:213 Percentile:99.2(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Kirihara, Akihiro*; Kondo, Koichi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ihara, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Yuma*; Someya, Hiroko*; Matsuba, Asuka*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Saito, Eiji; Yamamoto, Naoharu*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.23114_1 - 23114_7, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:90.69(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Heat-flow sensing is expected to be an important technological component of smart thermal management in the future. Conventionally, the thermoelectric (TE) conversion technique, which is based on the Seebeck effect, has been used to measure a heat flow by converting the flow into electric voltage. However, for ubiquitous heat-flow visualization, thin and flexible sensors with extremely low thermal resistance are highly desired. Recently, another type of TE effect, the longitudinal spin Seebeck effect (LSSE), has aroused great interest because the LSSE potentially offers favourable features for TE applications such as simple thin-film device structures. Here we demonstrate an LSSE-based flexible TE sheet that is especially suitable for a heat-flow sensing application. This TE sheet contained a Ni Zn
Zn Fe
Fe O
O film which was formed on a flexible plastic sheet using a spray-coating method known as ferrite plating. The experimental results suggest that the ferrite-plated film, which has a columnar crystal structure aligned perpendicular to the film plane, functions as a unique one-dimensional spin- current conductor suitable for bendable LSSE-based sensors. This newly developed thin TE sheet may be attached to differently shaped heat sources without obstructing an innate heat flux, paving the way to versatile heat-flow measurements and management.
film which was formed on a flexible plastic sheet using a spray-coating method known as ferrite plating. The experimental results suggest that the ferrite-plated film, which has a columnar crystal structure aligned perpendicular to the film plane, functions as a unique one-dimensional spin- current conductor suitable for bendable LSSE-based sensors. This newly developed thin TE sheet may be attached to differently shaped heat sources without obstructing an innate heat flux, paving the way to versatile heat-flow measurements and management.
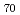 Cu
Cu interlayer
interlayerKikuchi, Daisuke*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Qiu, Z.*; Murakami, T.*; Saito, Eiji
Applied Physics Letters, 106(8), p.082401_1 - 082401_4, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:75.48(Physics, Applied)Uchida, Kenichi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Murakami, Tomoo*; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(34), p.343202_1 - 343202_15, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:203 Percentile:84.49(Physics, Condensed Matter)Kirihara, Akihiro*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Nakamura, Yasunobu*; Manako, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; Yorozu, Shinichi*
Nature Materials, 11(8), p.686 - 689, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:239 Percentile:98.59(Chemistry, Physical)Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi; Harii, Kazuya*; Ono, Masao*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yoshii, Kenji; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
no journal, ,
For development of spintronics applications in nuclear engineering, high energy swift ion irradiations on spin-Seebeck devices are achieved. The Tolerance of spin-Seebeck thermoelectricity of the devices against irradiation by swift heavy ions is tough enough under a harsh environment such as very close to a spent nuclear fuel.
Okayasu, Satoru; Takeyama, Akinori*; Oshima, Takeshi*; Harii, Kazuya*; Ieda, Junichi; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
no journal, ,
We are investigating the applications of spintronics devices in atomic fields. We reported the Tolerance of spin-Seebeck thermoelectricity against heavy swift ion irradiation previously. The tolerance of spin-Seebeck thermoelectricity against gamma ray irradiation will be reported at this conference. The spin thermoelectric properties after gamma ray irradiation up to  1MGy at room temperature and at 150
1MGy at room temperature and at 150 C will be reported.
C will be reported.
Ieda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Takeyama, Akinori*; Harii, Kazuya*; Oshima, Takeshi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
no journal, ,