Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurementsHori, Satoshi*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Kwon, O.*; Kato, Yuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.53(Chemistry, Physical) Fe
Fe GeO
GeO with andalusite structure
with andalusite structureKakimoto, Kazuo*; Takada, Saki*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054704_1 - 054704_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:28(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -xGeO
-xGeO with
with  = 0.09 and 0.15
= 0.09 and 0.15Kakimoto, Kazuo*; Ota, Hiroto*; Haraguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Katori, Hiroko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054707_1 - 054707_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sb
Sb O
O F
F observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffraction
observed by high-resolution synchrotron and neutron diffractionShimono, Seiya*; Ishibashi, Hiroki*; Nagayoshi, Yusuke*; Ikeno, Hidekazu*; Kawaguchi, Shogo*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Ichihashi, Katsuya*; Nishihara, Sadafumi*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 163, p.110568_1 - 110568_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.7(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Barucci, M. A.*; Reess, J.-M.*; Bernardi, P.*; Doressoundiram, A.*; Fornasier, S.*; Le Du, M.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Nakagawa, Hiromu*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Andr , Y.*; et al.
, Y.*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.211_1 - 211_28, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:80.63(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The MMX InfraRed Spectrometer (MIRS) is an imaging spectrometer on board of MMX JAXA mission. MIRS is built at LESIA-Paris Observatory in collaboration with four other French laboratories, collaboration and financial support of CNES and close collaboration with JAXA and MELCO. The instrument is designed to fully accomplish MMX's scientific and measurement objectives. MIRS will remotely provide near-infrared spectral maps of Phobos and Deimos containing compositional diagnostic spectral features that will be used to analyze the surface composition and to support the sampling site selection. MIRS will also study Mars atmosphere, in particular to spatial and temporal changes such as clouds, dust and water vapor.
Arai, Masatoshi*; Andersen, K. H.*; Argyriou, D. N.*; Schweika, W.*; Zanini, L.*; Harjo, S.; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Harada, Masahide
Journal of Neutron Research, 23(4), p.215 - 232, 2021/12
Mori, Kazuhiro*; Okumura, Ryo*; Yoshino, Hirofumi*; Kanayama, Masaya*; Sato, Setsuo*; Oba, Yojiro; Iwase, Kenji*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Hino, Masahiro*; Sano, Tadafumi*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011093_1 - 011093_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na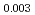 Sn
Sn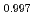 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
 Sr
Sr NiO
NiO studied by neutron diffraction
studied by neutron diffractionKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Fujita, Masaki*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Torii, Shuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Miao, P.*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 88(11), p.114602_1 - 114602_6, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Ito, Naoko*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Takahashi, Yuki*; Onodera, Mitsugi*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Nojima, Tsutomu*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Advanced Quantum Technologies (Internet), 1(3), p.1800057_1 - 1800057_7, 2018/12
Spin-state transition, also known as spin crossover, plays a key role in diverse systems. In theory, the boundary range between the low- and high-spin states is expected to enrich the transition and give rise to unusual physical states. However, no compound that realizes a nearly degenerate critical range as the ground state without requiring special external conditions has yet been experimentally identified. This study reports that the Sc substitution in LaCoO3 destabilizes its nonmagnetic low-spin state and generates an anomalous paramagnetic state accompanied by the enhancement of transport gap and magneto-lattice-expansion as well as the contraction of Co-O distance with the increase of electron site transfer. These phenomena are not well described by the mixture of conventional low- and high-spin states, but by their quantum superposition occurring on the verge of a spin-state transition.
Wu, P.*; Zhang, B.*; Peng, K. L.*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kofu, Maiko; Lee, S. H.*; Kumigashira, Hiroshi*; Hu, C. S.*; Qi, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:45.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering, we have studied how electronic structures and lattice dynamics evolve with temperature in Na-doped SnSe.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.

Li, B.; Luo, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Ren, W. J.*; Yano, S.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Gardner, J. S.*; Liss, K.-D.*; Miao, P.*; Lee, S.-H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(22), p.224405_1 - 224405_6, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:85.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakatani, Takeshi; Seto, Yusuke*; Nagai, Takaya*; Utsumi, Wataru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 780, p.55 - 67, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:99.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)PLANET is a time-of-flight (ToF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. The large six-axis multi-anvil high-pressure press designed for ToF neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell assembly. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (
 /
/
 0.6%) and the accessible
0.6%) and the accessible  -spacing range (0.2-8.4
-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:95.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Xu, P. G.; Tomota, Yo*; Vogel, S. C.*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 33(5), p.389 - 395, 2013/08
 He neutron spin filter in Japan
He neutron spin filter in JapanKira, Hiroshi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Oku, Takayuki; Suzuki, Junichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Arai, Masatoshi; Endo, Yasuo; Chang, L.-J.; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Arimoto, Yasushi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 294, p.012014_1 - 012014_5, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:94.52(Physics, Applied)