Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Sunagawa, Hikaru*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Fujihara, Masayoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.31_1 - 31_6, 2024/12
Shimomura, Koichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Pant, A. D.*; Natori, Hiroaki*; Fujimori, Hiroshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Teshima, Natsuki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012033_1 - 012033_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.21(Physics, Applied)Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t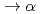 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Torii, Hiroyuki*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; Kanda, Sotaro*; Kawagoe, Kiyotomo*; Kawall, D.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kurosawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Physical Review A, 104(2), p.L020801_1 - L020801_6, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:84.11(Optics) X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:80.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:98.93(Quantum Science & Technology)Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.37(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:90.97(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical); Yamagata, Ichiro; Donomae, Takako; Akasaka, Naoaki
JNC TN9400 2000-046, 24 Pages, 2000/02
lt is well known that solute atoms are segregated on surface, grain boundary, etc. and composition changed partially in irradiated austenitic stainless steel. For understanding radiation induced segregation (RIS), we adopt a Fe-15Cr-20Ni-x (x: Si, Mo) which is basically alloy system in PNC1520, and size of Si, Mo are different from matrix atoms to investigate RIS behaviors. The specimens were irradiated by "Joyo" fast reactor that irradiation condition is 3.5  10
10 n/m
n/m (E>0.1Mev) at 476
(E>0.1Mev) at 476 C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
Mishima, Kaichiro*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Fujine, Shigenori*; Yoneda, Kenji*; Kanda, Keiji*; Nishihara, Hideaki*; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Tsuruno, Akira
Fifth World Conf. on Neutron Radiography, 0, p.140 - 147, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Mishima, Kaichiro*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Fujine, Shigenori*; Yoneda, Kenji*; Kanda, Keiji*; Nishihara, Hideaki*; Tsuruno, Akira; Matsubayashi, Masahito; Sobajima, Makoto
Proc. of 2nd Int. Topical Meeting on Neutron Radiography System Design and Characterization, 0, p.309 - 315, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Hibiki, Takashi*; Mishima, Kaichiro*; Yoneda, Kenji*; Fujine, Shigenori*; Kanda, Keiji*; Nishihara, Hideaki*; Tsuruno, Akira; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 30(6), p.516 - 523, 1993/06
no abstracts in English
*; *; *; Usui, Masahiro*; *; *; Terunuma, Seiichi*
PNC TN9410 89-099, 95 Pages, 1989/05
This report described plant operational management during the 7th annual inspection of Experimental Fast Reactor JOYO from September 1988 to January 1989. One of the important purposes of this inspection is to find a rationality inspection method for LMFBR plants. Therefore, almost inspection items with various modifications and preparation for irradiation were completed for about 3.5 months. This is the shortest record on JOYO. The inspection schedule was very tight and complicated, but it was successfully finished in cooperation with members of operation and maintenance section, by adequate operational management and advanced preparation for inspection. Useful operational management techniques for rationality inspection were obtained, through the experience of 7th annual inspection.
; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TN9410 89-052, 54 Pages, 1989/03
Control rod operation guidance system (named Rod Guider) has been developed for the development of the automatic control rod system in experimental reactor Joyo from 1986. The first step of this development was completed. The four sphere's programs (Critical approach, Power ascent, Power adjustment, Power descent) had already been completed and the system heat-up program, remained last sphere's program, was developed continuously. And, Menu program was completed in order to unite five sphere's programs. During the 16th 100 MW duty cycle operation of Joyo, all programs (five sphere's program) were verified. Rod Guider gave adequate guidances for the operators. The results of these developments are following. (1)The program of system heat-up had a very good control. (2)New functions that give various plant operating guidances to the operators, excepting control rod operating guidance, were good. (3)All sphere's programs had a good contact to the menu program. (4)All sphere's programs (Critical approach, System heat-up, Power ascent, Power adjustment, Power descent) were completed.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion (
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion ( CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed
CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed  CF cycles in the two layers (H
CF cycles in the two layers (H /D
/D and D
and D /T
/T ). The T
). The T concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.