Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamamura, Shuji*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aramaki, Noritaka*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*
Groundwater, 56(1), p.118 - 130, 2018/01
Groundwater saturated with gas forms bubble under atmospheric pressure, bothering most authorized methods to determine in-situ dissolved gas concentrations. To circumvent this problem, a simple theory to quantify effect of 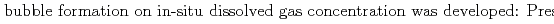 [bar]) of a gas component "
[bar]) of a gas component "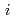 " (e.g., CH
" (e.g., CH , CO
, CO and H
and H ) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (
) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (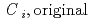 [mol L
[mol L  ]) was related to partial pressure of the
]) was related to partial pressure of the 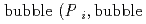 [bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form:
[bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form: 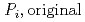 =
= 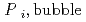 +
+ 
 (k
(k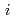 '
' 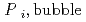 /(
/(
 k
k '
' 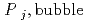 )), where
)), where 
 [bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the
[bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the 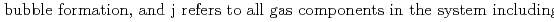 " The k
" The k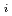 ' and k
' and k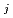 ' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol
' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol ] of
] of 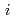 (k
(k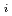 ) and
) and  (k
(k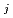 ), respectively, except for k
), respectively, except for k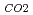 ', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH
', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of
concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of  4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.