Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Urano, Hajime; Fujita, Takaaki*; Ide, Shunsuke; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Matsunaga, Go; Matsukawa, Makoto
Fusion Engineering and Design, 100, p.345 - 356, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)The operation scenarios for plasma breakdown and current ramp-up phases in JT-60SA tokamak have been developed. The induced current in the in-vessel conducting elements such as vacuum vessel and stabilizing plate increases to the comparable level of plasma current of  600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
600 kA during the breakdown phase and thus enhances the strength of error field. The optimized scenarios for half and full pre-magnetization cases satisfied the conditions required for the plasma initiation. At the initial plasma, the vertical magnetic field required to sustain the plasma position was controlled by the outer equilibrium field (EF) coil currents which compensate for a vertical field due to a large eddy current. The condition for the formation of divertor configurations given by the combination of the magnetic flux for plasma and the plasma current enables us to develop the operational scenarios with a smooth transition from a limiter to a divertor configuration.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 53(8), p.083003_1 - 083003_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:79.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dependence of heat transport, edge pedestal and confinement on isotopic composition was investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas. Identical profiles for the electron density, electron temperature, and ion temperature were obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas, whereas the required power clearly increased for hydrogen, which resulted in reduction of heat diffusivity for deuterium. The inverse of the ion-temperature-gradient (ITG) scale length which is required for a given ion heat diffusivity increased by a factor of approximately 1.2 for deuterium compared with that for hydrogen.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 8(Sp.1), p.2405109_1 - 2405109_6, 2013/08
The precise control of the plasma position is a key issue in safe and stable plasma operation. A plasma equilibrium control simulator has been developed in order to study the techniques of plasma equilibrium control for JT-60SA. The simulator consists of an equilibrium solver and controller. The equilibrium solver identifies the plasma equilibrium under the given coil current and unknown eddy current by iteration. The function which calculates the self-consistent 
 with magnetic flux consumption has been incorporated in order to simulate the
with magnetic flux consumption has been incorporated in order to simulate the 
 control. The waveforms of JT-60SA plasma operation scenario during the
control. The waveforms of JT-60SA plasma operation scenario during the 
 ramp-up and the controllability of the plasma equilibrium control using the equilibrium control simulator were reported.
ramp-up and the controllability of the plasma equilibrium control using the equilibrium control simulator were reported.
Ide, Shunsuke; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Bolzonella, T.*; Challis, C. D.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Giruzzi, G.*; Joffrin, E.*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Schneider, M.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Baruzzo, M.*; Bolzonella, T.*; Farina, D.*; Figini, L.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/01
Dependence of heat transport on isotopic composition is investigated in conventional H-mode plasmas for the application to ITER. The identical profiles of 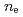 ,
, 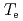 and
and 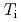 are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total
are obtained for hydrogen and deuterium plasmas while the required power becomes clearly larger for hydrogen, resulting in the reduction of the heat diffusivity for deuterium. The result of the identical temperature profiles in spite of different heating power suggests that the characteristics of heat conduction differs essentially between hydrogen and deuterium even at the same scale length of temperature gradient. On the other hand, the edge stability is improved by increased total 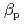 regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 52(11), p.114021_1 - 114021_10, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:65.97(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energy confinement properties for hydrogen and deuterium H-mode plasmas are investigated. The stored energy for deuterium becomes larger approximately by a factor of 1.7-2.0 than that for hydrogen at a given heating power. When the stored energy is fixed for both cases, the required power differs roughly a factor of 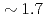 and the identical spatial profiles of electron density
and the identical spatial profiles of electron density 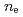 , electron temperature
, electron temperature 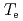 and ion temperature
and ion temperature 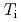 are obtained. Despite almost the same power crossing the separatrix, type-I ELM frequency for hydrogen becomes approximately in double from that for deuterium. The pedestal pressure differs approximately by a factor of
are obtained. Despite almost the same power crossing the separatrix, type-I ELM frequency for hydrogen becomes approximately in double from that for deuterium. The pedestal pressure differs approximately by a factor of 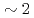 for the cases between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas at a given absorbed power. The relation between
for the cases between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas at a given absorbed power. The relation between 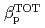 and
and 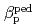 is almost identical regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
is almost identical regardless of the difference of the isotropic composition.
Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 52(10), p.103012_1 - 103012_7, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The unified effect of counter toroidal rotation and heating power on type-I ELMs was investigated in JT-60U tokamak. ELM frequency 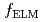 increased monotonically together with the power across the sepratrix
increased monotonically together with the power across the sepratrix 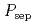 for all the cases of tangential NBs. However, dependence of
for all the cases of tangential NBs. However, dependence of 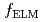 on
on 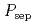 was explicitly stronger than a proportional relation when the perpendicular NBs were injected. The toroidal rotation velocity at the H-mode pedestal
was explicitly stronger than a proportional relation when the perpendicular NBs were injected. The toroidal rotation velocity at the H-mode pedestal 
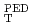 shifted continuously in counter direction when the perpendicular NBs were applied. At fixed values of
shifted continuously in counter direction when the perpendicular NBs were applied. At fixed values of 
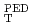 ,
, 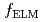 increased clearly in proportion to
increased clearly in proportion to 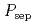 .
.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7, p.1405137_1 - 1405137_9, 2012/10
The plasma position and shape control is important issue in JT-60SA, ITER and future fusion reactor. In order to study the plasma position and shape control, we have developed a simulator which consists of an equilibrium solver and an "isoflux" controller. It is possible to simulate the position and shape control by using the "isoflux" technique and optimize the control logic of coil current in JT-60SA. It was demonstrated that the simulator can simulate the position and shape control in response to prescribed change in the configuration and internal parameters.
Ide, Shunsuke; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shiraishi, Junya; Kurita, Genichi; Fujita, Takaaki
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403131_1 - 2403131_4, 2012/09
no abstracts in English
Urano, Hajime; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Nakano, Tomohide; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 36F, p.P1.016_1 - P1.016_4, 2012/00
Energy confinement properties for hydrogen and deuterium H-mode plasmas were examined in JT-60U. The energy confinement time became larger by a factor of  1.2-1.3 for deuterium than for hydrogen at a given
1.2-1.3 for deuterium than for hydrogen at a given 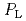 . When the plasma energy was fixed, the profiles of density and temperature became identical for both cases while higher heating power was required for hydrogen. The ion conductive heat flux for hydrogen became approximately two times that for deuterium. Hence, the ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen was higher than for deuterium. It was found that the ion-temperature-gradient scale length became smaller by a factor of
. When the plasma energy was fixed, the profiles of density and temperature became identical for both cases while higher heating power was required for hydrogen. The ion conductive heat flux for hydrogen became approximately two times that for deuterium. Hence, the ion heat diffusivity for hydrogen was higher than for deuterium. It was found that the ion-temperature-gradient scale length became smaller by a factor of  1.2 for deuterium than for hydrogen.
1.2 for deuterium than for hydrogen.
Shiraki, Fumiya*; Yoshikawa, Taeko*; Oshima, Akihiro*; Oshima, Yuji*; Takasawa, Yuya*; Fukutake, Naoyuki*; Oyama, Tomoko*; Urakawa, Tatsuya*; Fujita, Hajime*; Takahashi, Tomohiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(15), p.1777 - 1781, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)The graded energy deposition of heavy ion beam irradiation to polymeric materials was utilized to synthesize a novel proton exchange membrane (PEM) with the graded density of sulfonic acid groups toward the thickness direction. Stacked Poly(tetrafluoroethylene-co-hexafluoropropylene) (FEP) films were irradiated by Xe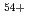 ion beam with the energy of 6 MeV/u under a vacuum condition. Irradiated films were grafted with styrene monomer and then sulfonated. The membrane electrode assembly (MEA) fabricated by the function graded PEM showed improved fuel cell performance in terms of voltage stability. It was expected that the function-graded PEM could control the graded concentration of sulfonic acid groups in PEM.
ion beam with the energy of 6 MeV/u under a vacuum condition. Irradiated films were grafted with styrene monomer and then sulfonated. The membrane electrode assembly (MEA) fabricated by the function graded PEM showed improved fuel cell performance in terms of voltage stability. It was expected that the function-graded PEM could control the graded concentration of sulfonic acid groups in PEM.
Litaudon, X.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Tala, T.*; Angioni, C.*; Benkadda, S.*; Beurskens, M. N. A.*; Bourdelle, C.*; Brix, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073020_1 - 073020_13, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:34.36(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A variety of triggering mechanisms and structures of internal transport barrier (ITB) has been observed in various devices or depending on operation scenarios. Thus identity experiments on ITB in JT-60U and JET have been performed to shed light on the physics behind ITBs. Because of their similar size, the dimensionless parameters between both devices are the same. These experiments were performed with near identical magnetic configurations, heating waveforms and normalized quantities such as safety factor, magnetic shear, normalized Larmor radius, normalized collision frequency, beta, temperatures ratio. Similarities of the ITB triggering mechanism and the ITB strength have been observed when a proper match is achieved of the most relevant profiles of the normalized quantities. This paper will report on the detail comparison of transport properties of ITBs obtained in these JET/JT-60U identity experiments.
Kamada, Yutaka; Barabaschi, P.*; Ishida, Shinichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Lackner, K.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Bolzonella, T.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Matsunaga, Go; Yoshida, Maiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073011_1 - 073011_11, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:92.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Kojima, Atsushi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kamada, Yutaka; Urano, Hajime; Kamiya, Kensaku; Fujita, Takaaki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Aiba, Nobuyuki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 49(11), p.115008_1 - 115008_8, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:61.58(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to understand the physics of the ELM trigger and determining the ELM size, the fast ELM dynamics of type I and grassy ELMs have been studied in JT-60U, using new fast diagnostics with high spatial and temporal resolutions. The evolution of the ion pressure profile in the pedestal region is evaluated for the first time by detailed edge profile measurements. Type I ELMs observed in co-rotating plasmas exhibited larger and wider ELM affected area than ctr-rotating plasmas. Just before type I ELM crash, the pedestal ion pressure and its maximum gradient in co-rotating plasmas are 20% and 12% higher than those in ctr-rotating plasmas, respectively. It is found that the radial extent of the ion pressure gradient at the pedestal region in co-rotating plasmas is 14% wider than that in ctr-rotating plasmas. The experimental results suggest that the ELM size is determined by the structure of the plasma pressure in the whole pedestal region.
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095006_1 - 095006_7, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.5(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)H-modes operated at higher 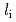 with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The
with the current ramp down have shown higher energy confinement with higher density in JT-60U. The  -factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on
-factor evaluated for the core plasma depends strongly on 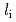 with the relation of
with the relation of 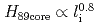 for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high
for the case without sawtooth activities. Center peaked profiles of electron density and electron temperature are obtained in high 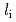 H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high
H-modes. The pedestal pressure is not significantly changed. The enhanced energy confinement in high 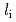 H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high
H-modes is attributed to the core improvement with the peaked profiles of electron density and temperature. The electron heat diffusivity is reduced at the plasma core in high 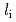 case, resulting in the center peaked
case, resulting in the center peaked 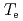 profile while the
profile while the 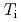 profiles are approximately unchanged.
profiles are approximately unchanged.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Urano, Hajime; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Dependence of the H-mode confinement and pedestal structure on the plasma current is investigated. Higher energy confinement is obtained in higher 
 H-mode. The profiles of the core
H-mode. The profiles of the core 
 and
and 
 are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on
are tends to be peaked. The H-factor for the core plasma depends strongly on 
 . Higher energy confinement obtained at higher
. Higher energy confinement obtained at higher 
 is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both
is attributed to the core confinement improvement. The edge pedestal pressure is not significantly changed by core current density profile. In both 
 ramp and
ramp and 
 scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core
scan experiments, the core energy confinement is improved by the increased core 
 value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
value. The effect of magnetic shear on the confinement should be investigated in next step study.
Urano, Hajime; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Yoshida, Maiko; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 48(8), p.085007_1 - 085007_9, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:35.29(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Relation between heat transport in the plasma core and toroidal rotation profile was examined in conventional ELMy H-mode plasmas in JT-60U. Energy confinement improvement is observed with toroidal rotation which increases in co-direction with respect to the plasma current. Heat transport in the plasma core varies while sustaining self-similar temperature profile in the variation of toroidal rotation profiles. Large increase in heat conduction imposes the resilient profile of ion temperature, under which local effect of toroidal rotation profile on the scale length of ion temperature gradient is very weak. When the pedestal temperature was fixed between the cases of co and counter-NBI by adjusting the plasma density, the identical temperature profiles were obtained in spite of totally different toroidal rotation profiles.
Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(7), p.465 - 467, 2008/07
no abstracts in English