Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
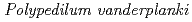
Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Okuda, Takashi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 113, 2008/03
We have shown that anhydrobiotic larvae of 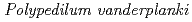 have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
have higher tolerance against both high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation than hydrated larvae. We therefore examined effects of high-LET radiation on four kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae.
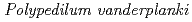 larvae
larvaeWatanabe, Masahiko*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Okuda, Takashi*
Journal of Insect Physiology, 53(6), p.573 - 579, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:65.12(Entomology)We examined effects of high-LET radiation on 4 kinds of larvae: (1) normal hydrated (intact) larva, (2) intermediates between the anhydrobiotic and normal hydrated state, (3) almost completely dehydrated (anhydrobiotic) larvae, and (4) immediately-rehydrated larvae that are assumed to have a similar molecular profile to anhydrobiotic larvae. The intermediates and immediately-rehydrated larvae survived longer after high-LET radiation than intact larvae, indicating that radiation tolerance could be enhanced even in hydrated larvae. Physiological changes toward anhydrobiosis, e.g. accumulation of protectants or increasing damage repair capacity, correlate with improved radiation tolerance in hydrated larvae. In addition, almost complete desiccation further enhanced radiation tolerance, possibly in a different way from the hydrated larvae.
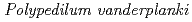
Watanabe, Masahiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Fujita, Akihiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 82(12), p.835 - 842, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.5(Biology)The aim of this study is to characterize the tolerance to high-LET radiations of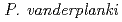 . Larval survival and subsequent metamorphoses were compared between anhydrobiotic (dry) and non-anhydrobiotic (wet) samples after exposure to 1 to 7000 Gy of three types of heavy ions with LET values ranging from 16.2 to 321 keV/
. Larval survival and subsequent metamorphoses were compared between anhydrobiotic (dry) and non-anhydrobiotic (wet) samples after exposure to 1 to 7000 Gy of three types of heavy ions with LET values ranging from 16.2 to 321 keV/ m. At all LET values measured, dry larvae consistently showed greater radiation tolerance than hydrated larvae, due to the disaccharide trehalose in anhydrobiotic animals. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values based on the median inhibitory doses reached a maximum at 116 keV/
m. At all LET values measured, dry larvae consistently showed greater radiation tolerance than hydrated larvae, due to the disaccharide trehalose in anhydrobiotic animals. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values based on the median inhibitory doses reached a maximum at 116 keV/ m (
m ( C). Anhydrobiosis potentiates radiation tolerance in terms of larval survival, pupation and adult emergence of
C). Anhydrobiosis potentiates radiation tolerance in terms of larval survival, pupation and adult emergence of 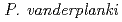 exposed to high-LET radiations.
exposed to high-LET radiations. 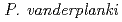 larvae might have more efficient DNA damage repair after radiation than other chironomid species.
larvae might have more efficient DNA damage repair after radiation than other chironomid species.
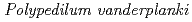 on radiation tolerance
on radiation toleranceWatanabe, Masahiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Fujita, Akihiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 82(8), p.587 - 592, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:90.02(Biology)The present study aims to evaluate effects of anhydrobiosis on radiation tolerance in an anhydrobiotic insect, Polypedilum vanderplanki. Larval survival (48 h), anhydrobiotic ability, metamorphosis and reproduction after exposure to 1 to 9000 Gy of  -rays at the larval stage were comparedbetween anhydrobiotic (dry) and normal (wet) phases. Wet larvae were killed in a dose-dependent manner at doses higher than 2000 Gy, and all died within 8 h after 4000 Gy exposure. In contrast, dry larvae survived even 5000 Gy, and some of them still tolerated 7000 Gy and were alive at 48 h after rehydration. Moreover, greater radiotolerance of dry larva, compared to wet ones, was demonstrated interms of metamorphoses. However, anhydrobiosis did not protect against radiation damage in terms of producing viable offspring. These results indicate that anhydrobiosis enhances radiotolerance, resulting in increases of successful metamorphoses.
-rays at the larval stage were comparedbetween anhydrobiotic (dry) and normal (wet) phases. Wet larvae were killed in a dose-dependent manner at doses higher than 2000 Gy, and all died within 8 h after 4000 Gy exposure. In contrast, dry larvae survived even 5000 Gy, and some of them still tolerated 7000 Gy and were alive at 48 h after rehydration. Moreover, greater radiotolerance of dry larva, compared to wet ones, was demonstrated interms of metamorphoses. However, anhydrobiosis did not protect against radiation damage in terms of producing viable offspring. These results indicate that anhydrobiosis enhances radiotolerance, resulting in increases of successful metamorphoses.
; Miura, Akihiko; ;
JNC TN8410 99-043, 135 Pages, 1999/10
All result of chemical analysis and operators observation suggest non-chemical mechanism raised the filling temperature of the bituminized product at the incident. We, Tokai reprocessing plant safety evaluation and analysis team, performed the experiment using laboratory scale extruder and viscosity measurement to explain the high temperature of mixture. The result of the experiment using laboratory scale extruder showed that the phenomena of salt enrichment and salt accumulation oceured and they raised mixture temperature at the decreased feeed rate. These phenomena depend on the feed rate and they have large contribution of heat transportation and rise of operational torque due to the friction between screw and mixture. Based on the experiment result and all information, we investigated the operation procedure, operational records and machine arrangement to try to explain the behavior of the mixture in the extruder. Judging from each torque and temperature behavior, we succeeded in explaining a sequential behavior in the incident. It is estimated that mixture temperature was raised by physical heat generation in the extruder and this report explains each operation, investigated result and estimated event sequences.
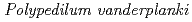
Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Gusev, O.*; Fujita, Akihiko*; Kikawada, Takahiro*; Horikawa, Daiki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Okuda, Takashi*
no journal, ,
The present study aims to evaluate effects of anhydrobiosis on radiation tolerance in an anhydrobiotic insect, 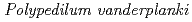 . Wet larvae were killed in a dose-dependent manner at doses higher than 2000 Gy, and all died within 8 h after 4000 Gy exposure. However, anhydrobiosis did not protect against radiation damage in terms of producing viable offspring. These results indicate that anhydrobiosis enhances radiotolerance in larvae, but not in the delayed effects of development.
. Wet larvae were killed in a dose-dependent manner at doses higher than 2000 Gy, and all died within 8 h after 4000 Gy exposure. However, anhydrobiosis did not protect against radiation damage in terms of producing viable offspring. These results indicate that anhydrobiosis enhances radiotolerance in larvae, but not in the delayed effects of development.
Hasegawa, Noboru*; Nishikino, Masaharu*; Mikami, Katsuhiro*; Okada, Hajime*; Kondo, Shuji*; Kawachi, Tetsuya*; Shimada, Yoshinori*; Kurahashi, Shinri*; Kitamura, Toshiyuki*; Kotyaev, O.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Tomoyuki*; Hirota, Akihiko*; Somaki, Takahiro*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Miyazaki, Masashi; Okamura, Shigeki*; Fujita, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Tomoyuki*; Yokoi, Shinobu*; Hirota, Akihiko*; Somaki, Takahiro*; Yukawa, Masaki*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Miyazaki, Masashi; et al.
no journal, ,
The seismic integrity of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) designs in nuclear power plants is of paramount importance. Based on the static loading test, this study investigates the force-displacement relationship and load transference in a three-dimensional seismic isolation system that is envisaged for use in reactor buildings. In SFR designs, the necessity for thin-walled structures to maintain high-temperature structure integrity can unintentionally compromise the seismic design. Consequently, addressing horizontal and vertical seismic forces become vital for ensuring seismic resilience. Currently, there are no specific codes or standards governing the integration of Three-dimensional seismic isolation systems into nuclear reactor buildings. However, current guidelines for the design of horizontal seismic isolation systems emphasize the necessity to clarify the force-displacement relationship and load transfer under conditions of superimposed horizontal and vertical loads. This study involves static loading tests performed on a half-scale specimen, which is subjected to horizontal and vertical loads exceeding the design basis ground motions for the SFR. The findings affirm that the system's horizontal supporting function maintains the segregation of horizontal and vertical load transference, even under seismic loads that exceed the design basis ground motions.