Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nasu, Mitsunori*; Yanai, Hiroshi*; Hirayama, Naoki*; Adachi, Hironori*; Kakizawa, Yu*; Shirase, Yuto*; Nishiyama, Hiromichi*; Kawamoto, Teppei*; Inukai, Junji*; Shinohara, Takenao; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 530, p.231251_1 - 231251_11, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:89.77(Chemistry, Physical)Theis, C.*; Carbonez, P.*; Feldbaumer, E.*; Forkel-Wirth, D.*; Jaegerhofer, L.*; Pangallo, M.*; Perrin, D.*; Urscheler, C.*; Roesler, S.*; Vincke, H.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08018_1 - 08018_5, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)At CERN, gas-filled ionization chambers PTW-34031 (PMI) are commonly used in radiation fields including neutrons, protons and  -rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target
-rays. A response function for each particle is calculated by the radiation transport code FLUKA. To validate a response function to high energy neutrons, benchmark experiments with quasi mono-energetic neutrons have been carried out at RCNP, Osaka University. For neutron irradiation with energies below 200 MeV, very good agreement was found comparing the FLUKA simulations and the measurements. In addition it was found that at proton energies of 250 and 392 MeV, results calculated with neutron sources underestimate the experimental data due to a non-negligible gamma component originating from the target  Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Li(p,n)Be reaction.
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Satoh, Daiki; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.08016_1 - 08016_3, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron energy spectra behind concrete and iron shields were measured for quasi-monoenergetic neutrons above 200 MeV using a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Li(p,xn) reaction with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons. The response function of BSS was also measured at neutron energies from 100 MeV to 387 MeV. In data analysis, the measured response function was used and the multiple neutron scattering effect between the BSS and the shielding material was considered. The neutron energy spectra behind the concrete and iron shields were obtained by the unfolding method using the MAXED code. Ambient dose equivalents were obtained as a function of a shield thickness successfully. For the case of the 244 MeV neutron incidence, the multiple neutron scattering effect on the effective dose is large under 50 cm thickness of the concrete shield.
Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nishiyama, Jun*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 849, p.94 - 101, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Quasi-monoenergetic high-energy neutron fields induced by  Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Li(p,n) reactions are used for the response evaluation of neutron-sensitive devices. The quasi-monoenergetic high-energy field consists of high-energy monoenergetic peak neutrons and unwanted continuum neutrons down to the low-energy region. A two-angle differential method has been developed to compensate for the effect of the continuum neutrons in the response measurements. In this study, the two-angle differential method was demonstrated for Bonner sphere detectors, which are typical examples of moderator-based neutron-sensitive detectors, to investigate the method's applicability and its dependence on detector characteristics. Through this study, the adequacy of the two-angle differential method was experimentally verified, and practical suggestions were made pertaining to this method.
Nishiyama, Jun*; Ohgama, Kazuya; Sakamoto, Tatsujiro*; Watanabe, Rin*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(2), p.123 - 125, 2015/02
, 57(2), p.123 - 125, 2015/02
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Hiroki; Narita, Takahiro; Nishiyama, Koichi; Usami, Hiroki; Sakaki, Hironao; Kasugai, Atsushi; Kojima, Toshiyuki*
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.799 - 802, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Harano, Hideki*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.332 - 336, 2014/04
Recently, many high-energy accelerators are used for various fields. Shielding data for high-energy neutrons are therefore very important from the point of view of radiation protection in high energy accelerator facilities. However, the shielding experimental data for high energy neutrons above 100 MeV are very poor both in quality and in quantity. In this study, neutron penetration spectral fluence and ambient dose through iron and concrete shields were measured with a Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS). Quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were produced by the  Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.
Li(p,xn) reaction by bombarding a 1-cm thick Li target with 246-MeV and 389-MeV protons in the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of the Osaka University. Shielding materials are iron blocks with a thickness from 10 cm to 100 cm and concrete blocks with a thickness from 25 cm to 300 cm.
Masuda, Akihiko*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nakamura, Takashi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 59(1), p.161 - 166, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.54(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, responses of Bonner sphere spectrometer (BSS) for 245 and 388 MeV neutrons was measured at RCNP, Osaka University. The neutrons are generated in the  Li(p,n) reaction and its spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy. Therefore, the observed counts of BSS caused by the continuum need to be subtracted. Adjusting a Li target angle and a collimator position, 0 deg and 30 deg component of generated neutron are available. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 30 deg component is considered to contain only the continuum. Therefore, the response of the peak is obtained. The spectra were measured using the time-of-flight (TOF) method with a NE213 scintillator.
Li(p,n) reaction and its spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy. Therefore, the observed counts of BSS caused by the continuum need to be subtracted. Adjusting a Li target angle and a collimator position, 0 deg and 30 deg component of generated neutron are available. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 30 deg component is considered to contain only the continuum. Therefore, the response of the peak is obtained. The spectra were measured using the time-of-flight (TOF) method with a NE213 scintillator.
 Li(p,n) reactions at 246-389 MeV
Li(p,n) reactions at 246-389 MeVIwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
Proceedings of 10th Meeting of the Task Force on Shielding Aspects of Accelerators, Targets and Irradiation Facilities (SATIF-10), p.53 - 61, 2011/03
The neutron energy spectra penetrating 10 to 100 cm thick iron and 25 to 200 cm thick concrete shields have been measured using 138, 243 and 387 MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutron sources at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) facility, Osaka University. The source neutrons were produced from a 1 cm thick lithium target bombarded with 140, 245 and 388 MeV protons. Two types of NE213 liquid organic scintillators and Bonner ball neutron spectrometers were used for the neutron energy spectrum measurement. The TOF and unfolding methods were applied to estimate the energy spectra behind the shield in the peak energy region and continuous energy region, respectively. We have also measured the neutron energy spectra and angular distribution of the source neutron above 1 MeV in the angular range from 0 to 30
to 30 with the TOF method. All measured data were compared with the PHITS Monte Carlo calculations.
with the TOF method. All measured data were compared with the PHITS Monte Carlo calculations.
 Li(p,n) reactions at angles from 0
Li(p,n) reactions at angles from 0 to 30
to 30
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 629(1), p.43 - 49, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:82.72(Instruments & Instrumentation)The authors measured the neutron energy spectra of a quasi-monoenergetic  Li(p,n) neutron source with 246 and 389 MeV protons set at seven angles (0
Li(p,n) neutron source with 246 and 389 MeV protons set at seven angles (0 , 2.5
, 2.5 , 5
, 5 , 10
, 10 , 15
, 15 , 20
, 20 and 30
and 30 ), using a time-of-flight (TOF) method employing organic scintillators NE213 at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. The energy spectra of the source neutrons were precisely deduced down to 2 MeV at 0
), using a time-of-flight (TOF) method employing organic scintillators NE213 at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP) of Osaka University. The energy spectra of the source neutrons were precisely deduced down to 2 MeV at 0 and 10 MeV at other angles. The cross sections of the peak neutron production reaction at 0
and 10 MeV at other angles. The cross sections of the peak neutron production reaction at 0 were on the 35-40 mb line of other experimental data, and the peak neutron angular distribution agreed well with the Taddeucci formula. Neutron energy spectra below 100 MeV at all angles were comparable, but the shapes of the continuum above 150 MeV changed considerably with the angle.
were on the 35-40 mb line of other experimental data, and the peak neutron angular distribution agreed well with the Taddeucci formula. Neutron energy spectra below 100 MeV at all angles were comparable, but the shapes of the continuum above 150 MeV changed considerably with the angle.
 and
and 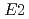 cross sections of the
cross sections of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at
O reaction at 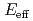
 1.2 MeV using pulsed
1.2 MeV using pulsed  beams
beamsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Nagai, Yasuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Fujimoto, Shinya*; Segawa, Mariko; Mishima, Kenji*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Igashira, Masayuki*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1269, p.283 - 288, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of
O reaction cross section plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of 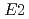 cross section to
cross section to  one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed
one. Hence, we have installed new system to make a precise measurement of the cross section. In this experiment, we used the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers with a large S/N ratio, an intense pulsed  beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the
beams, and the monitoring system of target thickness. With use of the system we succeeded in removing a background due to neutron and could clearly detect the  -ray from the
-ray from the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction with high statistics. We determined the
O reaction with high statistics. We determined the  and
and 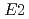 cross section down to
cross section down to 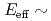 1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
1.2 MeV, and thus obtained results are compared to recent theoretical calculations.
 Ge spectrometer for neutron capture cross section measurements
Ge spectrometer for neutron capture cross section measurementsOshima, Masumi; Hori, Junichi*; Harada, Hideo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Igashira, Masayuki; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology (ND 2007), Vol.1, p.603 - 606, 2008/05
Neutron capture cross sections of minor actinides and long-lived fission products are important for the R&D of innovative nuclear reactors. However, those data are rather poor both in quality and in quantity at present. Thus, we have started projects for neutron cross section measurements. We will construct an innovative  -ray spectrometer consisting of Ge crystals and BGO shields. The neutron cross section measurements will be done at KUR linac and JAEA JRR-3M facilities, which will be extended at the high-intensity neutron source at J-PARC.
-ray spectrometer consisting of Ge crystals and BGO shields. The neutron cross section measurements will be done at KUR linac and JAEA JRR-3M facilities, which will be extended at the high-intensity neutron source at J-PARC.
 Np neutron capture cross section
Np neutron capture cross sectionMizumoto, Motoharu; Oshima, Masumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Nakamura, Shoji; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron capture cross section measurements of minor actinide nuclei have been carried out using a 4  Ge spectrometer. In the meeting, preliminary results of
Ge spectrometer. In the meeting, preliminary results of  Np capture cross sections measured at the KUR electron linac TOF facility are reported.
Np capture cross sections measured at the KUR electron linac TOF facility are reported.
 -ray spectroscopies on TOF experiments
-ray spectroscopies on TOF experimentsKimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Toh, Yosuke; Hori, Junichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Nishiyama, Jun*; Oshima, Masumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Segawa, Mariko; Nagai, Yasuki*; Masaki, Tomohiro*; Temma, Yasuyuki*; Shima, Tatsushi*; Makii, Hiroyuki*; Mishima, Kenji*; Ueda, Hitoshi*; Nakayoshi, Akira*; Ota, Takeshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
 Re-
Re- Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of
Os pair is known as the most promising nuclear cosmochronometer with considerable potential. However, there remains non-trivial problems related to an excited neutron capture reaction of  Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,
Os at a stellar temperature. Firstly,  Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of
Os is produced and depleted by the slow process nucleosynthesis. Hence, it is necessary to obtain both the production and depletion rates of  Os. Secondly,
Os. Secondly,  Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of
Os is depleted not only by its ground state neutron capture reaction but also by an excited state neutron capture reaction of  Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for
Os in a stellar temperature. In the present study, we have measured the neutron capture reaction cross sections for  Os,
Os,  Os and
Os and  Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for
Os accurately and neutron inelastic scattering reaction cross section for  Os off the ground state of
Os off the ground state of  Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt
Os to its 9.75-keV first excited statein the neutron energy range from 10 to 100 keV. The measurements of the neutron capture reactions have been carried out by detecting a prompt  -ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for
-ray by means fan anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometer. The (n, n') reaction cross section for  Os has been measured with use of four
Os has been measured with use of four  Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in
Li-glass scintillation detectors. Based on these new capture cross sections, we reestimate on the basis of a careful reaction cross section calculation the correction factor F for the neutron capture on the 9.75-keV first excited state in  Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
Os as a function of stellar temperature, as required to derive the age of the galaxy within the Re-Os chronology.
 Li(p,n) reactions in the 245 and 388 MeV
Li(p,n) reactions in the 245 and 388 MeVIwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Itoga, Toshiro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sakamoto, Yukio; et al.
no journal, ,
We have measured mono-energetic neutron energy spectra for the  Li(p,n) reaction in the energy region above 2 MeV using the time-of-flight method at RCNP, Osaka University. Neutron detector were NE213 organic liquid scintillators (5.08 cm, 12.7 cm, and 25.4 cm diameter and thickness). Detection angles were 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 degrees. As spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy, the observed data caused by the continuum was subtracted to obtain the peak neutron cross sections. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 10-30 deg component is considered to contain mainly the continuum. The angular distribution of the peak neutron cross section agreed with the Taddeucci formula.
Li(p,n) reaction in the energy region above 2 MeV using the time-of-flight method at RCNP, Osaka University. Neutron detector were NE213 organic liquid scintillators (5.08 cm, 12.7 cm, and 25.4 cm diameter and thickness). Detection angles were 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 degrees. As spectra consist of a high-energy peak and a continuum down to the low energy, the observed data caused by the continuum was subtracted to obtain the peak neutron cross sections. While the 0 deg component contains both the peak and the continuum, the 10-30 deg component is considered to contain mainly the continuum. The angular distribution of the peak neutron cross section agreed with the Taddeucci formula.
Mares, V.*; Pioch, C.*; R hm, W.*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
hm, W.*; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Satoh, Daiki; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Masuda, Akihiko*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Measurements of neutron spectra and neutron doses were performed in high-energy neutron fields at the Research Center for Nuclear Physics (RCNP), Osaka University, Japan, using two extended Bonner Sphere Spectrometers (BSS), a WENDI-II REM meter, a DARWIN dosimeter, an extended FUJI REM counter, and the time-of-flight (TOF) method employing NE213 liquid organic scintillators. The quasi-mono-energetic neutron fields were generated by the  Li(p,n)
Li(p,n) Be reaction from a Li target, injected by 246 and 389 MeV protons. The BSS and TOF neutron energy spectra were folded with H*(10) fluence-to-dose conversion coefficients and the resulting values for the neutron ambient dose equivalent were compared with those directly measured by various other instruments used in this experiment. Agreement among all H*(10) neutron doses was very reasonable considering the complexity of the experiment.
Be reaction from a Li target, injected by 246 and 389 MeV protons. The BSS and TOF neutron energy spectra were folded with H*(10) fluence-to-dose conversion coefficients and the resulting values for the neutron ambient dose equivalent were compared with those directly measured by various other instruments used in this experiment. Agreement among all H*(10) neutron doses was very reasonable considering the complexity of the experiment.