Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:90.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Murase, Kiyoka*; Kataoka, Ryuho*; Nishiyama, Takanori*; Nishimura, Koji*; Hashimoto, Taishi*; Tanaka, Yoshimasa*; Kadokura, Akira*; Tomikawa, Yoshihiro*; Tsutsumi, Masaki*; Ogawa, Yasunobu*; et al.
Journal of Space Weather and Space Climate (Internet), 12, p.18_1 - 18_16, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We identified two energetic electron precipitation (EEP) events during the growth phase of moderate substorms and estimated the mesospheric ionization rate for an EEP event for which the most comprehensive dataset from ground-based and space-born instruments was available. The mesospheric ionization signature reached below 70 km altitude and continued for ~15 min until the substorm onset, as observed by the PANSY radar and imaging riometer at Syowa Station in the Antarctic region. We also used energetic electron flux observed by the Arase and POES 15 satellites as the input for the air-shower simulation code PHITS to quantitatively estimate the mesospheric ionization rate. Combining the cutting-edge observations and simulations, we shed new light on the space weather impact of the EEP events during geomagnetically quiet times, which is important to understand the possible link between the space environment and climate.
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Aizawa, Kosuke; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu
JAEA-Research 2021-009, 29 Pages, 2021/11
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, high burnup of fuel is required for practical use. It is important to predict and evaluate the flow behavior in a fuel assembly because there is a concern that the heat removal capacity of the fuel assembly with high burnup will be locally reduced due to swirling and thermal deformation of the fuel rods. In this study, flow field measurement tests were conducted using a 3-pin bundle system test specimen for the purpose of elucidating the phenomenon and constructing a verification database for thermal hydraulics analysis code. The viewpoints of the experiment for elucidating the phenomenon are as follows; (1) Overall flow behavior in the subchannel including near the wrapping wire, (2) Relationship between Reynolds number including laminar flow region and flow field, and (3) Evaluation of the effect of the presence or absence of wrapping wire on the flow field. As a result, detailed flow field data in the subchannel was obtained by PIV measurement. It was found that when the wrapping wire crossed the subchannel, the flow occurred toward adjacent subchannel and the flow occurred that follows the winding direction of the wrapping wire. It was confirmed that the tendency of the flow velocity distribution of the Reynolds number in the laminar flow region is significantly different from that of the transition region and the turbulent region under the condition. The test was conducted using a same 3-pin bundle system without the wrapping wire, and it was confirmed that mixing by the wrapping wire occurred even in the laminar flow region.
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 170, p.112712_1 - 112712_4, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muonic molecule which consists of two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) and a muon decays immediately via nuclear fusion and the muon will be released as a recycling muon, and start to find another hydrogen isotope nucleus. The reaction cycle continues until the muon ends up its lifetime of 2.2  s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion (
s. Since the muon does not participate in the nuclear reaction, the reaction is so called a muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after
CF). The recycling muon has a particular kinetic energy (KE) of the muon molecular orbital when the nuclear reaction occurs. Since the KE is based on the unified atom limit where distance between two nuclei is zero. A precise few-body calculation estimating KE distribution (KED) is also in progress, which could be compared with the experimental results. In the present work, we observed recycling muons after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 169, p.112580_1 - 112580_5, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:44.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion between deuteron (d) and triton (t). These two nuclei are bound by  and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt
and form a muonic hydrogen molecular ion, dt . Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt
. Due to the short inter-nuclear distance of dt , the nuclear fusion, d +t
, the nuclear fusion, d +t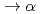 + n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion (
+ n + 17.6 MeV, occurs inside the molecule. This reaction is called muon catalyzed fusion ( CF). Recently, the interest on
CF). Recently, the interest on  CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of
CF is renewed from the viewpoint of applications, such as a source of high-resolution muon beam and mono-energetic neutron beam. In this work, we report a time evolution calculation of  CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
CF in a two-layered hydrogen isotope target.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ishida, Katsuji*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(4), p.20-00547_1 - 20-00547_11, 2021/08
A sodium-cooled fast reactor has been designed to attain a high burn-up core in commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. The sodium-cooled fast reactor adopts a wire spacer between fuel pins. The wire spacer performs functions of securing the coolant channel and the mixing between subchannels. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, the fuel pin deformation due to swelling and thermal bowing may decrease the local flow velocity in the subassembly and influence the heat removal capability. Therefore, understanding the flow field in a wire-wrapped pin bundle is important. This study performed particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements using a wire-wrapped three-pin bundle water model to grasp the flow field in the subchannel under conditions, including the laminar to turbulent regions. In the region away from the wrapping wire, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the Re number. Accordingly, the PIV measurements using the three-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were also conducted to understand the effect of the wrapping wires on the flow field in the subchannel. The results confirmed that the mixing due to the wrapping wire occurred, even in the laminar condition. These experimental results are useful not only for understanding the pin bundle thermal hydraulics, but also for the code validation.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ishida, Katsuji*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is designed to attain a high burn-up core in commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, the deformation of fuel pin due to the swelling and thermal bowing may decrease local flow velocity in the subassembly and influence the heat removal capability. Therefore, it is important to obtain the flow velocity distribution in a wire wrapped pin bundle. In this study, the detailed flow velocity distribution in the subchannel has been obtained by PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) measurement using a wire-wrapped 3-pin bundle water model. Flow velocity conditions in the pin bundle were set from 0.036 m/s (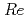 = 270) to 1.6m/s (
= 270) to 1.6m/s (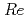 = 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the
= 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the 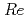 number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:55.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Naruto, Kenichi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1178 - 1189, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fuel subassemblies (FSAs) of fast breeder reactors (FBRs) are densely arranged and have high power densities. Therefore, PRA on LF which was initiated from LB was performed reflecting the state-of-the-art knowledge in this study. As the result, damage propagation from LF caused by LB in Monju can be negligible compared with the core damage due to ATWS or PLOHS in the viewpoint of both frequency and consequence.
Nishimura, Akihiko; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furusawa, Akinori; Torimoto, Kazuhiro; Ueda, Masashi; Fukuda, Naoaki*; Hirao, Kazuyuki*
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance (Internet), 9(2), p.52 - 59, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Fumiaki; Imaizumi, Yuya; Nishimura, Masahiro; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Arikawa, Mitsuhiro*
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/07
The loss-of-reactor-level (LORL) is one of the loss-of-heat-removal-system (LOHRS) of beyond-DBA (BDBA) severe accident. An evaluation method for the LORL which is caused by the coolant leakage in two positions of the primary heat transport system (PHTS) was developed for prototype JSFR which is loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor. The secondary leakage in cold standby which occurred in different loop from that of the first leakage in rated power operation can lead LORL by excessive declining of the sodium level. Therefore, the sodium level behavior in RV was studied in a representative accident sequence by considering the sodium pumping up into RV, siphon-breaking to stop pumping out from RV and maintain the sodium level, and calculation programs for the transient sodium level in RV. The representative sequence with lowest sodium level was selected by considering combinations of possible leakage positions. As a result of the evaluation considering the countermeasures above, it was revealed that the LOHRS can be prevented by maintaining the sodium level for the operation of decay heat removal system, even in the leakages in two positions of PHTS which corresponds to BDBA.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Fukano, Yoshitaka; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Naruto, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 13th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-13) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2016/10
Fuel subassemblies of fast breeder reactors (FBRs) are densely arranged and have high power densities. Therefore, the local fault (LF) has been considered as one of the possible initiating events of severe accidents. According to the LF evaluation under the condition of total flow blockage of one sub-channel in the analyses of design basis accident (DBA) for Monju, it was confirmed that the pin failures were limited locally without severe core damage. In addition, local flow blockage (LB) of 66% central planar in the subassembly was investigated as one of the beyond-DBA. However, it became clear that these deterministic analyses were not based on a realistic assumption by experimental studies. Therefore, PRA on LF which was initiated from LB was performed reflecting the state-of-the-art knowledge in this study. As the result, damage propagation from LF caused by LB in Monju can be included in CDF of ATWS or PLOHS in the viewpoint of both probability and consequence.
Fukano, Yoshitaka; Naruto, Kenichi*; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Nishimura, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(9), p.1122 - 1132, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental studies, deterministic approaches, and probabilistic risk assessments (PRAs) on local fault (LF) propagation in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) have been performed in many countries because LFs have been historically considered as one of the possible causes of severe accidents. Adventitious-fuel-pin-failures (AFPFs) have been considered to be the most dominant initiators of LFs in these PRAs because of their high frequency of occurrence during reactor operation and possibility of fuel-element-failure-propagation (FEFP). A PRA on FEFP from AFPF (FEFPA) in the Japanese prototype SFR (Monju) was performed in this study based on the state-of-the-art knowledge, reflecting the most recent operation procedures under off-normal conditions. Frequency of occurrence of AFPF in SFRs which was the initiating event of the event tree in this PRA was updated using a variety of methods based on the above-mentioned latest review on experiences of this phenomenon. As a result, the frequency of occurrence of, and the core damage frequency (CDF) from AFPF in Monju was significantly reduced to a negligible magnitude compared with those in the existing PRAs. It was therefore concluded that the CDF of FEFPA in Monju could be comprised in that of anticipated-transient-without-scram or protected-loss-of-heat-sink events from both the viewpoint of occurrence probability and consequences.
Kikuchi, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Imai, Yasutomo*; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Ibaraki Koenkai 2015 Koen Rombunshu, p.179 - 180, 2015/08
In an economically improved sodium-cooled fast reactor, a narrower gap is considered among the fuel pins so as to achieve a high burn-up. Therefore, it is needed to evaluate thermal-hydraulic characteristics in case of a change of the gap geometry due to deformation of fuel pin caused by such as a swelling and a thermal bowing. For this purpose, a FEM analysis code, SPIRAL has been being developed in JAEA and the code validations using water or sodium experimental results have also being performed. In this study, a numerical analysis of a flow field around wire-wrapped fuel pins based on a 3-pin bundle water experiment was carried out as a validation study of SPIRAL. As a result, it was demonstrated that the hybrid-type turbulent model incorporated in SPIRAL has a high applicability to investigate the flow structure of the narrow gap in the fuel assembly.
Fukano, Yoshitaka; Nishimura, Masahiro; Yamada, Fumiaki
Proceedings of 16th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-16) (USB Flash Drive), p.5687 - 5698, 2015/08
The following safety criteria for anticipated operational occurrences are commonly and uniformly employed for all the DBAs in the Japanese prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor to prevent fuel melting and cladding failure:(a) Maximum fuel temperature shall be below the melting point,(b) Maximum cladding temperature shall be below 830 C, and (c) Maximum coolant temperature shall be below the boiling point. Cladding failure is allowed, on the contrary to that, in beyond DBAs (BDBAs) or severe accidents (SAs), whereas the core cooling capability is also needed to be secured as in DBAs. No fuel melting enables this by keeping the core in a coolable geometry, and is thus conservatively required even under such a condition. Protected loss-of-heat-sink (PLOHS) events are identified as one of the most dominant sequences. Safety margins for significant core damage in PLOHS events were therefore studied in this paper assuming fuel cladding failure. The following three possible mechanisms leading to degradation of the core were then identified to be scrutinized by a thorough and state-of-the-art review of open papers on the phenomena anticipated to occur under cladding failure conditions:(1) Fuel melting due to fuel-sodium reaction product (FSRP) formation, (2) Thermal transient due to FP gas impingement from adjacent failed fuel pins, and (3) Mechanical load due to the same FP gas impingement. It was clarified through simulation analyses on each phenomenon mentioned above using the FUCA code that there was no significant core damage at the coolant temperatures of up to 950
C, and (c) Maximum coolant temperature shall be below the boiling point. Cladding failure is allowed, on the contrary to that, in beyond DBAs (BDBAs) or severe accidents (SAs), whereas the core cooling capability is also needed to be secured as in DBAs. No fuel melting enables this by keeping the core in a coolable geometry, and is thus conservatively required even under such a condition. Protected loss-of-heat-sink (PLOHS) events are identified as one of the most dominant sequences. Safety margins for significant core damage in PLOHS events were therefore studied in this paper assuming fuel cladding failure. The following three possible mechanisms leading to degradation of the core were then identified to be scrutinized by a thorough and state-of-the-art review of open papers on the phenomena anticipated to occur under cladding failure conditions:(1) Fuel melting due to fuel-sodium reaction product (FSRP) formation, (2) Thermal transient due to FP gas impingement from adjacent failed fuel pins, and (3) Mechanical load due to the same FP gas impingement. It was clarified through simulation analyses on each phenomenon mentioned above using the FUCA code that there was no significant core damage at the coolant temperatures of up to 950 C. It was therefore concluded that large safety margins are provided during PLOHS events even in failure of fuel cladding.
C. It was therefore concluded that large safety margins are provided during PLOHS events even in failure of fuel cladding.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Fukano, Yoshitaka
Proceedings of 10th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2014/12
Deterministic evaluation of localflow blockage (LB) on the basis of state-of-the-art knowledge was performed using ASFRE code. In order to evaluate the effect of the realistic accidental condition, nominal power and flow rate were used for the analyses. Moreover the realistic blockage feature in the subassembly was newly adopted on the basis of existing experimental data which means LB in hound's-tooth pattern at a cross-section was assumed for the fuel subassemblies of wire spacer type. As the result, it was founds that the temperature increase in the downstream of LB was smaller than that in the past safety licensing because the flow pass is available around the blockage. And it was concluded that LB never lead to the large core damage from the evaluation results even if the blockage conditions beyond design criteria are assumed.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Imai, Yasutomo*
Proceedings of 9th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-9) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/11
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Nishimura, Akihiko; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo; Sugiyama, Akira; Chiyatani, Keiji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.944 - 950, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:91.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, it is necessary to survey the locations and conditions of fuel debris inside reactor pressure vessels or primary containment vessels under water and radiation environment in preparation for removing fuel debris. An optical fiber is well known for features such as signal transmission, light weight, superior insulation performance, water resistance and electromagnetic noise resistance. These features allow the optical fiber to simplify the instrumentation systems for in-vessel inspection, as long as provide that the optical fiber can be used under high radiation dose environment. The radiation resistance of an optical fiber was improved by increasing the amount of hydroxyl up to 1000 ppm in pure silica fiber. The improved optical fibers were irradiated with  -ray up to 1
-ray up to 1  10
10 Gy using a
Gy using a  Co source. They indicated a large peak around 600 nm and a peak tail from ultraviolet region, but no large absorption in infrared region except a hydroxyl absorption peak of 945 nm. We have confirmed that the optical fiber containing 1000 ppm hydroxyl has enough radiation resistance for radiation induced transmission losses and the infrared imaging is effective for observation under high radiation doses.
Co source. They indicated a large peak around 600 nm and a peak tail from ultraviolet region, but no large absorption in infrared region except a hydroxyl absorption peak of 945 nm. We have confirmed that the optical fiber containing 1000 ppm hydroxyl has enough radiation resistance for radiation induced transmission losses and the infrared imaging is effective for observation under high radiation doses.
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Ito, Keisuke; Ishikawa, Takashi; Nishimura, Akihiko; Wakaida, Ikuo; Sekine, Takashi
Proceedings of 22nd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-22) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The radiation resistance of an optical fiber was improved by increasing the amount of hydroxyl up to 1000 ppm in pure silica fiber. The improved image fiber consists of common cladding and a large number of fiber cores made from pure silica that contains 1000 ppm hydroxyl. The transmissive rate of an infrared image was not affected after the irradiation of 1 MGy. We have developed the fiber-coupled LIBS system to detect plasma emission efficiently in near-infrared region. In addition, we have performed a  ray dose rate measurement using an optical fiber of which scintillator is attached to the tip. As a result, the concept of applicability of a probing system using the high-radiation resistant optical fibers has been confirmed.
ray dose rate measurement using an optical fiber of which scintillator is attached to the tip. As a result, the concept of applicability of a probing system using the high-radiation resistant optical fibers has been confirmed.
Fukano, Yoshitaka; Naruto, Kenichi*; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Nishimura, Masahiro
Proceedings of 12th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (PSAM-12) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2014/06
Experimental studies, deterministic and probabilistic and risk assessments (PRAs) on local fault (LF) propagation in sodium cooled fast reactors (SFRs) have been performed in many countries because LFs have been historically considered as one of the possible causes of severe accidents. Adventitious fuel pin failures were considered to be the most dominant initiators of LFs in these PRAs because of high frequency of occurrence during reactor operation and possibility of subsequent pin-to-pin failure propagation. Therefore event tree analysis (ETA) on fuel element failure propagation initiated from adventitious fuel pin failure (FEFPA) in Monju was performed in this study based on state-of-the-art knowledge on experimental and analytical studies on FEFPA and reflecting latest operation procedure at emergency in Monju. Probability of adventitious fuel pin failures in SFRs which is the initiating event of this ETA was also updated in this study. It was clarified that FEFPA in Monju was negligible and could be included in core damage fraction of the anticipated transient without scram and protected loss of heat sink in the viewpoint of both probability and consequence.