Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sihver, L.*; Kohama, Akihisa*; Iida, Kei*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 334, p.34 - 39, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:85.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Accurate calculations of the nucleon + nucleus and nucleus + nucleus total reaction cross sections are of great importance for designing accelerator facilities and estimating dose in particle therapy with particle and heavy ion transport calculations, because the probability of nuclear reactions in the calculations depends on the cross sections. The Kurotama model assumes a target nucleus to be Black Sphere (BS), and gives the total reaction cross sections systematically using its radius determined from proton-nucleus elastic scattering data. However, the BS model breaks down below around 100 MeV/u. In this study, we developed the "hybrid Kurotama" model by connecting the BS model to the semi-empirical model of Tripathi et al. at low energies. The model has been tested against available p + He, p + nucleus, and nucleus + nucleus data and an overall better agreement has been found than for earlier published models. This model is suitable to be used in particle transport calculations.
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
Physical Review C, 82(2), p.027301_1 - 027301_4, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:78.37(Physics, Nuclear)We investigate how the neutron drip line is related to the density dependence of the symmetry energy, by using a macroscopic nuclear model that allows us to calculate nuclear masses in a way dependent on the equation of state of asymmetric nuclear matter. The neutron drip line obtained from these masses is shown to appreciably shift to a neutron-rich side in a nuclear chart as the density derivative of the symmetry energy increases. Such shift is clearly seen for light nuclei, a feature coming mainly from the surface property of neutron-rich nuclei.
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
Aichi Shukutoku Daigaku Gendai Shakai Kenkyuka Kenkyu Hokoku, (3), p.1 - 10, 2008/06
Liquid drop model is a representative model to describe binding energy and size of nuclei. This model is conventional and well reproduces bulk properties of nuclei even in current studies on nuclei. Nowadays structure of neutron-rich nuclei is paid attention to not only in nuclear physics but also in astrophysics because these nuclei play a quite important role to solve a problem of origin of elements in universe. In this paper, we investigate nuclear symmetry energy and nuclear surface energy by using the nuclear liquid drop model with some higher-order terms. The coefficients of these term are determined so as to reproduce measured nuclear masses of approximately 2200 nuclides. From this analysis, we find an indication that the fourth-order term of the symmetry energy is required and the curvature term of it is negligible. Regarding a mass-number dependency on nuclear radius, we also find that the dependency of lighter nuclei (typically with mass number, A, less than 50) is larger than that of heavier nuclei.
Yoshida, Tadashi*; Okajima, Shigeaki; Sakurai, Takeshi; Nakajima, Ken; Yamane, Tsuyoshi; Katakura, Junichi; Tahara, Yoshihisa*; Zukeran, Atsushi*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Osawa, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.136 - 139, 2002/08
no abstracts in English
Katakura, Junichi; Yoshida, Tadashi*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Tachibana, Takahiro*
JAERI 1343, 79 Pages, 2001/07
no abstracts in English
 - and
- and  -ray spectra for JENDL FP decay data file
-ray spectra for JENDL FP decay data fileKatakura, Junichi; Yoshida, Tadashi*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Tachibana, Takahiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(7), p.470 - 476, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 -ray bursts
-ray burstsMao, G.; Chiba, Satoshi; Greiner, W.*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*
International Journal of Modern Physics E, 9(2), p.185 - 192, 2000/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 -ray bursts
-ray burstsMao, G.; Chiba, Satoshi; Greiner, W.*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*
JAERI-Research 99-072, p.15 - 0, 1999/12
no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Toshiki; Niita, Koji*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Maruyama, Tomoyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi; Iwamoto, Akira
Nuclear Physics A, 654(3-4), p.908C - 911C, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Toshiki; Niita, Koji*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Maruyama, Tomoyuki*; Iwamoto, Akira; Chiba, Satoshi
Physical Review C, 57(2), p.655 - 665, 1998/02
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.06(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Keiichi; Fukahori, Tokio; Takano, Hideki; *; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Kobayashi, Katsuhei*; *; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(10), p.863 - 865, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
The symmetry energy density derivative coefficient  in the symmetry energy of the equation of state of the nuclear matter must affect masses and radii of unstable nuclei. In the previous work we have investigated a sensitivity of
in the symmetry energy of the equation of state of the nuclear matter must affect masses and radii of unstable nuclei. In the previous work we have investigated a sensitivity of  to the nuclear radii and applied for the possibility of existence of the "pasta" nuclei in the neutron-star crust. In this work we examine a sensitivity of
to the nuclear radii and applied for the possibility of existence of the "pasta" nuclei in the neutron-star crust. In this work we examine a sensitivity of  to the nuclear masses in the light nuclidic region up to nickel isotopes. We extract a macroscopic feature from the nuclear masses based on the Yamada-Matsumoto-type systematics, and try to give a value of
to the nuclear masses in the light nuclidic region up to nickel isotopes. We extract a macroscopic feature from the nuclear masses based on the Yamada-Matsumoto-type systematics, and try to give a value of  determined by the experimental masses. We will discuss an ambiguity of
determined by the experimental masses. We will discuss an ambiguity of  in this presentation.
in this presentation.
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Iida, Kei*; Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
Liquid drop model is a representative model to describe binding energy and size of nuclei. This model is well reproduces bulk properties of nuclei even in current studies on nuclei. In this presentation, we investigate nuclear symmetry energy and nuclear surface energy by using the nuclear liquid drop model with some higher-order terms. The coefficients of these term are determined so as to reproduce measured nuclear masses of approximately 2200 nuclides. From this analysis we find an indication that the fourth-order terms of the symmetry energy is required and the curvature term of it is negligible. Regarding a mass-number dependency on nuclear radius, we also find that the dependency of lighter nuclei (typically with mass number, 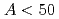 ) is larger than that of heavier nuclei.
) is larger than that of heavier nuclei.
Kohama, Akihisa*; Iida, Kei*; Oyamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Koura, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English