Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi*; Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Okada, Michio*; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, C, 130(10), p.1723 - 1729, 2010/10
The oxidation processes on a TiAl surface induced by a hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al
molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al O
O near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O
near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al
backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al O
O , Ti
, Ti O
O , TiO
, TiO ) on the TiAl surface were independent of the translational energy of incident O
) on the TiAl surface were independent of the translational energy of incident O molecule. The present results suggest that the oxidation on TiAl surface proceeds via precursor molecular states.
molecule. The present results suggest that the oxidation on TiAl surface proceeds via precursor molecular states.
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Tode, Mayumi; Okada, Michio*; Harries, J.; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
We have studied chemical reactions of TiAl surface with oxygen molecules by using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy to clarify the generation process of Al oxides. The experiment was conducted with the surface chemistry experimental station (SUREAC2000) at the soft X-ray beamline (BL23SU) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency in the SPring-8 facilities. The surface (50at.%) was cleaned by Ar ion sputtering and annealing. Comparing the Al-2p and Ti-2p XPS spectra of the clean surface with those of the surface exposed to the oxygen of 350L at 673K, it has been found that the peak position and profile were changed. It shows that both Ti and Al atoms were oxidized. Moreover, the Ti oxides was decreased by heating up to 1123K.
ion sputtering and annealing. Comparing the Al-2p and Ti-2p XPS spectra of the clean surface with those of the surface exposed to the oxygen of 350L at 673K, it has been found that the peak position and profile were changed. It shows that both Ti and Al atoms were oxidized. Moreover, the Ti oxides was decreased by heating up to 1123K.
Harries, J.; Tode, Mayumi; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
Photoelectron spectroscopy is predominantly a surface-sensitive technique, but by recording spectra at a range of angles information on the depth-dependent distribution of elements in specific chemical states can also be obtained. Compared to other techniques such as Rutherford back-scattering, the technique has the advantage of chemical-state specificity, but the drawback that it requires very careful data analysis to produce reliable and quantitative results. Here we report progress in obtaining chemical-state depth profiles from photoelectron spectra recorded using the SUREAC2000 apparatus at SPring-8's BL23SU. Results will be presented for ARXPS data recorded for N and O layers on Al(111), and also a VCrTi sample, both in its as-received state and following deuterium ion dosing.
Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Study of thermal desorption characteristics of native oxide layer on the surface of the hydrogen storage materials is very important. Thermal instability of native oxide layer on VCrTi and deuterated VCrTi was observed by high resolution soft X-ray synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments have been conducted at the surface chemistry experimental station (SUREAC2000) at BL23SU, SPring-8. Before thermal annealing, the satellite peak from the native oxide layer and the V-2p peak from the bulk were observed. The O-1s peak consisted of at least two components. After thermal annealing, the O-1s peak decreases and the V-2p peak increases. Deuterium implantation affected the thermal stability of the native oxide.
Harries, J.; Tode, Mayumi; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
Using the high energy resolution surface chemistry apparatus at SPring-8's BL23SU it is possible to record angular and chemical-state resolved X-ray photoelectron spectra. Chemical-state specific depth profile information can be obtained from these spectra using the maximum entropy method. Here we describe progress made in the combination of these two techniques, with the specific example of the depth-profiling of various nitridation states present in a Al(111) sample nitrided using a supersonic molecular beam.
Harries, J.; Tode, Mayumi; Inoue, Keisuke; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
There are many available methods for determining the elemental distributions within a sample in the depth direction, but angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy offers the advantage of chemica-state specificity. At the surface chemistry station at BL23SU, SPring-8, we have recorded depth-profiles for thin films generated using supersonic molecular beams and ion beams. To extract the depth-direction information from the angular resolved spectra we use the maximum entropy method. We explain the techniques, and present the specific example of the natural oxide of VCrTi, a hydrogen storage material. Also, we investigate the thermal stability of the oxide by generating depth profiles during annealing of the sample.
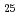 Cr
Cr Ti
Ti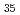 ) using high-resolution soft X-ray synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy
) using high-resolution soft X-ray synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopyTode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Thermal stability of native oxide layer on the hydrogen storage materials is related to the hydrogen absorption and desorption. Thermal instability of native oxide layer on VCrTi and deuterated VCrTi was observed by high resolution soft X-ray synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments have been conducted at the surface chemistry experimental station (SUREAC2000) at BL23SU, SPring-8. After thermal annealing, the peak that shows the oxidation weakens, and the peak that shows the metal strengthens. The thermal stability of a natural oxide layer was observed to stabilize by about 100 degrees by deuterium ion implanted.
Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Inoue, Keisuke; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Thermal stability of native oxide layer on the hydrogen storage materials is related to the hydrogen absorption and desorption. In this study, thermal degradation process of native oxide layer on VCrTi was observed by high resolution soft X-ray synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy. All experiments have been conducted at the surface chemistry experimental station (SUREAC2000) at BL23SU, SPring-8. Before thermal annealing, photoemission spectrum of oxide was observed. After thermal annealing, the oxide peak was decreased, and the metal peak was increased. When the deuterium ion was implanted into the surface, the degeneration temperature of a natural oxide layer was observed to rise about 100 degrees.
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Okada, Michio*; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
The oxidation processes on TiAl are complex and the composition of the oxide layer depends on various oxidation parameters like sample temperature and oxygen pressure. Therefore, the aim of this work was to examine the initial stages of oxidation of TiAl under different oxidation temperatures and the different kinetic energy of incident oxygen by using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. All experiments were performed with a surface reaction analysis apparatus (SUREAC2000) constructed in BL23SU at SPring-8. The TiAl sample was cleaned by repeatedly argon ion sputtering and annealing. The Oxygen molecules were dosed on the TiAl by hyperthermal oxygen molecular beams or by backfilling oxygen gas.
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi; Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Okada, Michio*; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
Titanium-based intermetallic alloys have attracted great attention as hydrogen storage materials. However, the oxide layer formed on the surface, which reduces the initial activation, has come to an issue. Therefore, improvements on the composition and structure in oxide layer are required. In this study, we investigated the oxidation on TiAl intermetallic alloys by hyperthermal Oxygen molecular beam (HOMB) and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation (SR-XPS).
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi*; Tode, Mayumi; Okada, Michio*; Harries, J.; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
The oxidation processes on a TiAl surface induced by a hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al
molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al O
O near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O
near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al
backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al O
O , Ti
, Ti O
O , TiO
, TiO ) on the TiAl surface were independent on the translational energy of incident O
) on the TiAl surface were independent on the translational energy of incident O molecules. The present results suggest that the oxidation on a TiAl surface proceed via molecular adsorption as a precursor state.
molecules. The present results suggest that the oxidation on a TiAl surface proceed via molecular adsorption as a precursor state.
Hashinokuchi, Michihiro*; Sumimoto, Yuichi*; Tode, Mayumi; Harries, J.; Okada, Michio*; Teraoka, Yuden; Kasai, Toshio*
no journal, ,
The oxidation processes on a TiAl surface induced by a hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al
molecular beam (HOMB) with a translational energy of 2.2 eV was studied by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. At a surface temperature of 300 K, the simultaneous growth of Al and Ti oxides accompanied with the segregation of Al O
O near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O
near the surface was observed. The efficiency of oxidation for the HOMB incidence was smaller than that for O backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al
backfilling (25 meV). Furthermore, the chemical compositions of oxide species (Al O
O , Ti
, Ti O
O , TiO
, TiO ) on the TiAl surface were independent on the translational energy of incident O
) on the TiAl surface were independent on the translational energy of incident O molecule. The present results suggest that the oxidation on TiAl surface proceed via precursor molecular states.
molecule. The present results suggest that the oxidation on TiAl surface proceed via precursor molecular states.