Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 SR study of an layered organic superconductor
SR study of an layered organic superconductor  -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) Hg
Hg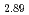 Br
Br
Sato, Kazuhiko*; Fujita, Hidemi*; Katayama, Kazuhiro*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.597 - 599, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.31(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field muon spin relaxation and high-field transverse muon spin rotation have been measured for an organic superconductor  -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) Hg
Hg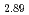 Br
Br . No anomaly is found in zero-field relaxation spectrum at the superconducting transition temperature, 4.2 K. The muon Knight shift determined by transverse muon spin rotation at 6 T exhibits Curie-Weiss like behavior down to 2 K, whereas static magnetic susceptibility shows a peak around 30 K. The muon Knight shift does not scale with the magnetic susceptibility at low temperatures.
. No anomaly is found in zero-field relaxation spectrum at the superconducting transition temperature, 4.2 K. The muon Knight shift determined by transverse muon spin rotation at 6 T exhibits Curie-Weiss like behavior down to 2 K, whereas static magnetic susceptibility shows a peak around 30 K. The muon Knight shift does not scale with the magnetic susceptibility at low temperatures.
 SR study of organic antiferromagnet
SR study of organic antiferromagnet  '-(BEDT-TTF)
'-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl under high pressure
under high pressureSato, Kazuhiko*; Sato, Koichi*; Yoshida, Tetsushige*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Goko, Tatsuro*; Ito, Takashi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(5-7), p.600 - 602, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.75(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field muon spin relaxation was measured for organic antiferromagnet  '-(BEDT-TTF)
'-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl under high pressure of up to 1.37 GPa. Neel temperature, which is 22 K at ambient pressure, increases with increasing pressure and becomes approximately 48 K at 1.37 GPa. Muon precession frequency at 1.37 GPa, becomes about 5 times larger than that at ambient pressure.
under high pressure of up to 1.37 GPa. Neel temperature, which is 22 K at ambient pressure, increases with increasing pressure and becomes approximately 48 K at 1.37 GPa. Muon precession frequency at 1.37 GPa, becomes about 5 times larger than that at ambient pressure.
 SR study of an antiferromagnetic insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ)
SR study of an antiferromagnetic insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ)Sato, Kazuhiko*; Fujita, Hidemi*; Sato, Ryosuke*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.102 - 105, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.95(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field  SR measurements for an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ) were performed in order to study the microscopic magnetic properties of this organics. Slight increase of the relaxation rate is observed below 20K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of BEDT-TTF dimers, whereas clear muon precession signal is observed below 3K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of TCNQ. Below 3K, there exist at least two antiferromagnetic domains whose volume fractions changes with temperature.
SR measurements for an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator (BEDT-TTF)(TCNQ) were performed in order to study the microscopic magnetic properties of this organics. Slight increase of the relaxation rate is observed below 20K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of BEDT-TTF dimers, whereas clear muon precession signal is observed below 3K owing to the antiferromagnetic ordering of TCNQ. Below 3K, there exist at least two antiferromagnetic domains whose volume fractions changes with temperature.
 SR study of an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
SR study of an antiferromagnetic Mott insulator 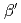 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl
Sato, Kazuhiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kawamoto, Atsushi*; Higemoto, Wataru
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 374-375, p.99 - 101, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.18(Physics, Condensed Matter)Zero-field  SR measurements on the antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
SR measurements on the antiferromagnetic Mott insulator 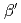 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl were performed in order to study themicroscopic magnetic properties of this organics. The volume fraction of the antiferromagnetic phase was found to be temperature independent. Muon precession frequency, which is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic moment at the dimer of two BEDTTTF molecules, does not follow the simple model based on the mean-field approximation.
were performed in order to study themicroscopic magnetic properties of this organics. The volume fraction of the antiferromagnetic phase was found to be temperature independent. Muon precession frequency, which is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic moment at the dimer of two BEDTTTF molecules, does not follow the simple model based on the mean-field approximation.
Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Taniguchi, Hiromi*
no journal, ,
There is no report of application of inelastic neutron scattering on organic conductors until today because of the tiny size and amount of their crystals. Recently, it was reported that synthesis of huge single crystal (a few mm class) of 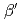 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl had been succeeded. The system exhibits an antiferromagnetic order below 22 K. We performed a neutron scattering experiment on this system as the first step toward observation of the magnetic excitation in the organic conductor. The measurement was carried out using a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed in J-PARC. About 230 pieces of the single crystals (1.5 g) was aligned to mount onto a sample holder. Bragg diffractions from the crystal were indexed along the [100] direction, which is perpendicular to the two-dimensional (2D) plane. Magnetic Bragg peak was not observed in this direction because of rapid damping of the magnetic form factor.
had been succeeded. The system exhibits an antiferromagnetic order below 22 K. We performed a neutron scattering experiment on this system as the first step toward observation of the magnetic excitation in the organic conductor. The measurement was carried out using a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed in J-PARC. About 230 pieces of the single crystals (1.5 g) was aligned to mount onto a sample holder. Bragg diffractions from the crystal were indexed along the [100] direction, which is perpendicular to the two-dimensional (2D) plane. Magnetic Bragg peak was not observed in this direction because of rapid damping of the magnetic form factor.
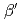 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl
Kawamura, Seiko; Matsuura, Masato*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kubota, Aiko*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Kawakita, Yukinobu; et al.
no journal, ,
A molecular dimer-Mott insulator 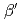 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl is a candidate for a new type of ferroelectric system which shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. We performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements on this system by using a chopper specrometer, and observed phonon spectra in a wide wave vector (
is a candidate for a new type of ferroelectric system which shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. We performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements on this system by using a chopper specrometer, and observed phonon spectra in a wide wave vector ( )-energy (
)-energy ( ) region for the first time. Clear optical modes with the energies up to
) region for the first time. Clear optical modes with the energies up to  36 meV were observed together with an acoustic phonon dispersion. The intensity of the optical mode with the lowest energy
36 meV were observed together with an acoustic phonon dispersion. The intensity of the optical mode with the lowest energy  = 4.2 meV increases at a zone boundary along the
= 4.2 meV increases at a zone boundary along the  * axis below
* axis below 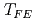 = 62 K, at which a glassy ferroelectricity appears, and it further increases all over the measured
= 62 K, at which a glassy ferroelectricity appears, and it further increases all over the measured  range below the antiferromangetic transition temperature
range below the antiferromangetic transition temperature  = 22 K. The results suggest that the lattice dynamics characterized by this optical phonon mode is significantly coupled with strongly correlated charge and spin degrees of freedom.
= 22 K. The results suggest that the lattice dynamics characterized by this optical phonon mode is significantly coupled with strongly correlated charge and spin degrees of freedom.
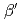 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl studied by inelastic neutron scattering
studied by inelastic neutron scatteringKawamura, Seiko; Matsuura, Masato*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kubota, Aiko*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakajima, Kenji
no journal, ,
Recently it has been reported that a molecular dimer-Mott insulator 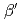 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl is a candidate of a new type of ferroelectric system which shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state below
is a candidate of a new type of ferroelectric system which shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state below  = 62 K and long-range antiferromagnetic order below
= 62 K and long-range antiferromagnetic order below  = 22 K. We have performed inelastic neutron scattering experiments on this system by using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed at BL14 in MLF. The phonon intensity at
= 22 K. We have performed inelastic neutron scattering experiments on this system by using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed at BL14 in MLF. The phonon intensity at  18 and
18 and  21 meV decreases with lowering temperature, while that at
21 meV decreases with lowering temperature, while that at  13.5 meV increases. We have already found that a period-doubled optical phonon mode at 4.2 meV is enhanced below around
13.5 meV increases. We have already found that a period-doubled optical phonon mode at 4.2 meV is enhanced below around  and then is suppressed below
and then is suppressed below  , indicating significant relationship to both charge and spin dynamics. In sharp contrast to this low-energy mode, the intensity of the optical mode at
, indicating significant relationship to both charge and spin dynamics. In sharp contrast to this low-energy mode, the intensity of the optical mode at  18 meV decreases below
18 meV decreases below  to reach a constant value at a low temperature.
to reach a constant value at a low temperature.
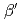 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl by inelastic neutron scattering
by inelastic neutron scatteringKawamura, Seiko; Matsuura, Masato*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kubota, Aiko*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Kenji
no journal, ,
It has been reported that in a molecular dimer-Mott insulator 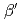 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state associated with charge disproportionation within the dimer, where a hole (
shows a relaxor-like dielectric response. The system exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state associated with charge disproportionation within the dimer, where a hole ( = 1/2) is localized, below
= 1/2) is localized, below  = 62K, and a long-range antiferromagnetic order below
= 62K, and a long-range antiferromagnetic order below  = 22K. For such molecule-based materials, it is expected that low-energy phonon modes are coupled with spin/charge degrees of freedom. In order to observe the phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements in a wide wave-vector and energy region using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at J-PARC MLF. The lowest energy mode shows remarkable temperature dependence of its intensity, while any softening is not observed. The result suggests that this phonon mode reflects changes in the spin/charge dynamics.
= 22K. For such molecule-based materials, it is expected that low-energy phonon modes are coupled with spin/charge degrees of freedom. In order to observe the phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering measurements in a wide wave-vector and energy region using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS at J-PARC MLF. The lowest energy mode shows remarkable temperature dependence of its intensity, while any softening is not observed. The result suggests that this phonon mode reflects changes in the spin/charge dynamics.
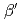 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl coupled with charge and spin studied by inelastic neutron scattering
coupled with charge and spin studied by inelastic neutron scatteringKawamura, Seiko; Matsuura, Masato*; Iguchi, Satoshi*; Sasaki, Takahiko*; Taniguchi, Hiromi*; Kubota, Aiko*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Kenji
no journal, ,
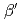 -(BEDT-TTF)
-(BEDT-TTF) ICl
ICl is an organic dimer-Mott insulator which exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state below
is an organic dimer-Mott insulator which exhibits a glassy ferroelectric state below  = 62K and an antiferromagnetic order below
= 62K and an antiferromagnetic order below  = 22K. It is expected in such molecule-based materials that low-energy phonon modes lie in the energy region of charge and spin, and then the lattice is expected to couple with charge and spin degrees of freedom. To observe such phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering study using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed at J-PARC MLF. The system shows the lowest-energy optical phonon mode at
= 22K. It is expected in such molecule-based materials that low-energy phonon modes lie in the energy region of charge and spin, and then the lattice is expected to couple with charge and spin degrees of freedom. To observe such phonon modes in this system, we have performed inelastic neutron scattering study using a chopper spectrometer AMATERAS installed at J-PARC MLF. The system shows the lowest-energy optical phonon mode at  = 4.2 meV. which is significantly related to the charge degree of freedom. Analyzing the data more in detail, the intensity of the 4.2 meV-mode monotonically increases with lowering temperature toward
= 4.2 meV. which is significantly related to the charge degree of freedom. Analyzing the data more in detail, the intensity of the 4.2 meV-mode monotonically increases with lowering temperature toward  , becomes constant below
, becomes constant below  and drastically increases below
and drastically increases below  . The behavior of the optical phonons at some representative
. The behavior of the optical phonons at some representative  positions are reported.
positions are reported.