Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Akira; Kitagishi, Shigeru; Watashi, Katsumi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Omi, Masao; Sozawa, Shizuo; Naka, Michihiro
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-13-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.290 - 297, 2016/07
The exhaust stack of Japan Materials Testing Reactor Hot laboratory is a part of gaseous waste treatment system. It was built in 1970 and is 40 m in height. In 2015, thinning was found at some anchor bolts on base of the stack. When thinning of anchor bolts were investigated, gaps between anchor bolt nuts and flange plate was found. JAEA removed steel cylinder of stack which is 33 m in height for safety. In the end of investigation, thinning was found in all anchor bolts of the stack. Cause investigation for the thinning and the gaps were performed. It is concluded that the thinning was caused by water infiltration over a long period of time and the gaps were caused by elongation of thinning part of anchor bolts by the 2011 earthquake off the Pacific coast of Tohoku.
Okada, Yuji; Magome, Hirokatsu; Hanawa, Hiroshi; Omi, Masao; Kanno, Masaru; Iida, Kazuhiro; Ando, Hitoshi; Shibata, Mitsunobu; Yonekawa, Akihisa; Ueda, Haruyasu
JAEA-Technology 2013-019, 236 Pages, 2013/10
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in order to solve the problem in the long-term operation of a light water reactor, preparation which does the irradiation experiment of light-water reactor fuel and material is advanced. JMTR stopped after the 165th operation cycle in August 2006, and is advancing renewal of the irradiation facility towards re-operation. This material irradiation test facility and power ramping test facility for doing the neutron irradiation test of the fuel and material for light water reactors is scheduled to be manufactured and installed between the 2008 fiscal year and the 2012 fiscal year. This report summarizes manufacture and installation of the material irradiation test facility for IASCC research carried out from the 2008 fiscal year to the 2010 fiscal year.
Okada, Yuji; Magome, Hirokatsu; Iida, Kazuhiro; Hanawa, Hiroshi; Omi, Masao
UTNL-R-0483, p.10_4_1 - 10_4_10, 2013/03
In JAEA(Japan Atomic Energy Agency), about the irradiation embrittlement of the reactor pressure vessel and the stress corrosion cracking of reactor core composition apparatus concerning the long-term use of the light water reactor (BWR), in order to check the influence of the temperature, pressure, and water quality, etc on BWR condition. The water environmental control facility which performs irradiation assisted stress corrosion-cracking (IASCC) evaluation under BWR irradiation environment was fabricated in JMTR. (Japan Materials Testing Reactor). This report is described the outline of manufacture of the water environmental control facility for doing an irradiation test using the saturation temperature capsule after JMTR re-operation.
Shibata, Akira; Kitagishi, Shigeru; Kimura, Nobuaki; Saito, Takashi; Nakamura, Jinichi; Omi, Masao; Izumo, Hironobu; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Conf 2011-003, p.185 - 188, 2012/03
To get measurement data with high accuracy for fuel and material behavior studies in irradiation tests, two kinds of measuring equipments have been developed; these are the Electrochemical Corrosion Potential (ECP) sensor, the Linear Voltage Differential Transformer (LVDT) type gas pressure gauge. The ECP sensor has been developed to determine the corrosive potential under high temperature and high pressure water condition. The structure of the joining parts was optimized to avoid stress concentration. The LVDT type gas pressure gauge has been developed to measure gas pressure in a fuel element during neutron irradiation. To perform stable measurements with high accuracy under high temperature, high pressure and high dosed environment, the coil material of LVDT was changed to MI cable. As a result of this development, the LVDT type gas pressure gauge showed high accuracy at 1.8% of a full scale, and good stability.
Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Omi, Masao; Kawamata, Kazuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 422(1-3), p.14 - 19, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To simulate Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) behavior by in-pile experiments, it is necessary to irradiate specimens up to a neutron fluence that is higher than the IASCC threshold fluence. Pre-irradiated specimens must be relocated from pre-irradiation capsules to in-pile capsules. Hence, a remote welding machine has been developed. And the integrity of capsule housing for a long term irradiation was evaluated by tensile tests in air and slow strain rate tests in water. Two type specimens were prepared. Specimens were obtained from the outer tubes of capsule irradiated to 1.0-3.9  10
10 n/m
n/m (E
(E 1 MeV). And specimens were irradiated in a leaky capsule to 0.03-1.0
1 MeV). And specimens were irradiated in a leaky capsule to 0.03-1.0  10
10 n/m
n/m . Elongation more than 15% in tensile test at 423 K was confirmed and no IGSCC fraction was shown in SSRT at 423 K which was estimated as temperature at the outer tubes of the capsule under irradiation.
. Elongation more than 15% in tensile test at 423 K was confirmed and no IGSCC fraction was shown in SSRT at 423 K which was estimated as temperature at the outer tubes of the capsule under irradiation.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Shibata, Akira; Ise, Hideo; Kasahara, Shigeki; Kawaguchi, Yoshihiko*; Nakano, Junichi; Omi, Masao; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of Enlarged Halden Programme Group Meeting 2011 (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
In order to load a large specimen of 0.5T-CT up to a high stress intensity factor of  30 MPa
30 MPa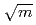 , we have adopted a lever type loading unit for in-pile irradiation-assisted stress corrosion crack (IASCC) growth tests in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In this unit, the applied load is generated by shrinking a bellows with lower inner gas pressure than surrounding water pressure and enlarged by leverage. The crack length of the specimen is monitored by potential drop method (PDM) using mineral insulator (MI) cables. In this paper, technical concerns of the in-pile crack growth test unit, especially the estimation procedure of applied load to the specimen inside the irradiation capsule and the evaluation of precision of the PDM signals are presented.
, we have adopted a lever type loading unit for in-pile irradiation-assisted stress corrosion crack (IASCC) growth tests in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In this unit, the applied load is generated by shrinking a bellows with lower inner gas pressure than surrounding water pressure and enlarged by leverage. The crack length of the specimen is monitored by potential drop method (PDM) using mineral insulator (MI) cables. In this paper, technical concerns of the in-pile crack growth test unit, especially the estimation procedure of applied load to the specimen inside the irradiation capsule and the evaluation of precision of the PDM signals are presented.
Ito, Masayasu; Kawamata, Kazuo; Tayama, Yoshinobu; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu; Yonekawa, Minoru; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Omi, Masao; Iwamatsu, Shigemi
JAEA-Technology 2011-022, 44 Pages, 2011/07
Hot laboratory are facilities that execute the post irradiation examination of sample irradiated in material testing reactors etc. The handling of high burn-up fuel is scheduled in the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) Hot Laboratory with JMTR re-operate in FY 2011. This report describes evaluation, production and installation of shielding of the hot cells in the JMTR Hot Laboratory.
Ishida, Takuya; Tanimoto, Masataka; Shibata, Akira; Kitagishi, Shigeru; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Nakamura, Jinichi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Testing 2011-001, 44 Pages, 2011/06
The Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center has developed new irradiation technologies to provide irradiation data with high technical value for the refurbishment and resume of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). For the purpose to perform assembling of capsules, materials tests, materials inspection and analysis of irradiation specimens for the development of irradiation capsules, improvement and maintenance of facilities were performed. The RI application development building was refurbished and maintained for above-mentioned purpose. After refurbishment, the building was named Irradiation Technology Development Building. It contains eight laboratories based on the purpose of use, and experimental apparatuses were installed. This report describes the refurbishment work of the RI application development building, the installation work and operation method of the experimental apparatuses and the basic management procedure of the Irradiation Technology Development Building.
Shibata, Akira; Kimura, Tadashi; Nagata, Hiroshi; Aoyama, Masashi; Kanno, Masaru; Omi, Masao
JAEA-Testing 2010-003, 22 Pages, 2010/11
Type 316 stainless steels (SSs) were used for tube material of the Oarai water loop No.2 (OWL-2) in the reactor. But data of highly irradiated Type 316 SSs has been insufficient since OWL-2 was installed. Therefore surveillance tests of type 316 SSs which were irradiated up to 3.4  10
10 n/m
n/m in fast neutron fluence (
in fast neutron fluence ( 1 MeV) were performed. But type 316 SSs were widely used in JMTR, then additional data of type 316 SSs irradiated higher was required. Therefore PIEs of type 316 SSs surveillance specimens which were irradiated up to 1.0
1 MeV) were performed. But type 316 SSs were widely used in JMTR, then additional data of type 316 SSs irradiated higher was required. Therefore PIEs of type 316 SSs surveillance specimens which were irradiated up to 1.0  10
10 n/m
n/m in fast neutron fluence were performed and reported in this paper. Tendency of results has good agreement with results of 10
in fast neutron fluence were performed and reported in this paper. Tendency of results has good agreement with results of 10 -10
-10 n/m
n/m in fast neutron fluence. More than 37 % in total elongation was confirmed in all test conditions. It is confirmed that type 316 SS irradiated up to 1.0
in fast neutron fluence. More than 37 % in total elongation was confirmed in all test conditions. It is confirmed that type 316 SS irradiated up to 1.0  10
10 n/m
n/m in fast neutron fluence has enough ductility as structure material.
in fast neutron fluence has enough ductility as structure material.
Kitagishi, Shigeru; Tanimoto, Masataka; Iimura, Koichi; Inoue, Shuichi; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Review 2010-046, 19 Pages, 2010/11
The Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been utilized for the various neutron irradiation tests of fuels and materials, as well as for radioisotope production since achieving the first criticality in March 1968. The operation of JMTR was halted for the refurbishment in August 2006. The new JMTR is expected to contribute to many fields: the lifetime extension of LWRs and the expansion of industry use. To meet a wide range of users' needs, the development of new irradiation technologies has been carried out for the new JMTR. This report summarizes the present conditions of the development of FP gas pressure gauges, multi-paired thermocouples, ECP and ceramics sensors.
Sozawa, Shizuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hayashi, Koji; Tayama, Yoshinobu; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yonekawa, Minoru; Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu; Omi, Masao
JAEA-Technology 2009-070, 27 Pages, 2010/03
Refurbishment of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), which is recognized as one of important facilities in Japan for safety research, is in progress by the JAEA. In Extensive safety research of light-water reactor (LWR) fuels and materials under a contract with the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency of Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the irradiation tests are planned in order to examine integrity of the LWR fuels and structure materials. For the irradiation tests of high burnup fuels and irradiated materials in the JMTR, modification of the hot laboratory facilities are needed, which are (1) making of application books for strengthening JMTR hot-lab. cell-shielding, (2) the capsule assembling device of detailed design, (3) safety analysis for domestic transportation cask and (4) confirmatory testing of diamond drill of fuel-rod center-hole processing device.
Sozawa, Shizuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Omi, Masao; Hayashi, Koji; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Kawamata, Kazuo; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kanazawa, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Technology 2009-069, 32 Pages, 2010/03
Refurbishment of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), which is recognized as one of important facilities in Japan for safety research, is in progress by the JAEA. In Extensive safety research of light-water reactor (LWR) fuels and materials under a contract with the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency of Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, the irradiation tests are planned in order to examine integrity of the LWR fuels and structure materials. For the irradiation tests of high burnup fuels and irradiated materials in the JMTR, modification of the hot laboratory facilities are needed, which are (1) strengthening JMTR hot-lab. cell-shielding, (2) the capsule assembling device, (3) domestic transportation cask, (4) fuel-rod center-hole processing device, (5) master-slave manipulators, (6) power manipulator, and (7) scanning electron microscope.
Kitagishi, Shigeru; Inoue, Shuichi; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
UTNL-R-0475, p.2_5_1 - 2_5_9, 2010/03
no abstracts in English
Kitagishi, Shigeru; Inoue, Shuichi; Saito, Takashi; Omi, Masao; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Testing 2009-010, 14 Pages, 2010/02
It is important for neutron irradiation tests of materials and fuels to clarify the irradiation environment. Especially, the oxygen and hydrogen peroxide concentrations are required to measure for the analysis of corrosion mechanism of the structure materials in the light-Water Reactor (LWR) conditions. In this report, the trial fabrication tests of the ceramic gas sensor were carried out by the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) method and basic performance results of the sensor were described.
Yonekawa, Minoru; Sozawa, Shizuo; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
UTNL-R-0471, p.5_6_1 - 5_6_7, 2009/03
no abstracts in English
Taguchi, Taketoshi; Kato, Yoshiaki; Takada, Fumiki; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
UTNL-R-0471, p.5_7_1 - 5_7_8, 2009/03
no abstracts in English
Kawamata, Kazuo; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Omi, Masao; Hayashi, Koji; Shibata, Akira; Saito, Junichi; Niimi, Motoji
JAEA-Conf 2008-011, p.78 - 86, 2009/01
The JMTR-HL was founded to examine the objects mainly irradiated in the JMTR in 1971. The JMTR-HL has an advantage that the hot cell is connected with the reactor vessel of the JMTR by a canal. Hence it is easy to transport irradiated radioactive capsules and specimens through the canal. Since 1971, about 2,400 irradiated capsules have been treated in the JMTR-HL and various PIEs have been widely performed there. In recent years, several new techniques, e.g., an in-cell IASCC test, a scanning-electron microscope (SEM) / electron-back scattering-diffraction pattern (EBSD) observation, were added to the conventional PIEs. In addition, the JMTR-HL had contributed to realize an in-pile IASCC test program at the JMTR through the development of a TIG welding technique by remote-handling with manipulators in the hot cell for re-assembling of capsules. A modification of the facility to treat high burn-up fuels, up to about 100 GWD/t, is planned at the JMTR-HL now.
Shibata, Akira; Omi, Masao; Nakagawa, Tetsuya
JAEA-Conf 2008-010, p.54 - 66, 2008/12
The hot laboratory accompanied with the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR-HL) was founded in 1971 to examine objects irradiated mainly at the JMTR. The JMTR-HL has three kinds of beta- hot-cell lines for research and development of nuclear fuels and materials. The JMTR-HL has the advantage of being connected by a canal between the hot cell and the JMTR. Hence it is easy to transport irradiated capsules and specimens through the canal. Since 1971, about 2,400 irradiated capsules have been treated in the JMTR-HL. Many various post irradiation examinations (PIEs) have been widely performed here. Mentioned in this report are overview of the hot laboratory, the present organization, the current status of the PIEs, and the modification plan of the facility to treat high burn-up fuels up to about 100 GWD/t in this presentation.
hot-cell lines for research and development of nuclear fuels and materials. The JMTR-HL has the advantage of being connected by a canal between the hot cell and the JMTR. Hence it is easy to transport irradiated capsules and specimens through the canal. Since 1971, about 2,400 irradiated capsules have been treated in the JMTR-HL. Many various post irradiation examinations (PIEs) have been widely performed here. Mentioned in this report are overview of the hot laboratory, the present organization, the current status of the PIEs, and the modification plan of the facility to treat high burn-up fuels up to about 100 GWD/t in this presentation.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Izumo, Hironobu; Inoue, Shuichi; Abe, Shinichi; Naka, Michihiro; Akashi, Kazutomo; Omi, Masao; Miyazawa, Masataka; Baba, Osamu*; Nagao, Yoshiharu
JAEA-Review 2008-051, 36 Pages, 2008/10
The JMTR has been refurbished to restart operation in FY2011. The restarted JMTR plays roles of (1) measures for long-term operation of light water reactors, (2) improvement in scientific technique, (3) increase of industrial use, (4) training of human resources, etc. It is needed to operate the restarted JMTR safety and stably and maintain high available factor (50 70%) because of increasing of irradiation utilization demand. In this report, measures for training of reactor operators, organization for operating, etc were proposed to operate reactor safety and smoothly. And also reactor operation procedure was examined to improve available factor up to world level for materials testing reactor. As a result, it was turned out to be possible to realize stably 210 days operation per year (available factor: 60%).
70%) because of increasing of irradiation utilization demand. In this report, measures for training of reactor operators, organization for operating, etc were proposed to operate reactor safety and smoothly. And also reactor operation procedure was examined to improve available factor up to world level for materials testing reactor. As a result, it was turned out to be possible to realize stably 210 days operation per year (available factor: 60%).
Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ugachi, Hirokazu; Tsukada, Takashi; Nakano, Junichi; Matsui, Yoshinori; Kawamata, Kazuo; Shibata, Akira; Omi, Masao; Nagata, Nobuaki*; Dozaki, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(8), p.725 - 734, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is one of the critical concerns when stainless steel components have been in service in light water reactors for a long period. In-core IASCC growth tests have been carried out using the compact tension type specimens of type 304 stainless steel that had been pre-irradiated up to a neutron fluence level around 1 10
10 n/m
n/m in pure water simulated boiling water reactor (BWR) coolant condition at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In order to investigate the effect of synergy of neutron/
in pure water simulated boiling water reactor (BWR) coolant condition at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). In order to investigate the effect of synergy of neutron/ radiation and stress/water environment on IASCC growth rate, we performed ex-core IASCC tests on irradiated specimens at several dissolved oxygen contents environments under the same electrochemical potential condition. In this paper, results of the in-core SCC growth tests will be discussed and compared with the result obtained by ex-core tests from a viewpoint of the synergistic effects on IASCC.
radiation and stress/water environment on IASCC growth rate, we performed ex-core IASCC tests on irradiated specimens at several dissolved oxygen contents environments under the same electrochemical potential condition. In this paper, results of the in-core SCC growth tests will be discussed and compared with the result obtained by ex-core tests from a viewpoint of the synergistic effects on IASCC.