Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 /MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditions
/MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditionsLiu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 37, p.101532_1 - 101532_5, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mohamad, A. B.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.215 - 222, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Liu, J.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Shirasu, Noriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.484 - 490, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Chikashi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.345 - 356, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)During a severe accident (SA) such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, fission products (FP) can be retained on the surface of structural materials in reactors. Cesium (Cs) is an important FP, and various Cs compounds such as Cs silicates are formed on the surface of stainless steel (SS) in a reactor during a SA. We calculated total energies of Cs-Si-O compounds for evaluation on phase stability within an adiabatic approximation. The calculations indicate that Cs Si
Si O
O is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi
is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi FeO
FeO is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
Osaka, Masahiko; Gou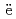 llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.292 - 305, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research on the fission product chemistry made after the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station were reviewed with focus on the Cesium chemistry in terms of two regimes, namely the accidental source term and the long-term source term via aqueous phase towards the decommissioning. For the accidental source term, Cs chemical interaction with Mo, B and Si were reviewed. Regarding the unique issue of long-term source term via aqueous phase, Cs penetration into concrete and fuel debris leaching were mentioned as the main sources of FPs. Efforts on the preparation of thermodynamic data for the Cs complex oxides were described. All these Cs chemical behaviors should be modelled and validated/verified through the analysis and evaluation of the actual samples including fuel debris that would be taken from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in near future.
Rizaal, M.; Miwa, Shuhei; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei; Osaka, Masahiko; Gou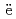 llo, M.*
llo, M.*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(48), p.32695 - 32708, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Imoto, Jumpei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(4), p.179 - 187, 2021/12
Some of the Cs inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station would be deposited in chemical forms such as CsI and Cs MoO
MoO . Since Cs compounds are generally water-soluble, it is predicted that the migration of Cs through the aqueous phase occurs in the long term. Knowledge of the solubility in water is required as basic data for such migration behavior evaluation. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the dissolution properties of CsI and Cs
. Since Cs compounds are generally water-soluble, it is predicted that the migration of Cs through the aqueous phase occurs in the long term. Knowledge of the solubility in water is required as basic data for such migration behavior evaluation. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the dissolution properties of CsI and Cs MoO
MoO in water at 20
in water at 20 C and 25
C and 25 C. The solubilities of CsI at 25
C. The solubilities of CsI at 25 C calculated using thermodynamic data and the Pitzer ion interaction model were in good agreement with the literature value. It was found that the literature value of CsI at around room temperature is highly reliable. The experimental value of CsI at 20
C calculated using thermodynamic data and the Pitzer ion interaction model were in good agreement with the literature value. It was found that the literature value of CsI at around room temperature is highly reliable. The experimental value of CsI at 20 C obtained by the OECD test guideline 105 flask method (test guideline) was also in good agreement with the literature value. The measured solubility of Cs
C obtained by the OECD test guideline 105 flask method (test guideline) was also in good agreement with the literature value. The measured solubility of Cs MoO
MoO was 256.8
was 256.8  6.2 (g/100 g H
6.2 (g/100 g H O) at 20
O) at 20 C using the test guideline. This measured solubility of Cs
C using the test guideline. This measured solubility of Cs MoO
MoO was found to be comparable to those of other alkaline molybdates and considered to be more reliable than the literature value.
was found to be comparable to those of other alkaline molybdates and considered to be more reliable than the literature value.
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Kino, Chiaki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111256_1 - 111256_19, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to grasp the long-term distributions of FP as well as fuel debris all over the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) for safe completion of its decommissioning projects. The fuel debris is going to be removed from the plant under the severe conditions of FP being scattered during major decommissioning work, and then, the decommissioning projects are going to be terminated by storing safely the removed debris as recovered fertile materials or as materials for final radioactive disposal. In order to determine the FP distribution in the plant for the long period from the accident occurrence to the termination of the plant decommissioning, procedures for analyzing multi-term FP behaviors were proposed. The proposed procedures should be improved by applying the FP data measured in the plant and validated based on the feedback data. Then, the accuracy-improved procedures should be applied to estimate FP distribution during each period of the decommissioning projects.
Liu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 26, p.100916_1 - 100916_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Gou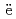 llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1287 - 1296, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to clarify the cesium iodide (CsI) transport behavior with a focus on the mechanisms of gaseous iodine formation in the reactor coolant system of LWR under a severe accident condition, a reproductive experiment of CsI transport behavior was conducted using a facility equipped with a thermal gradient tube. Various analyses on deposits and airborne materials during transportation could elucidate two mechanisms for the gaseous iodine formation. One was the gaseous phase chemical reaction in Cs-I-O-H system at relatively high-temperature region, which led to gaseous iodine transport to the lower temperature region without any further changes in gas species due to the kinetics limitation effects. The other one was the chemical reactions related to condensed phase of CsI, namely those of CsI deposits on walls with surface of stainless steel to form Cs CrO
CrO compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)The interaction of cesium hydroxide and a calcium silicate insulation material was experimentally investigated at high temperature conditions. A thermogravimetry equipped with differential thermal analysis was used to analyze thermal events in the samples of mixed calcium silicate and cesium hydroxide under Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 with maximum temperature of 1100
0 with maximum temperature of 1100 C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca
C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca Si
Si 0
0 (0H)
(0H) ), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730
), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730 C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0
C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0 ), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100
), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100 C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H
C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0
0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0 was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
 Si
Si O
O
Suzuki, Eriko; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko; Oishi, Yuji*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Kurosaki, Ken*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(7), p.852 - 857, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)The low temperature heat capacity of Cs Si
Si O
O , which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity,
, which is one of the cesium chemisorbed compounds onto stainless steel during severe accident of the light water nuclear reactor, was experimentally determined for the first time in the temperature range of 1.9 - 302 K. The experimentally determined heat capacity, 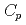
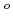 (298.15K), and the standard entropy,
(298.15K), and the standard entropy, 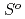 (298.15K), were 249.4
(298.15K), were 249.4  1.1 J K
1.1 J K mol
mol and 322.1
and 322.1  1.3 J K
1.3 J K mol
mol , respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs
, respectively. The standard Gibbs energy of formation of Cs Si
Si O
O at high temperatures,
at high temperatures, 

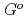 (
( ), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained
), were reevaluated by using the presently obtained 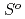 (298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation,
(298.15K) and the previously reported experimental results of the standard enthalpy of formation, 

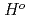 (298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures,
(298.15K), and the standard enthalpy increments at high temperatures, 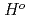 (
( )-
)-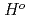 (298.15K).
(298.15K).
Rizaal, M.; Saito, Takumi*; Okamoto, Koji*; Erkan, N.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00563_1 - 19-00563_10, 2020/06
The adsorption of cesium (Cs) on calcium silicate insulation of primary piping system is postulated to contribute in high dose rate of surrounding pedestal area in Fukushima Daiichi NPP unit 2. In this study, room-temperature experiment of Cs adsorption on calcium silicate has been studied as an initial approach of Cs adsorption behavior toward higher temperature condition. As the result of analyzing of Cs adsorption kinetics, it was expected that the underlying adsorption mechanism is chemisorption. Furthermore, analysis of adsorption isotherm suggested unrestricted monolayer formation followed by multilayer formation.
Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miyahara, Naoya; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Liu, J.; Miradji, F.; Imoto, Jumpei; Afiqa, B. M.; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00537_1 - 19-00537_11, 2020/06
We constructed the fission product (FP) chemistry database named ECUME for LWR severe accident. This version of ECUME is equipped with dataset of the chemical reactions and their kinetics constants for the reactions of cesium(Cs)-iodine(I)-boron(B)-molybdenum(Mo)-oxygen(O)-hydrogen(H) system in gas phase, the elemental model for the high temperature chemical reaction of Cs with stainless steel applied as the structural material in a reactor, and thermodynamic data for CsBO vapor species and solids of Cs
vapor species and solids of Cs Si
Si O
O and CsFeSiO
and CsFeSiO for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
for these chemical reactions. The ECUME will provide estimation of Cs distribution due to the evaluation of effects of interaction with BWR control material B and stainless steel on Cs behavior in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Nakajima, Kunihisa; Nishioka, Shunichiro*; Suzuki, Eriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00564_1 - 19-00564_14, 2020/06
A large amount of cesium (Cs) chemisorbed onto stainless steel is predicted to be present especially in the upper region of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) during light water reactor severe accident (LWR SA) and a chemisorption model was developed for estimation of such amounts of Cs for stainless steel type 304 (SS304). However, this existing chemisorption model cannot accurately reproduce experimental results. Therefore, in this study, a modified Cs chemisorption model which accounts for silicon content in SS304 and concentration of cesium hydroxide (CsOH) in gaseous phases was constructed by combining penetration theory for gas-liquid mass transfer with chemical reaction and mass action law for CsOH decomposition at interface between gaseous and solid phases. As a result, it was found that the modified model was able to reproduce the experimental data more accurately than the existing model.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Osaka, Masahiko; Li, Y.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00560_1 - 19-00560_12, 2020/06
Since the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, we have been developing a failure evaluation method that considers creep damage mechanisms using detailed three-dimensional finite element analysis model of lower head including penetration, stub tubes, and weld parts, etc., for the early completion of the decommissioning of the nuclear power plants in Fukushima Daiichi. For the finite element analysis, we have been obtaining material properties for which no data are provided in existing databases or in the literature. In particular, creep data corresponding to the high temperature region near the melting point of materials is important in evaluating creep deformation under severe accident conditions. In this study, we obtained the uniaxial tensile and creep properties for low-alloy steel, stainless steel, and Ni-based alloy. In particular, creep test data with long rupture times at high temperatures are expanded using a tensile test machine that can measure the elongation of test specimens in a noncontact measurement system. The parameters related to the failure evaluation were improved on the basis of the expanded creep database.
Miwa, Shuhei; Takase, Gaku; Imoto, Jumpei; Nishioka, Shunichiro; Miyahara, Naoya; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(3), p.291 - 300, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the evaluation of transport behavior of control material boron in a severe accident of BWR from the viewpoint of chemical effects on cesium and iodine behavior, boron chemistry during transportation in the high temperature region above 400 K was experimentally investigated. The heating tests of boron oxide specimen were conducted using the dedicated experimental apparatus reproducing fission product release and transport in steam atmosphere. Released boron oxide vapor was deposited above 1,000 K by the condensation onto stainless steel. The boron deposits and/or vapors significantly reacted with stainless steel above 1,000 K and formed the stable iron-boron mixed oxide (FeO) BO
BO . These results indicate that released boron from degraded BWR control blade in a severe accident could remain in the high temperature region such as a Reactor Pressure Vessel. Based on these results, it can be said that the existence of boron deposits in the high temperature region would decrease the amount of transported cesium vapors from a Reactor Pressure Vessel due to possible formation of low volatile cesium borate compounds by the reaction of boron deposits with cesium vapors.
. These results indicate that released boron from degraded BWR control blade in a severe accident could remain in the high temperature region such as a Reactor Pressure Vessel. Based on these results, it can be said that the existence of boron deposits in the high temperature region would decrease the amount of transported cesium vapors from a Reactor Pressure Vessel due to possible formation of low volatile cesium borate compounds by the reaction of boron deposits with cesium vapors.