Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawaguchi, Maho*; Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/10
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has been working on an experimental approach for evaluating the criticality of fuel debris produced by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNP) accident since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). As part of the approach, JAEA has modified the STAtic experiment Critical facilitY (STACY) for critical experiments to evaluate characteriscs of pseudo-fuel debris. As the preliminary analyses, we verified critical characteristics with major nuclear data libraries for the proposed core configuration patterns. The three-dimensional continuous-energy Monte Carlo neutron and photon transport code, SERPENT-V2.2.0 was used with the latest JENDL, JENDL-5. As a result, larger multiplication factors of JENDL-5 across the modified STACY core configuration patterns were evaluated in comparison to the other libraries. And,  H scattering and
H scattering and  U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S(
U fission sensitivity coefficients of JENDL-5 were different from those of the other libraries. Comparing among analyses with those libraries, the updated S( ,
,  ) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
) of JENDL-5 might affect the result of critical characteristics in the critical analyses for the modified STACY core configuration.
Shiba, Shigeki*; Iwahashi, Daiki*; Okawa, Tsuyoshi*; Gunji, Satoshi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) has tackled the experimental approach for determining the criticality of pseudo-fuel debris plausibly simulating actual fuel debris since 2014, collaborating with the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. To elucidate the characteristics of the pseudo-fuel debris, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency modified the STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) to conduct critical experiments simulating fuel debris. Thus, we proposed three types of modified STACY core configurations. In critical experiments in the modified STACY core, it is important to judge whether the proposed modified STACY core configurations are representative of molten core-concrete interaction debris or not. In this study, we built pseudo-fuel debris models considering a volume ratio of pseudo-fuel debris to moderation (V /V
/V ) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C
) and calculated uncertainty-based similarity values (C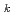 ) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V
) between the modified STACY core configurations and pseudo-fuel debris models using Tools for Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis Methodology Implementation-Indices and Parameters (TSUNAMI-IP) in SCALE 6.2. Consequently, the modified STACY core configuration loading structure rods we proposed completely resulted in high similarity to the pseudo-fuel debris models through V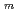 /V
/V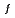 values. The main contributions to C
values. The main contributions to C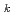 values were
values were  U
U 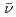 ,
,  U
U  , and
, and  Fe (n,
Fe (n, ), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
), except for the pseudo-fuel debris model, including extremely high concrete components.
Hirakawa, Yasushi; Yoshida, Eiichi; Gunji, Shigeru*
JAEA-Technology 2006-033, 22 Pages, 2006/06
The sodium removal technology containing radioactive nuclides is required for inspection and repair of sodium system components and decommissioning of sodium cooled fast reactors. In order to evaluate the efficient sodium removal conditions, the sodium removal rate by the moisture gas cleaning process was examined. Experiments were conducted by simulating residual sodium in the bottom of a vessel and in the crevice parts of components. The experimental parameters were sodium temperature, moisture concentration in career gas (N ), and surface area of sodium. (1)The effect of the moisture gas cleansing parameters has been investigated and quantitative data for the sodium removal rate were obtained in this study. (2)Sodium temperature and sodium-phase (liquid or solid) did not affect sodium removal rate from 80
), and surface area of sodium. (1)The effect of the moisture gas cleansing parameters has been investigated and quantitative data for the sodium removal rate were obtained in this study. (2)Sodium temperature and sodium-phase (liquid or solid) did not affect sodium removal rate from 80  C to 150
C to 150  C sodium temperature. However, at the 180
C sodium temperature. However, at the 180  C sodium temperature of sodium removal rate declined. (3)Moisture concentration in the nitrogen gas greatly affected the sodium removal rate increased with increasing moisture. (4)The sodium removal rate was influenced of sodium surface direction (facing upward or downward). Facing upward the sodium surface had higher sodium removal rate than facing downward. (5)The unstable rapid reaction similar to combustion was observed in some cases during experiments of sodium removal by wet nitrogen gas.
C sodium temperature of sodium removal rate declined. (3)Moisture concentration in the nitrogen gas greatly affected the sodium removal rate increased with increasing moisture. (4)The sodium removal rate was influenced of sodium surface direction (facing upward or downward). Facing upward the sodium surface had higher sodium removal rate than facing downward. (5)The unstable rapid reaction similar to combustion was observed in some cases during experiments of sodium removal by wet nitrogen gas.