Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Morooka, Satoshi; Tominaga, Aki; Tanida, Hajime; Shobu, Takahisa; Konno, Azusa; Owada, Kenji*; Ono, Naoko*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 528, p.151890_1 - 151890_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have developed an anomalous small-angle X-ray scattering (ASAXS) diffractometer in SPring-8 to investigate irradiation-induced nanostructural change in ion-beam irradiated stainless steel. A thermally-aged MA956 stainless steel sample displays power-law scattering that follows the Porod law at the magnitude of scattering vector, Q, below 0.5 nm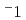 and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm
and an overlapped shoulder around 0.7 nm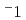 . After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
. After the ion-beam irradiation, the intensity of the shoulder remained unchanged, whereas that of the power-law scattering nearly doubled. This result indicates that none of the structural parameters of the Cr-rich nanoprecipitates, such as the number density, size, and interface roughness, were changed by the irradiation.
 ' precipitates in nickel based oxide dispersion-strengthened superalloys under high-temperature and heavy irradiation conditions
' precipitates in nickel based oxide dispersion-strengthened superalloys under high-temperature and heavy irradiation conditionsKonno, Azusa; Ono, Naoko*; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Kondo, Sosuke*; Hashitomi, Okinobu*; Kimura, Akihiko*
Materials Transactions, 60(11), p.2260 - 2266, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A stability of cuboidal  ' phase under heavy irradiation was studied for newly developed Ni-based Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) superalloy as a candidate for the core structural materials in VHTR or GFR. The ion irradiation was applied at 873K, 1073K, 1273K and the dose was 100 dpa. The
' phase under heavy irradiation was studied for newly developed Ni-based Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) superalloy as a candidate for the core structural materials in VHTR or GFR. The ion irradiation was applied at 873K, 1073K, 1273K and the dose was 100 dpa. The  ' phase remained the cuboidal shape at 873K but got out of the shape at 1073K after irradiation. Those growths can be explained by the Nelson-Hudson-Mazey (NHM) model. For the result of 1273K irradiation, however, huge
' phase remained the cuboidal shape at 873K but got out of the shape at 1073K after irradiation. Those growths can be explained by the Nelson-Hudson-Mazey (NHM) model. For the result of 1273K irradiation, however, huge  ' phase appeared in the whole irradiated area at the post irradiation-observation. This behavior is interpreted in terms of disordering of the ordered
' phase appeared in the whole irradiated area at the post irradiation-observation. This behavior is interpreted in terms of disordering of the ordered  ' phase due to cascade collision, and thus increasing Gibbs free energy of the disordered phase induces a change of the element distribution inside the irradiated area. The ordered
' phase due to cascade collision, and thus increasing Gibbs free energy of the disordered phase induces a change of the element distribution inside the irradiated area. The ordered  ' phase was reproduced from the disordered state at the cooling after ion irradiation.
' phase was reproduced from the disordered state at the cooling after ion irradiation.
Konno, Azusa
no journal, ,
High temperature fission reactor HTR is used at high temperature about 1000  C, so Ni-based alloys are expected to use the core components of it. But Ni-based alloys is happened intergranular embrittlement by transmutated He. Then, there is some report that Fe-based ODS steel is one of the most effective candidate to overcome the problem; it has an excellent irradiation resistance. Because cavity is segregated at the interface of the oxide particles and matrix. So, the aim of this study is to evaluate the He cavity trapping effect at the interface of oxide particles and matrix in Ni-based ODS alloy and compare with those of Fe-based ODS.
C, so Ni-based alloys are expected to use the core components of it. But Ni-based alloys is happened intergranular embrittlement by transmutated He. Then, there is some report that Fe-based ODS steel is one of the most effective candidate to overcome the problem; it has an excellent irradiation resistance. Because cavity is segregated at the interface of the oxide particles and matrix. So, the aim of this study is to evaluate the He cavity trapping effect at the interface of oxide particles and matrix in Ni-based ODS alloy and compare with those of Fe-based ODS.
Konno, Azusa; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Kumada, Takayuki; Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Morooka, Satoshi; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Ono, Naoko*; Shobu, Takahisa; et al.
no journal, ,
Duplex stainless steels is composed by austenite and ferrite phases, offering superior toughness, high strength properties, good weldability, and corrosion-resistance. It has been used as the heat exchanger components for the chemical industrial plants and pipes for the Pressurized light-Water Reactors (PWR). However, the duplex stainless steels is also known to suffer from the embrittlement due to the phase separation into the Cr-rich phase and Fe-rich one when it is annealed at longer time at the temperature over 300 degrees. In this study, we focused on the Anomalous Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (A-SAXS) technique that can analyze "arbitrary element" by using absorption edge of a specific element and estimated the chromium separation quantitatively by utilizing the A-SAXS method, considering the availability of this new technique as the quantitative and non-destructive analysis method for microstructure in metallic material.
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Owada, Kenji*; Tanida, Hajime; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In steel materials, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method at BL22XU.
Tominaga, Aki; Oba, Yojiro; Shobu, Takahisa; Tanida, Hajime; Owada, Kenji*; Konno, Azusa; Morooka, Satoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki
no journal, ,
In development of oxide-dispersed ferritic steels, it is known that precipitation of Cr rich phase hardens ferrite phase and decreases toughness in base material. Small angle X-ray scattering is a promising method for analysis of this precipitation process because the precipitate is nanometer size. However, it is usually difficult to separate the scattering between the Fe phase and Cr phase since Fe and Cr are close in atomic number. Therefore, in order to observe the state of phase separation of Cr, we developed an anomalous X-ray small angle scattering (A-SAXS) method using synchrotron radiation.
Konno, Azusa; Ono, Naoko*; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Kondo, Sosuke*; Hashitomi, Okinobu*; Kimura, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
A newly developed Ni-based Oxide Dispersion Strengthened (ODS) superalloy as a candidate for the core structural materials in VHTR or GFR is studied to evaluate the stability of cuboidal-gamma prime phase under heavy irradiation in the presence of oxide particles. The ion irradiation was applied at 873K, 1073K, 1273K and the dose was 100 dpa. The gamma prime phase kept the cuboidal shape at 873K and got out of the shape at 1073K after irradiation, where these growths can be explained by the NHM model. For the result of 1273K irradiation, where huge gamma prime phase appeared in the whole irradiated area, changing Gibbs free energy by irradiation could induce the order-disorder transformation.

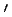 precipitates in nickel based oxide dispersion-strengthened superalloys under severe conditions
precipitates in nickel based oxide dispersion-strengthened superalloys under severe conditionsKonno, Azusa; Ono, Naoko*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Kondo, Sosuke*; Hashitomi, Okinobu*; Kimura, Akihiko*
no journal, ,
It is essential to develop the structural materials in Very High-temperature Reactors (VHTR) or Gas-cooled Fast Reactors (GFR) which reactor core environment is severe as the temperature is over 1273 K and irradiation level is up to 100 dpa. In the past, Ni-based alloys which are superior to Fe-based alloys as high-temperature strength were studied because of its 
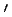 precipitates for reactor core materials. However,
precipitates for reactor core materials. However, 
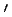 dissolves and reprecipitates at grain boundaries by irradiation at about 873 K. In order to show the suppression of this embrittlement, we newly developed a
dissolves and reprecipitates at grain boundaries by irradiation at about 873 K. In order to show the suppression of this embrittlement, we newly developed a 
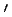 precipitation type Ni-based Oxide Dispersion-Strengthened (ODS) superalloy in which nano-sizeed oxide particles are finely dispersed. In this research, the stability of cuboidal
precipitation type Ni-based Oxide Dispersion-Strengthened (ODS) superalloy in which nano-sizeed oxide particles are finely dispersed. In this research, the stability of cuboidal 
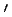 precipitates under heavy irradiation was studied for newly developed Ni-based ODS superalloys, to explore the suitability of these as core materials. The specimen composition was equivalent to the MS4 produced by modifying the commercial superalloy CMSX10 to which the oxide particles are added.
precipitates under heavy irradiation was studied for newly developed Ni-based ODS superalloys, to explore the suitability of these as core materials. The specimen composition was equivalent to the MS4 produced by modifying the commercial superalloy CMSX10 to which the oxide particles are added.
Konno, Azusa; Oba, Yojiro; Tominaga, Aki; Morooka, Satoshi; Ono, Naoko*; Hashimoto, Naoyuki*; Ukai, Shigeharu; Owada, Kenji*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,
An ODS alloy is one of the promising candidate materials applicable to the fusion reactor because of its high-temperature creep strength and irradiation resistance. However, the ODS ferritic stainless steel with high Cr content sometimes suffers from the embrittlement related to phase separation below 748 K for a long term using in the reactor. It is, therefore, an important issue to understand embrittlement phenomena from not only macrostructural viewpoint but also microstructural one. Anomalous Small Angle X-ray Scattering (A-SAXS) is a unique and potential evaluation method that can analyze complex microstructure. This method can extract the signal only from an element of interest to implant the X-ray of the wavelength near orbit electron of the element. In this study, we performed both the A-SAXS analysis and TEM observation for high Cr-ODS alloy in order to assess the applicability of the A-SAXS technique as a microstructure determination and compared the A-SAXS signal with the TEM micrograph. The specimen of the commercial MA956 (Fe-20Cr-4.8Al-0.4Ti-0.02C-0.4Y O
O (mass%)) were thermally-aged at 748 K for 1, 10, 100 and 1000 hrs, and measured using the A-SAXS diffractometer at BL22XU in SPring-8 and a TEM. The A-SAXS data reveal that the average size of Cr precipitations increases with increasing the aging time. Also, using the A-SAXS profiles, it was estimated that there were two cases; one is the case that the microstructure does have a distinct interface between the matrix and Cr precipitate. The other case is the microstructure does not have the distinct interface. On the other hand, in TEM observation, the periodic modulated structure was observed for 10 hrs thermally-aged sample, and the sphere precipitation was confirmed for 100 hrs thermally-aged sample. It was suggested that there would be a crucial phase separation mode from spinodal decomposition to nucleation-growth between 10 and 100 hrs.
(mass%)) were thermally-aged at 748 K for 1, 10, 100 and 1000 hrs, and measured using the A-SAXS diffractometer at BL22XU in SPring-8 and a TEM. The A-SAXS data reveal that the average size of Cr precipitations increases with increasing the aging time. Also, using the A-SAXS profiles, it was estimated that there were two cases; one is the case that the microstructure does have a distinct interface between the matrix and Cr precipitate. The other case is the microstructure does not have the distinct interface. On the other hand, in TEM observation, the periodic modulated structure was observed for 10 hrs thermally-aged sample, and the sphere precipitation was confirmed for 100 hrs thermally-aged sample. It was suggested that there would be a crucial phase separation mode from spinodal decomposition to nucleation-growth between 10 and 100 hrs.
Abe, Yosuke; Sato, Yuki*; Okubo, Nariaki; Konno, Azusa
no journal, ,
We examined a role of 1D migration of SIA clusters in their nucleation and growth behavior in electron-irradiated alpha-iron below 300 K. Using 1D random walk theory, we derived the analytical expression of trapping probability of SIA clusters by impurity atoms within a foil specimen. By incorporating this modelinto a reaction rate theory, it was shown that the saturated cluster number density significantly decreases due to the decrease in the cluster nucleation rate. Also, the dependence of the irradiation beam intensity on the saturated cluster number density becomes weaker when the absorption probability of one-dimensionally migrating SIA clusters by other stationary SIA clusters is higher than the trapping probability by impurity atoms. The irradiation-induced detrapping increases the annihilation rate of the liberated SIA clusters at specimen surfaces, leading to the decrease in the cluster number density at higher irradiation doses, as observed experimentally.