Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Osamu*; Shibui, Yohei*; Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(1), p.16_1 - 16_15, 2020/03
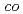 -tetrafluoroethylene) films using different media
-tetrafluoroethylene) films using different mediaNuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 40(4), p.359 - 362, 2015/12
The ion-track grafting of a vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) into a poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) film is necessary for preparing nanostructured hydroxide-ion-conductive electrolyte membranes. A key for success here is to obtain as high graft levels as possible (for higher conductivity) in a smaller number of tracks (for improving the other membrane properties). To this end, therefore, the effect of the medium for the VBC grafting was investigated as part of our continuing effort to optimize the experimental conditions. A 25  m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV
m-thick ETFE film was irradiated in a vacuum chamber with 560 MeV  Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60
Xe at different fluences, and then the grafting was performed by immersing the irradiated films in a 20vol% VBC monomer at 60 C. A medium was a mixture of water (H
C. A medium was a mixture of water (H O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H
O) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at different volume ratios. The degree of grafting increased as the H O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H
O content became higher, and reached a maximum in pure H O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
O. These results can be explained by considering the well-known Trommsdorff effect, in which poor solubility of the grafted polymer in polar media leads to an increased polymerization rate probably due to a lower termination rate.
Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi*; Morii, Yukio*; Gong, W.; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo; Lutterotti, L.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.031022_1 - 031022_6, 2015/09
 -methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancerSuzuki, Shigemasa*; Kaira, Kyoichi*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Ishioka, Noriko; Soda, Makoto*; Yokobori, Takehiko*; Miyazaki, Tatsuya*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Kanai, Yoshikatsu*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(8), p.1985 - 1991, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:60.43(Oncology)Kato, Sho; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.149 - 152, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)We implanted 100 keV W in unpolished GC substrates at nominal fluences up to
in unpolished GC substrates at nominal fluences up to 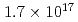 ions/cm
ions/cm . The implanted samples were electrochemically anodized in a NaOH aqueous solution to etch the surface layer. The analyses were performed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XPS W 4f spectra indicated the formation of carbides as reported previously. The electrochemical etching clearly increased the W concentration on the surface. According to the RBS results, half of the implanted W atoms were retained in the substrate, while the rest should escape to the etching solution. The cross-sectional TEM image revealed a uniform distribution of WC particles with a diameter of less than 10 nm just near the surface region.
. The implanted samples were electrochemically anodized in a NaOH aqueous solution to etch the surface layer. The analyses were performed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XPS W 4f spectra indicated the formation of carbides as reported previously. The electrochemical etching clearly increased the W concentration on the surface. According to the RBS results, half of the implanted W atoms were retained in the substrate, while the rest should escape to the etching solution. The cross-sectional TEM image revealed a uniform distribution of WC particles with a diameter of less than 10 nm just near the surface region.
Xu, P. G.; Tomota, Yo*; Vogel, S. C.*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 33(5), p.389 - 395, 2013/08
Kato, Sho; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.81 - 84, 2013/03
Nanoparticles were formed by 100 keV tungsten-ion implantation in unpolished glassy carbon substrates at nominal fluences of 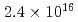 -
- 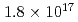 ions/cm
ions/cm . The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
. The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Xu, P. G.
Sosei To Kako, 54(625), p.106 - 110, 2013/02
no abstracts in English
Kurata, Yuji; Sato, Hidetomo*; Yokota, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Proceedings of 2nd International Workshop on Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems (SMINS-2), p.177 - 188, 2012/12
Liquid lead-bismuth is a candidate material used for innovative nuclear systems such as accelerator driven reactors and fast reactors. Development of corrosion resistant materials in liquid lead-bismuth is one of important research subjects to realize these systems. In this study, improvement of corrosion properties in lead-bismuth by Al alloy coating was investigated. Aluminum alloys were coated on 316SS using sheets made of Al, Ti and Fe powders, and laser heating. Adjustments of chemical composition in sheets and scanning rate of laser beam enabled us to control Al concentration in coating layers. The corrosion tests were conducted at 550 C for 1,000 hours or 3,000 hours in oxygen-controlled lead-bismuth. As a result of the corrosion tests, it was found that the coating with Al concentration of 5 to 8 mass% showed good corrosion resistance.
C for 1,000 hours or 3,000 hours in oxygen-controlled lead-bismuth. As a result of the corrosion tests, it was found that the coating with Al concentration of 5 to 8 mass% showed good corrosion resistance.
Fukui, Kunihiro*; Igawa, Yusuke*; Arimitsu, Naoki*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Segawa, Tomoomi; Fujii, Kanichi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Hideto*
Chemical Engineering Journal, 211-212, p.1 - 8, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.13(Engineering, Environmental)The process for synthesizing metallic oxide powders by the microwave denitration method was investigated using hexahydrated nickel nitrate and trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solutions, and the electrical field and the temperature distributions in the reactor were numerically simulated. Although CuO powder can be obtained from a trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solution by the microwave denitration method, a hexahydrated nickel nitrate aqueous solution cannot be heated up to over 270  C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Hiroshi; Moriai, Atsushi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Yukutake, Eitaro*
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-46-Kai X Sen Zairyo Kyodo Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.24 - 27, 2012/07
Kurata, Yuji; Yokota, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 134(6), p.062902_1 - 062902_7, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:39.15(Engineering, Mechanical)Nuclear systems using lead alloys are one of the promising reactor concepts with improved safety. This paper focuses on development of Al-alloy coating for nuclear systems using liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE). It is necessary to improve corrosion resistance of steels because of high corrosiveness of liquid LBE at high temperatures. An Al-alloy coating method using Al, Ti and Fe powders and laser beam heating has been developed. Main defects formed in an Al-powder-alloy coating process are surface defects and cracks. Conditions required to avoid these defects have been studied. According to results of the corrosion tests at 550 C in liquid LBE, the Al-alloy coating layers on 316SS prevent severe corrosion attack observed in 316SS without coating. The good corrosion resistance of the Al-alloy coating is based on the thin Al-oxide film regenerated in liquid LBE. It is estimated that the range of the adequate Al concentration in the coating layer is from 4 to 12 wt%.
C in liquid LBE, the Al-alloy coating layers on 316SS prevent severe corrosion attack observed in 316SS without coating. The good corrosion resistance of the Al-alloy coating is based on the thin Al-oxide film regenerated in liquid LBE. It is estimated that the range of the adequate Al concentration in the coating layer is from 4 to 12 wt%.
Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Yamanaka, Keisuke*; Ishino, Mayuko*; Shinohara, Yasuhiro*; Nagai, Kensuke*; Tsuru, Eiji*; Xu, P. G.
Tetsu To Hagane, 98(6), p.262 - 266, 2012/06
Kurata, Yuji; Yokota, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 424(1-3), p.237 - 246, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:87.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An Al-alloy coating method using Al, Ti and Fe powders and the laser beam heating has been developed for nuclear systems using liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE). The main defects formed in the Al-alloy coating process are surface defects and cracks. Conditions required to avoid such defects have been studied. A static corrosion test was conducted in liquid LBE at the controlled oxygen concentrations of 10 to 10
to 10 wt% at 550
wt% at 550 C for 3000h. The Al-alloy coating layer on 316SS prevents severe corrosion attack such as Ni dissolution, partial loss of grains and LBE penetration observed in the 316SS without Al-alloy coating. The Al-alloy coating layer, which is formed without surface defects and cracks under the optimum condition, exhibits good corrosion resistance in liquid LBE.
C for 3000h. The Al-alloy coating layer on 316SS prevents severe corrosion attack such as Ni dissolution, partial loss of grains and LBE penetration observed in the 316SS without Al-alloy coating. The Al-alloy coating layer, which is formed without surface defects and cracks under the optimum condition, exhibits good corrosion resistance in liquid LBE.
Xu, P. G.; Akita, Koichi; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-61-Ki Tsujo Sokai, Gakujutsu Koenkai Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2012/05
Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Proceedings in Radiochemistry, 1(1), p.409 - 413, 2011/09
In polymer electrolyte fuel cells, the water transport properties of the polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) would affect the cell performance. In this study, we investigated the self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules in the PEMs by using radioactivated-tracer permeation technique. The PEMs were synthesized from crosslinked-polytetrafluoroethylene (cPTFE) by the radiation-induced grafting method. The Dw of the PEMs increased with their ion exchange capacities (IECs), and reached the maximum value of 3.7 10
10 m
m /s at the IEC of 2.4 meq/g. interestingly, commercially-available Nafion membrane exhibited the highest Dw of 4.9
/s at the IEC of 2.4 meq/g. interestingly, commercially-available Nafion membrane exhibited the highest Dw of 4.9 10
10 m
m /s despite of its low IEC. The lower Dw in the cPTFE PEMs is probably attributed to the geometry of hydrophilic regions phase-separated from the surrounding hydrophobic polymers.
/s despite of its low IEC. The lower Dw in the cPTFE PEMs is probably attributed to the geometry of hydrophilic regions phase-separated from the surrounding hydrophobic polymers.
Kurata, Yuji; Yokota, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Proceedings of ASME 2011 Small Modular Reactors Symposium (SMR 2011) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/09
Small and medium reactors using lead alloys as coolant are one of the promising reactor concepts with improved safety. This paper focuses on development of Al-alloy coating for nuclear systems using liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE). Since corrosion attack becomes severe against steels at high temperatures, it is necessary to improve corrosion resistance. An Al-alloy coating method using Al, Ti and Fe powders, and laser beam heating has been developed. Main defects formed in an Al-powder-alloy coating process are surface defects and cracks. Conditions required to avoid these defects were found. According to results of the corrosion tests at 550  C in liquid LBE, the Al-alloy coating layers on 316SS protect severe corrosion attack observed in 316SS without coating. From the viewpoints of the soundness of coating layers and preservation of their corrosion resistance, it is estimated that the range of the adequate Al concentration in the coating layer is from 4 to 12 wt%.
C in liquid LBE, the Al-alloy coating layers on 316SS protect severe corrosion attack observed in 316SS without coating. From the viewpoints of the soundness of coating layers and preservation of their corrosion resistance, it is estimated that the range of the adequate Al concentration in the coating layer is from 4 to 12 wt%.
Kurata, Yuji; Sato, Hidetomo*; Yokota, Hitoshi*; Suzuki, Tetsuya*
Materials Transactions, 52(5), p.1033 - 1040, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A new Al-alloy coating method using Al, Ti and Fe powders has been applied to 316SS in order to develop corrosion resistant coating in lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE). The 316SS plates with coating layers of different Al concentrations were tested at 550 C for 1000h in liquid LBE with controlled oxygen concentrations of 10
C for 1000h in liquid LBE with controlled oxygen concentrations of 10
 10
10 mass%. While surface oxidation and grain boundary corrosion accompanied by LBE penetration are observed in 316SS without Al-alloy coating, the Al-alloy coating is effective to protect such severe corrosion attacks in LBE. Although the coating layer containing 2.8 mass% Al does not always keep sufficient corrosion resistance, good corrosion resistance is obtained in the coating layer where the average Al concentration is 4.2 mass%. Cracks are found in the coating layer containing 17.8 mass% Al. The Al-powder-alloy coating applied to 316SS is promising as a corrosion resistant coating method in liquid LBE environment.
mass%. While surface oxidation and grain boundary corrosion accompanied by LBE penetration are observed in 316SS without Al-alloy coating, the Al-alloy coating is effective to protect such severe corrosion attacks in LBE. Although the coating layer containing 2.8 mass% Al does not always keep sufficient corrosion resistance, good corrosion resistance is obtained in the coating layer where the average Al concentration is 4.2 mass%. Cracks are found in the coating layer containing 17.8 mass% Al. The Al-powder-alloy coating applied to 316SS is promising as a corrosion resistant coating method in liquid LBE environment.
Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Ozawa, Taku*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Maekawa, Yasunari
ECS Transactions, 33(1), p.1067 - 1078, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:89.29(Electrochemistry)In order to investigate water transport in polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs), we calculated the self-diffusion coefficient of water, D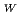 , by dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulation. The simulation target materials are Nafion and radiation-grafted PEMs in the fully-hydrated states. D
, by dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulation. The simulation target materials are Nafion and radiation-grafted PEMs in the fully-hydrated states. D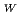 was obtained by the following steps: (1) molecular modeling with the coarse-grained particles representing groups of several atoms; (2) calculation of the water particle diffusivity, D
was obtained by the following steps: (1) molecular modeling with the coarse-grained particles representing groups of several atoms; (2) calculation of the water particle diffusivity, D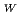
 , in the PEMs; (3) determination of the unit time in the DPD simulation; (4) conversion of D
, in the PEMs; (3) determination of the unit time in the DPD simulation; (4) conversion of D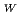
 of the PEMs into D
of the PEMs into D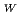 in the standard SI unit. Interestingly, D
in the standard SI unit. Interestingly, D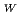 was found to decrease with the diffusion time period,
was found to decrease with the diffusion time period,  t, probably owing to the geometrical confinement effect by water-transport hydrophilic regions. Quantitative analysis of this D
t, probably owing to the geometrical confinement effect by water-transport hydrophilic regions. Quantitative analysis of this D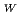 -
- t relationship provided us with the size of hydrophilic regions.
t relationship provided us with the size of hydrophilic regions.
Sawada, Shinichi; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Ozawa, Taku*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 67(3), p.224 - 227, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:31.95(Polymer Science)We investigated for the first time the mesoscopic structure of crosslinked-polytetrafluoroethylene (cPTFE) based radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) by using dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulation. Based on the molecular structures, the fully-hydrated PEM systems were constructed with the coarse-grained particles representing several atom groups. In the equilibrium state, water appeared to percolate into poly(styrene sulfonic acid) (PSSA) graft chains to give a mixed phase, separated from the hydrophobic PTFE chains. This phase-separation picture is quite different from that of Nafion, in which only water particles were gathered excluding any polymer parts (a so-called water cluster). In order to obtain a deep insight into the phase-separation structure, the radial distribution function between water particles was calculated. As a result, there were found to be small water clusters with a diameter of only 1.8 nm in the water/grafts mixture regions.