Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuru, Daigo; Sakurai, Shinji; Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Ozaki, Hidetsugu; Seki, Yohji; Yokoyama, Kenji; Suzuki, Satoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1403 - 1406, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
Fusion Engineering and Design, 98-99, p.1113 - 1117, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kamada, Yutaka; Barabaschi, P.*; Ishida, Shinichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Lackner, K.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Bolzonella, T.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Matsunaga, Go; Yoshida, Maiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073011_1 - 073011_11, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:92.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Masaki, Kei; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Ezato, Koichiro; Suzuki, Satoshi; Sakasai, Akira
Fusion Engineering and Design, 85(10-12), p.1732 - 1735, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Steady-state research is indispensable to establish scientific and technological basis for the next fusion devices. In JT-60, long pulse operation of up to 65s (OH) with a neutral beam heating power of  12 MW (30s) was conducted to investigate the plasma behavior in several tens of seconds. However, the structure of the JT-60U first wall, which was composed of bolted graphite tiles and backings, restricted the flexibility of the plasma operation, because the first wall was not actively cooled. To improve the heat transfer characteristics of the first wall taking into account the cost, a candidate is to insert a graphite sheet between the graphite tile and the backing plate. Aiming at a design study for next fusion devices, the heat transfer characteristics of the first wall structure were investigated with a variety of graphite sheets and fixing-bolt torque conditions. The first wall mockup used for the experiment was composed of three CFC tiles (125(L)
12 MW (30s) was conducted to investigate the plasma behavior in several tens of seconds. However, the structure of the JT-60U first wall, which was composed of bolted graphite tiles and backings, restricted the flexibility of the plasma operation, because the first wall was not actively cooled. To improve the heat transfer characteristics of the first wall taking into account the cost, a candidate is to insert a graphite sheet between the graphite tile and the backing plate. Aiming at a design study for next fusion devices, the heat transfer characteristics of the first wall structure were investigated with a variety of graphite sheets and fixing-bolt torque conditions. The first wall mockup used for the experiment was composed of three CFC tiles (125(L)  110(W)
110(W) 24(T) mm for each tile) and a cupper-alloy heat sink (377(L)
24(T) mm for each tile) and a cupper-alloy heat sink (377(L) 100(W)
100(W) 20(T) mm) with two cooling channels of 10 mm diameter. Four types of the graphite sheets, 0.1-mm thickness PGS (Pyrolytic Graphite Sheet; Panasoic Co., Ltd), 0.2-mm PF (Perma Foil; Toyo Tanso Co., Ltd) 0.38-mm PF, 0.6-mm PF, were examined in the experiment. The heat load tests of the mockup were performed with the heat fluxes of 1 and 3 MW/m
20(T) mm) with two cooling channels of 10 mm diameter. Four types of the graphite sheets, 0.1-mm thickness PGS (Pyrolytic Graphite Sheet; Panasoic Co., Ltd), 0.2-mm PF (Perma Foil; Toyo Tanso Co., Ltd) 0.38-mm PF, 0.6-mm PF, were examined in the experiment. The heat load tests of the mockup were performed with the heat fluxes of 1 and 3 MW/m on the JAERI electron beam irradiation stand. The experimental results showed that the structure with 0.1-mm thickness
on the JAERI electron beam irradiation stand. The experimental results showed that the structure with 0.1-mm thickness  3 PGSs had the highest heat transfer performance in the experiment. The first wall structure with the PGS sheets withstood the heat flux of 1 MW/m
3 PGSs had the highest heat transfer performance in the experiment. The first wall structure with the PGS sheets withstood the heat flux of 1 MW/m
 100s. The maximum surface temperature of the CFC tile was 500
100s. The maximum surface temperature of the CFC tile was 500 C. Furthermore, the results indicated that the structure could be used at the steady-state condition with the heat flux of
C. Furthermore, the results indicated that the structure could be used at the steady-state condition with the heat flux of  1 MW/m
1 MW/m . In the paper, detail of the results will be presented and discussed.
. In the paper, detail of the results will be presented and discussed.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:139 Percentile:97.7(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
Higashijima, Satoru; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Yokoyama, Kenji; Kashiwa, Yoshitoshi; Masaki, Kei; Shibama, Yusuke; Takechi, Manabu; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(2-6), p.949 - 952, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)An upgrading device of JT-60 tokamak with fully superconducting coils (JT-60SA) is constructed under both the Japanese domestic program and the international program "Broader Approach". The maximum heat flux to JT-60SA divertor is estimated to 15 MW/m for 100 s, and a monoblock-type CFC divertor armor is promising. The JT-60SA armor consists of CFC monoblocks, a cooling CuCrZr screw-tube, and a thin OFHC-Cu buffer layer, and the brazed joints are essential for the armor. Metalization inside CFC monoblock is applied for further improvement, and we confirmed again that the mock-up has heat removal capability in excess of ITER requirement. For optimization of the fabrication method and understanding of the production yield, the mock-ups corresponding to quantity produced in one furnace is also produced, and the half of the mock-ups could remove 15 MW/m
for 100 s, and a monoblock-type CFC divertor armor is promising. The JT-60SA armor consists of CFC monoblocks, a cooling CuCrZr screw-tube, and a thin OFHC-Cu buffer layer, and the brazed joints are essential for the armor. Metalization inside CFC monoblock is applied for further improvement, and we confirmed again that the mock-up has heat removal capability in excess of ITER requirement. For optimization of the fabrication method and understanding of the production yield, the mock-ups corresponding to quantity produced in one furnace is also produced, and the half of the mock-ups could remove 15 MW/m as required. This summarizes the recent progress of design and mock-up test results for JT-60SA divertor armor.
as required. This summarizes the recent progress of design and mock-up test results for JT-60SA divertor armor.
Matsukawa, Makoto; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Hayashi, Takao; Higashijima, Satoru; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ishida, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.795 - 803, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Fujita, Takaaki; Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Bialek, J.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1512 - 1523, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:63.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Design of modification of JT-60U, JT-60SA, has been optimized in viewpoint of plasma control, and operation regimes have been evaluated. Upper and lower divertors with different geometry are prepared for flexibility of plasma shape control. The beam lines of negative-ion NBI are shifted downward for off-axis current drive, in order to obtain a weak/reversed shear plasma. The feedback control coils along the port hole in the stabilizing plate are found effective to suppress the resistive wall mode (RWM) and sustain high 
 close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
close to the ideal wall limit. The regime of full current drive operation has been extended with upgraded heating and current drive power. Full current drive operation for 100 s with reactor-relevant high values of normalized beta and bootstrap current fraction (
 = 2.4 MA,
= 2.4 MA, 
 = 4.4,
= 4.4, 
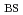 = 0.70,
= 0.70, 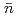
 /
/
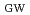 = 0.86, H
= 0.86, H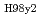 = 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration (
= 1.3) is expected in a highly-shaped low-aspect-ratio configuration ( = 2.65). High
= 2.65). High 
 , high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
, high-density ELMy H-mode is also expected.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Kizu, Kaname; Kurita, Genichi; Masaki, Kei; Matsukawa, Makoto; Miura, Yukitoshi; Sakurai, Shinji; Sukegawa, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(5-14), p.541 - 547, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)JT-60SA is positioned as the ITER satellite tokamak to conduct research elements to support and supplement ITER towards DEMO under the joint collaboration of Japan and EU. After the discussions in JA-EU Satellite Tokamak Working Group in 2005, the heating power is increased up to 41MW, 100s to ensure the ITER support research. With such increased heating power, the prospective plasma performances are analysed by the equilibrium and transport analysis codes. Operation window of a fully non-inductive current drive is extended to high density region. Simultaneous achievement of high equivalent Q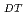 and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
and high normalised beta is also expected in wide operational margin. Those prospects strongly indicate that JT-60SA is suitable machine to conduct the advanced research orienting to ITER and DEMO.
Shibama, Yusuke; Arai, Takashi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Suzuki, Yutaka; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Miya, Naoyuki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.2462 - 2470, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The structural design of the tile as a ripple reduction for toroidal magnetic field in JT-60U was outlined. 8Cr-2W-0.2V ferritic steel plates were fabricated and mechanical and vacuum properties were evaluated to assess the design conditions. Tensile properties were uniform in yield and tensile strength at ambient temperature and sufficient strength as the structural integrity at operational temperature of 423 K and 573 K. Vacuum property was measured with the baking at 473 K and similar to the conventional stainless steel but not satisfy the JT-60 standard of the in-situ material of the vacuum vessel. The ferritic steel was judged as an installable because of that the JT-60 baking temperature is 573 K higher than this test temperature of 473 K, and of that residual out-gassing was hydrogen which was the fuel of the operational plasma.
Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Ishikawa, Masao; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Yutaka; Masaki, Kei; Naito, Osamu; Kurihara, Kenichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.997 - 1004, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:40 Percentile:78.29(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Ferritic steel plates have been installed to improve the energetic ion confinement through reducing a toroidal magnetic field ripple. Aiming at cost-effective installation, orbit following calculations of energetic ions were performed for a design of ferritic installation on JT-60U by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field Orbit-Following Monte-Carlo (F3D OFMC) code. The installed ferritic steel adds the non-linear magnetic field on magnetic sensors for a plasma control and an equilibrium calculation. The code for a real-time control has been modified to take into account the magnetic field by ferritic steel. The plasma operation was successfully resumed and a real-time plasma control was successfully carried out after usual preparation processes. The heat load measurement indicates the improved confinement of energetic ions. These results are important for practical application of ferritic steel which is a leading candidate of a structural material on a demo reactor.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.892 - 899, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.53(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The concept for a compact DEMO reactor named "SlimCS" is presented. Distinctive features of the concept is low aspect ratio ( = 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low-
= 2.6) and use of a reduced-size center solenoid (CS) which has a function of plasma shaping rather than poloidal flux supply. The reduced-size CS enables us to introduce a thin toroidal field (TF) coil system which contributes to reducing the weight and construction cost of the reactor. SlimCS is as compact as advanced commercial reactor designs such as ARIES-RS and produces 1 GWe in spite of moderate requirements for plasma parameters. Merits of low- , i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
, i.e. vertical stability for high elongation and high beta limit are responsible for such reasonable physics requirements.
Sasajima, Tadayuki; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibama, Yusuke; Hayashi, Takao; Suzuki, Yutaka; Takahashi, Ryukichi
Heisei-18-Nendo Nagoya Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Sochi Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.148 - 151, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Ishikawa, Masao; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Yutaka; Masaki, Kei; Naito, Osamu; Kurihara, Kenichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Ferritic steel plates have been installed to improve the energetic ion confinement through reducing a toroidal magnetic field ripple. Aiming at cost-effective installation, orbit following calculations of energetic ions were performed for a design of ferritic installation on JT-60U by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field Orbit-Following Monte-Carlo (F3D OFMC) code. The installed ferritic steel adds the non-linear magnetic field on magnetic sensors for a plasma control and an equilibrium calculation. The code for a real-time control have been modified to take into account the magnetic field by ferritic steel. The plasma operation was successfully resumed and a real-time plasma control was successfully carried out after usual preparation processes. The heat load measurement indicates the improved confinement of energetic ions. These results are important for practical application of ferritic steel which is a leading candidate of a structural material on a demo reactor.
Kudo, Yusuke; Sawai, Tomotsugu; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Suzuki, Yutaka; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Hayashi, Takao; Takahashi, Ryukichi*; Honda, Masao; Jitsukawa, Shiro; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49(96), p.S297 - S301, 2006/12
Installation of ferritic steel tiles was proposed in JT-60U to reduce the toroidal magnetic field ripple and to improve the fast ion loss, which degrades heating efficiency and increases heat load on plasma facing component under large volume plasma operations. We selected a 8Cr-2W-0.2V ferritic steel with the cost-effectiveness, in which concentration limits of activation elements in F82H were relaxed because of the less number of neutron generations from deuterium operations on JT-60U. The fabricated ferritic steel has clear tempered martensitic microstructure, and sufficient magnetic and mechanical properties. The saturated magnetization was estimated to 1.7 Tesla at 573 K, lower than expected, but effectiveness in JT-60U was confirmed by numerical analyses. To research the effect of material conditions, such as microstructure and heat treatment, on saturated magnetization of the ferritic steel based on 8-9Cr is important for the future fusion reactors which will be planned to install the ferritic steel as the in-vessel components.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Sakurai, Shinji; Hayashi, Takao; Shibama, Yusuke; Isono, Takaaki; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/10
no abstracts in English
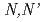 -dialkyl-2,6-pyridinedimethanaminium halide
-dialkyl-2,6-pyridinedimethanaminium halideKobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Sugo, Yumi; Suda, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Fujii, Yuki*; Nakano, Yoshiharu*
Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 43(3), p.549 - 557, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:13.41(Chemistry, Organic)Shinohara, Koji; Suzuki, Yutaka; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Fujita, Takaaki; Miura, Yukitoshi
NIFS-PROC-63, p.158 - 162, 2006/04
For the further pursuit of the steady-state advanced tokamak research, the ferritic insertion was proposed to reduce the toroidal field (TF) ripple. The reduction of energetic ion loss due to the TF ripple reduction brings: (1) the enhancement of the heating and current drive "effective" efficiency, (2) the extended pulse length and the improved efficiency of RF injection due to the reduced heat flux on antennas and improved coupling between antennas and a plasma, (3) the availability of a wall stabilization without losing heating power, and (4) the possibility of an enhanced availability of the rotation control to improve the MHD stability and transport. The design work of ferritic inserts was carried out aiming at an effective, machine-safe, and short-term installation. Here, the design work for ferritic inserts is described from the viewpoint of the behavior of energetic ions. The confinement of energetic ions and the absence of the unfavorable heat flux on the first wall was assessed by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field OFMC code, which was developed for a ferrite insert program in JFT-2M. In the final design, the confinement of energetic ions is improved by about 1.3 times in a large volume plasma with Bt0 = 1.9T.