Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Nankawa, Takuya; Onuki, Toshihiko
Chemistry Letters, 42(8), p.888 - 890, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Yoshida, Takahiro*
Energy Procedia, 39, p.175 - 182, 2013/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:84.68(Energy & Fuels)Accumulation ability of actinides and lanthanides by microorganisms has been studied. In the presence of organic acids, reduced U(IV) by microorganism was still dissolved, and Ce(IV) was present by complexing with Fe-chelate agents, causing Ce anomaly in the adsorption of lanthanides series elements. We introduce the application of these ability to Cs remediation.
 ST13
ST13 in the family
in the family 
Sugiyama, Tomoyasu*; Sugito, Hironori*; Mamiya, Ko*; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Ando, Katsuhiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 113(3), p.367 - 371, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:67.71(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)An isolated strain  ST13
ST13 was examined for the reducing activity of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)). XANES analysis of the precipitate shows the presence of Cr(OH)
was examined for the reducing activity of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)). XANES analysis of the precipitate shows the presence of Cr(OH) , indicating the bacterial reduction of Cr(VI) to trivalent chromium (Cr(III)). The bacterial Cr(VI) reduction was more efficient in minimal medium supplemented with molasses than with glucose. These results strongly suggest that the isolate
, indicating the bacterial reduction of Cr(VI) to trivalent chromium (Cr(III)). The bacterial Cr(VI) reduction was more efficient in minimal medium supplemented with molasses than with glucose. These results strongly suggest that the isolate  ST13
ST13 is a novel actinobacterium with Cr(VI) reducing activity that is stimulated by molasses.
is a novel actinobacterium with Cr(VI) reducing activity that is stimulated by molasses.
Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Iefuji, Haruyuki*; Sakai, Takuro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(8), p.1206 - 1213, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:53.37(Nuclear Science & Technology)The accumulation and chemical states change of Co have been studied to elucidate the role of yeast  in the migration of radioactive-cobalt in the environment. These results indicate that the yeast performs higher retardation of the migration of Co in the metabolically active condition than the resting one.
in the migration of radioactive-cobalt in the environment. These results indicate that the yeast performs higher retardation of the migration of Co in the metabolically active condition than the resting one.

Jiang, M.; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kamiishi, Eigo*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*
Chemical Geology, 277(1-2), p.61 - 69, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:66.93(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We have investigated the mechanism underlying Ce sequestration by yeast  after exposure to Ce(III) solution at pH 3, 4, or 5. We found that needle-shaped Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites with a monazite structure formed on the yeast cells by exposure to Ce(III) for 42 h, even though the initial solutions did not contain any P species. These results suggest that the sorbed Ce on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites.
after exposure to Ce(III) solution at pH 3, 4, or 5. We found that needle-shaped Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites with a monazite structure formed on the yeast cells by exposure to Ce(III) for 42 h, even though the initial solutions did not contain any P species. These results suggest that the sorbed Ce on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of Ce(III) phosphate nanocrystallites.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Tani, Yukinori*; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Tanimizu, Masaharu*; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(19), p.5463 - 5477, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:89 Percentile:89.15(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We carried out sorption experiments of Ce by biogenic Mn oxide produced by a Mn(II)-oxidizing fungus strain KR21-2. The results of the sorption experiments indicated that Ce(III) was oxidized to Ce(IV) by biogenic Mn oxide in solution with pH 3.8 - 7. Furthermore, oxidized Ce(IV) by biogenic Mn oxide was complexed with organic ligands released from fungal cells under circumneutral conditions.
Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Nankawa, Takuya; Francis, A. J.*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Radiochimica Acta, 98(7), p.397 - 402, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.1(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Ozaki, Takuo; Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Francis, A. J.*
Geomicrobiology Journal, 27(3), p.225 - 230, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:21.61(Environmental Sciences)The recent research results on the interation of heavy-elements and microorganisms are shown. (1) Adsorption of Pu(IV), Th(IV) and Eu(III)-DFO complexes on bacteria, (2) Biodegradation of Eu(III) in the presence of malic acids.
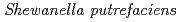
Suzuki, Yoshinori; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Onuki, Toshihiko
Geomicrobiology Journal, 27(3), p.245 - 250, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:60.1(Environmental Sciences)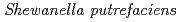 was cultured in the anarobic medium containing U(VI)-organic complexes. The weak complexes were reduced to U(IV) and uraninite was formed. The strong complexes were reduced to U(IV)-complexes remaining in the solution. These results suggest that organic acids affect the bioreduction behavior of U(VI).
was cultured in the anarobic medium containing U(VI)-organic complexes. The weak complexes were reduced to U(IV) and uraninite was formed. The strong complexes were reduced to U(IV)-complexes remaining in the solution. These results suggest that organic acids affect the bioreduction behavior of U(VI).
Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Onuki, Toshihiko
Chemistry Letters, 38(11), p.1090 - 1091, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.6(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report the first in situ and real-time observation of UV-vis absorption spectra of uranium electrodeposited on indium-tin-oxide electrodes by slab optical waveguide spectroscopy. An absorption peak around 670 nm was distinguished after a 30-min holding period at -0.2 V (vs. Ag/AgCl). X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy confirmed the presence of uranium(IV) in the uranium electrodeposited on the ITO electrode.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Onuki, Toshihiko
Chemistry Letters, 38(11), p.1032 - 1033, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:45.54(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Sorption experiments of Pu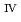 on synthetic Mn oxide were made in 0.1 M NaCl + 0.1 mM sodium citrate solutions under acidic to alkaline pH conditions. As the results of the sorption experiments, Pu was efficiently removed from the solutions under neutral pH conditions, where Pu forms the stable 1:2 Pu
on synthetic Mn oxide were made in 0.1 M NaCl + 0.1 mM sodium citrate solutions under acidic to alkaline pH conditions. As the results of the sorption experiments, Pu was efficiently removed from the solutions under neutral pH conditions, where Pu forms the stable 1:2 Pu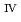 -citrate complex. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that Pu
-citrate complex. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that Pu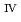 was oxidized to Pu
was oxidized to Pu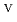 and Pu
and Pu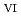 on Mn oxide.
on Mn oxide.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Ozaki, Takuo; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Francis, A. J.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 46(1), p.55 - 59, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Model analysis of the transformation of Pu(VI) in a mixture of a common soil bacterium, Bacillus subtilis, and kaolinite clay was carried out. When we assumed in the model analysis that reduction rate of Pu(V) to Pu(IV) was higher on B. subtilis than on kaolinite, the estimated fractions of Pu in the solution and in the mixture, oxidation states of Pu in the solution and in the mixture were in good agreement with the measured ones. On the contrary, assumption that reduction rate of Pu(V) to Pu(IV) was the same on kaolinite as on 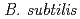 gave wrong prediction of Pu association with the mixture. These results strongly suggested the electron transfer from the bacteria to Pu(V) on the bacterial cell to be reduced to Pu(IV) during the accumulation of Pu(VI) to the mixture.
gave wrong prediction of Pu association with the mixture. These results strongly suggested the electron transfer from the bacteria to Pu(V) on the bacterial cell to be reduced to Pu(IV) during the accumulation of Pu(VI) to the mixture.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Ozaki, Takuo; Kozai, Naofumi; Nankawa, Takuya; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Sakai, Takuro; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Francis, A. J.*
Chemical Geology, 253(1-2), p.23 - 29, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:55.18(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We examined the changes in the chemical states of Ce(III) during the formation of manganese oxide occasioned by Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria. The oxidation states of Ce and Mn then were measured by X-ray Absorption Near Edge Structure (XANES). We also determined the elemental distributions in the bacteria and precipitates by Scanning-Proton Induced X-ray Emission (S-PIXE). We found that the precipitation of Ce is preceded by its accumulation by the bacterium, followed by its oxidization to Ce(IV) by the Mn(III, IV)-containing precipitates that the bacteria generate.
Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori; Ozaki, Takuo; Francis, A. J.; Onuki, Toshihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(3), p.251 - 256, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sorption of U(VI) on the 4-mercaptopyridine self-assembled-monolayer (4-PyS-SAM) on Au(111) was studied by cyclic voltammetry. Cyclic voltammograms (CV) of the 4-PyS-SAM working electrode was obtained by contact with 1 mM UO (NO
(NO )
) solution, 1 mM UO
solution, 1 mM UO (NO
(NO )
) and 50 mM acetic acid solution, or 1 mM UO
and 50 mM acetic acid solution, or 1 mM UO (NO
(NO )
) and 50 mM oxalic acid solution for 6 h at pH 4. Reduction current of uranium(VI) to U(V) was detected in the CV. The CV of the U(VI) associated 4-PyS-SAM after transporting to U(VI) free 0.1 M NaClO4 solution showed that the reduction current was detected in the cases of UO
and 50 mM oxalic acid solution for 6 h at pH 4. Reduction current of uranium(VI) to U(V) was detected in the CV. The CV of the U(VI) associated 4-PyS-SAM after transporting to U(VI) free 0.1 M NaClO4 solution showed that the reduction current was detected in the cases of UO (NO
(NO )
) and U(VI)-acetate, but not in the case of U(VI)-oxalate solutions, indicating that U(VI) was adsorbed on the 4-PyS-SAM from the UO
and U(VI)-acetate, but not in the case of U(VI)-oxalate solutions, indicating that U(VI) was adsorbed on the 4-PyS-SAM from the UO (NO
(NO )
) and U(VI)-acetate solutions, but not from U(VI)-oxalate solution. These results suggests that stability of U(VI)-4-PyS-SAM is not so high that U(VI)-4-PyS-SAM cannot be formed in the presence of 50 mM oxalate.
and U(VI)-acetate solutions, but not from U(VI)-oxalate solution. These results suggests that stability of U(VI)-4-PyS-SAM is not so high that U(VI)-4-PyS-SAM cannot be formed in the presence of 50 mM oxalate.
Suzuki, Yoshinori; Nankawa, Takuya; Ozaki, Takuo; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.*; Enokida, Yoichi*; Yamamoto, Ichiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(9), p.1227 - 1232, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:72.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)We examined electrochemical redox reactions of UO
 in organic acid (oxalic, malonic, succinic, adipic, L-malic, and L-tartaric acids) solutions using cyclic voltammetry. A redox reaction of UO
in organic acid (oxalic, malonic, succinic, adipic, L-malic, and L-tartaric acids) solutions using cyclic voltammetry. A redox reaction of UO
 /UO
/UO
 and an oxidation reaction of U(IV) were observed. The peak potentials of the UO
and an oxidation reaction of U(IV) were observed. The peak potentials of the UO
 reduction showed a good linear relationship with the log of the stability constants of 1:1 UO
reduction showed a good linear relationship with the log of the stability constants of 1:1 UO
 -organic complexes. We also revealed the redox reactions of UO
-organic complexes. We also revealed the redox reactions of UO
 in the presence of malonic or oxalic acids between pH 1 and 6.
in the presence of malonic or oxalic acids between pH 1 and 6.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Ozaki, Takuo; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Francis, A. J.
Environmental Science & Technology, 41(9), p.3134 - 3139, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:57.04(Engineering, Environmental)We investigated the interactions of Pu(VI) with Bacillus subtilis, kaolinite clay, and a mixture of the two to determine and delineate the role of the microbes in regulating the environmental mobility of Pu. The amount of Pu sorbed by B. subtilis increased with time, but had not reached equilibrium in 48 h, whereas equilibrium was attained in kaolinite within 8 h. After 48 h, the oxidation state of Pu in the solutions exposed to B. subtilis and the mixture had changed to Pu(V), whereas the oxidation state of Pu associated with B. subtilis and the mixture was Pu(IV). In contrast, there was no change in the oxidation state of Pu in the solution or on kaolinite after exposure to Pu(VI). SEM-EDS analysis indicated that most of the Pu in the mixture was associated with B. subtilis. These results suggest that Pu(IV) is preferably sorbed to bacterial cells in the mixture, and that Pu(VI) is reduced to Pu(V) and Pu(IV).
Suzuki, Yoshinori; Nankawa, Takuya; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Ozaki, Takuo; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.; Tsushima, Satoru*; Enokida, Yoichi*; Yamamoto, Ichiro*
Radiochimica Acta, 94(9-11), p.579 - 583, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:78.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We examined the reduction behavior of UO
 in citrate media at pH 2.0-7.0 by column electrodes. At pH 2.0, UO
in citrate media at pH 2.0-7.0 by column electrodes. At pH 2.0, UO
 was reduced to U(IV) through a one-step reduction process, while it was reduced to U(IV) through a two-step reduction process at pH 3.0-5.0. The reduction potential of UO
was reduced to U(IV) through a one-step reduction process, while it was reduced to U(IV) through a two-step reduction process at pH 3.0-5.0. The reduction potential of UO
 shifted to lower values with an increase in pH from 2.0 to 7.0. At pH 6.0 and 7.0, UO
shifted to lower values with an increase in pH from 2.0 to 7.0. At pH 6.0 and 7.0, UO
 was not reduced to U(IV) completely at the electrode potential above -0.8 V. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and speciation calculation of UO
was not reduced to U(IV) completely at the electrode potential above -0.8 V. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy and speciation calculation of UO
 in citrate media indicated that uranium existed as a mainly UO
in citrate media indicated that uranium existed as a mainly UO
 at pH 2-3, and a predominant species at pH 3-5 was [(UO
at pH 2-3, and a predominant species at pH 3-5 was [(UO )
) Cit
Cit ]
] . At pH 5-7, polymeric complexes were present. These findings suggest that the reduction of UO
. At pH 5-7, polymeric complexes were present. These findings suggest that the reduction of UO
 is more difficult by polymerization of UO
is more difficult by polymerization of UO
 with citric acid at higher pHs.
with citric acid at higher pHs.
Nankawa, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Ozaki, Takuo; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1329 - 1333, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.65(Chemistry, Physical)We studied the biodegradation of Eu(III)-malic acid complexes by  . Ten milimolar Malic acid was degraded in the absence and in the presence of Eu(III) of 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mM. The degradation rate of malic acid increased with decreasing the ratios of Eu(III) to malic acid. These results suggest that the toxicity of Eu(III) can be masked through its complexation with malic acid. The degradation of malic acid was followed by the production of unidentified metabolites which were associated with Eu(III). One of the unidentified organic acids was analysed to be pyruvic acid. Our findings suggest that metabolites can influence the environmental behavior of Eu(III) by biologically transformed through subsequent complexation with Eu(III).
. Ten milimolar Malic acid was degraded in the absence and in the presence of Eu(III) of 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mM. The degradation rate of malic acid increased with decreasing the ratios of Eu(III) to malic acid. These results suggest that the toxicity of Eu(III) can be masked through its complexation with malic acid. The degradation of malic acid was followed by the production of unidentified metabolites which were associated with Eu(III). One of the unidentified organic acids was analysed to be pyruvic acid. Our findings suggest that metabolites can influence the environmental behavior of Eu(III) by biologically transformed through subsequent complexation with Eu(III).
Ozaki, Takuo; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Nankawa, Takuya; Yoshida, Takahiro; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kimura, Takaumi; Francis, A. J.*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.1334 - 1338, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:87.21(Chemistry, Physical)We investigated the interactions of Eu(III) with the common soil bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens and organic ligands, such as malic acid, citric acid, and a siderophore (DFO). Malic acid formed complexes with Eu(III), but degradation of malic acid was observed when the ratio of malic acid to Eu(III) was high. Citric acid formed a stoichiometric complex with Eu(III) that was not degraded by P. fluorescens. Adsorption of Eu(III) from the DFO complex occurred as a free ion dissociated from DFO and not as the Eu(III)-DFO complex. Time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy analysis showed that adsorption of Eu(III) on P. fluorescens was through a multidentate and predominantly inner-spherical coordination.
Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Nankawa, Takuya; Ozaki, Takuo; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Francis, A. J.*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(1), p.65 - 67, 2005/07
no abstracts in English