Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Nagasawa, Makoto*; Qin, H.-B.*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemistry Letters, 49(8), p.909 - 911, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.1(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.583 - 586, 2015/12
Effects of liner energy transfer (LET) and dose rate on the optical property of polymer gel dosimeters were investigated. The dosimeter prepared by using a radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel and methacrylate monomers such as 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and nonaethylene glycol dimethacrylate showed the color change from colorless to white with the He, C, Fe ions irradiation. Absorbance of the irradiated dosimeters increased with the dose up to 10 Gy. The absorbance of the dosimeters at the same total dose decreased with increasing dose rate in the range of 0.1 to 6.8 Gy/min. The absorbance decreased in order of He, C, Fe ions, which was in agreement with a change of LET. The increase in LET affected the decrease in the number of polymerization initiator such as OH radical and hydrated electron, resulting in the reduction of the absorbance of the dosimeters.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi; Sato, Yuichi*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 444, p.012028_1 - 012028_4, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:91.72(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Polymer gel dosimeters consisting of less toxic methacrylate-type monomers such as 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol 400 dimethacrylate (9G) with hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) gel were prepared. We investigated the effect of monomer compositions on the dose response of the polymer gel dosimeter. The HPC gels as a matrix for the polymer gel dosimeter were obtained by electron beam irradiation to 20wt% of HPC aqueous solution. The dried HPC gels were immersed into mixed monomer solutions, and then the swollen gels were vacuum-packed to prepare the polymer gel dosimeters. The polymer gel dosimeters showed cloudiness by exposing to  Co
Co  -ray, in which the cloudiness increased with the dose up to 10 Gy. At the same dose, the increase in the cloudiness appeared with increasing concentration of 9G. It was found that the dose response depended on the composition ratio between HEMA and 9G.
-ray, in which the cloudiness increased with the dose up to 10 Gy. At the same dose, the increase in the cloudiness appeared with increasing concentration of 9G. It was found that the dose response depended on the composition ratio between HEMA and 9G.
 rays
raysKawahara, Yutaka*; Washika, Shingo*; Ikeda, Yoshimitsu*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
Nihon Shiruku Gakkai-Shi, 21, p.11 - 13, 2013/00
Silk fibroin fabrics were irradiated with  rays of 25 kGy doses, and the changes in their tensile properties and hue were investigated. Both the breaking tensile strength of the fabrics and their elongation at break were decreased after the irradiation, accompanied by their yellowing. However, the values of their tensile properties after the irradiation has been retained more than 90% of those without the irradiation. The degree of crystallinity was almost unchanged even after the irradiation.
rays of 25 kGy doses, and the changes in their tensile properties and hue were investigated. Both the breaking tensile strength of the fabrics and their elongation at break were decreased after the irradiation, accompanied by their yellowing. However, the values of their tensile properties after the irradiation has been retained more than 90% of those without the irradiation. The degree of crystallinity was almost unchanged even after the irradiation.
Takeda, Seiji; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Nagasawa, Hirokazu; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Sekioka, Yasushi; Kanzaki, Yutaka; Sasaki, Toshihisa; Ochiai, Toru; Munakata, Masahiro; Tanaka, Tadao; et al.
JAEA-Research 2009-034, 239 Pages, 2009/11
In safety assessment for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, it is of consequence to estimate the uncertainties due to the long-term frame associated with long-lived radionuclides and the expanded geological environment. The uncertainties result from heterogeneity intrinsic to engineered and natural barrier materials, insufficient understanding of phenomena occurring in the disposal system, erroneous method of measurement, and incomplete construction. It is possible to quantify or to reduce the uncertainties according to scientific and technological progress. We applied a deterministic and a Monte Carlo-based probabilistic method simulation techniques to the uncertainty analysis for performance of hypothetical geological disposal system for high level radioactive waste. This study provides the method to evaluate the effects of the uncertainties with respect to scenarios, models and parameters in engineering barrier system on radiological consequence. The results also help us to specify prioritized models and parameters to be further studied for long-term safety assessment.
Makabe, Takeshi*; Prawitwong, P.*; Takahashi, Ryo*; Takigami, Machiko*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Takigami, Shoji*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(2), p.471 - 474, 2008/06
Konjac mannan (KM) is a water soluble glucomannan with high molar mass. KM aqueous solution shows extremely high viscosity. The effects of  -rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
-rays irradiation and acid hydrolysis on molar mass were studied. The hydrolysis was carried out using citric acid. Characteristics of the irradiated and hydrolyzed KM were investigated using GPC-MALLS and a viscometer. The chemical structure of KM scarcely changed by both treatments. Molar mass of the irradiated KM decreased gradually with increasing dose. Molar mass of the hydrolyzed KM also decreased gradually with acid concentration. The viscosity of both treated KM aqueous solutions decreased with decreasing molar mass. High molar mass KM solution showed pseudo-plastic fluids behavior of the non-Newtonian fluid at dilute region and changed to Newtonian fluid with decrease of molar mass. Low molar mass KM solution showed behavior of Newtonian fluid at semi-dilute region. The critical concentration at the overlap limit of KM solution increased with decreasing of molar mass.
 -irradiations in terms of turbidity
-irradiations in terms of turbidityYamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Polymer gel dosimeters based on hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) hydrogel crosslinked by an irradiation of 2-MeV electron beam have been developed. Gel properties of the radiation-crosslinked HPC hydrogel were estimated with varying HPC concentration, absorbed dose, and type of radiation. Such hydrogel was utilized as gel matrix for polymer gel dosimeters which are more environment-friendly and easily handled than "toxic" polymer gel dosimeters composed of methacrylic acid or acrylamide. In the present study, solutes of the gel dosimeters were 2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate (HEMA), polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEG), and tetrakis hydroxyphosphonium chloride (THPC). Ratio of the concentrations of the solutes was varied to investigate sensitivity from the viewpoint of absorbance in a UV-vis region. As a result, absorbance increase in shorter-wavelength region (i.e. 300-500 nm) was different from that in longer-wavelength region. It was found that a peak appears in 300-400 nm with about 4-Gy irradiation, which is thought to be corresponding to productions of microgels, and that this peak slightly shift to longer wavelength with further irradiation.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
We have developed a less toxic and environment-friendly polymer gel dosimeter by employing radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropylcellulose hydrogel. It was found that this dosimeter becomes white and cloud-like state after  -irradiation of dose clinically used in cancer therapy. Quantitative evaluation of this white cloudiness, the haze and the absorbance were measured. The increases of the haze and absorbance were different for different composition of solute monomer and crosslinker which are permeated into gel matrix to detect radiation. In conclusion, it can be possible to control the sensitivity of our gel dosimeter by controlling the composition.
-irradiation of dose clinically used in cancer therapy. Quantitative evaluation of this white cloudiness, the haze and the absorbance were measured. The increases of the haze and absorbance were different for different composition of solute monomer and crosslinker which are permeated into gel matrix to detect radiation. In conclusion, it can be possible to control the sensitivity of our gel dosimeter by controlling the composition.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
We developed a polymer gel dosimeter with low toxicity by employing a cellulose derivative, hydroxypropyl cellulose, as a base matrix, 2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate as a polymerizing monomer, polyethylene glycol ester dimethacrylate as a crosslinker, and tetrakis (hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride as an oxygen scavenger. The gel dosimeter was irradiated with  Co
Co 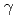 -rays at dose rate of 3-8 Gy/h, resulting in visual change from transparent to white cloud-like state. The irradiated dosimeters were analyzed by UV-vis spectrometry and measurement of haze, which is defined as the ratio of diffractive transmission to sum of diffractive and parallel transmissions. There is no obvious difference in UV-vis spectra among the dosimeters with different compositions. No peak but a broad and downward curve was observed in wavelength from 300 to 800 nm. This would be attributed to scattering by microgel of polymerized solutes or to chemical bonds produced during the polymerization. Haze almost monotonically increases with increasing
-rays at dose rate of 3-8 Gy/h, resulting in visual change from transparent to white cloud-like state. The irradiated dosimeters were analyzed by UV-vis spectrometry and measurement of haze, which is defined as the ratio of diffractive transmission to sum of diffractive and parallel transmissions. There is no obvious difference in UV-vis spectra among the dosimeters with different compositions. No peak but a broad and downward curve was observed in wavelength from 300 to 800 nm. This would be attributed to scattering by microgel of polymerized solutes or to chemical bonds produced during the polymerization. Haze almost monotonically increases with increasing 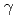 -dose although difference at low dose region (smaller than 1 Gy) was difficult to be quantitatively identified.
-dose although difference at low dose region (smaller than 1 Gy) was difficult to be quantitatively identified.
Yamanashi, Koichi*; Fujibuchi, Toshio*; Kawamura, Taku*; Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Mimura, Koichi*; Ushiba, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Murakami, Takeshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
A new polymer gel dosimeter was developed to overcome weakness of earlier polymer gel dosimeters. Hydroxyethyl 2-methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol ester dimethacrylate (9G) were less toxic constituents, which polymerize with irradiations. One of cellulose derivatives, hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), was crosslinked by irradiations of electron beam and used as a gel matrix, which doesn't soften with increasing temperature. Hydrogel of HPC is very transparent, so light scattering and absorption of products of radiation-induced polymerization are easily observable. As a result of irradiation, white turbidity was observed inside the gel at around 1-2 Gy. Increasing behavior of white turbidity with irradiation depended on composition of constituent monomers. White turbidity appears at rather lower dose and its increase saturates at around 10 Gy of 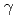 -irradiation when 9G is predominant. On the other hand, it becomes stronger even beyond 10 Gy when HEMA is predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after
-irradiation when 9G is predominant. On the other hand, it becomes stronger even beyond 10 Gy when HEMA is predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after  Co
Co 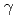 -irradiation.
-irradiation.
 rays irradiation
rays irradiationKawahara, Yutaka*; Washika, Shingo*; Ikeda, Yoshimitsu*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Murakami, Takeshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Murakami, Takeshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
We have developed a polymer gel dosimeter by utilizing EB-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) as gel matrix and methacrylate-type monomers as radiation detector agents. Our dosimeter is less toxic than those consisting of acrylate- or acrylamide-type monomers. Another advantage of our dosimeter is high transparency of hydrogel of HPC and the fact that radiation-induced white turbidity formation in the gel matrix can easily be visually observed. White turbidity formation behaviors with irradiations were investigated for different types of radiations;  Co
Co  -rays, 400 MeV/u C ions, and 500 MeV/u Fe ions. White turbidity could be confirmed even at 1 Gy irradiation of ion beams, however, the degrees of white turbidity were approximately half of that induced by
-rays, 400 MeV/u C ions, and 500 MeV/u Fe ions. White turbidity could be confirmed even at 1 Gy irradiation of ion beams, however, the degrees of white turbidity were approximately half of that induced by  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Murakami, Takeshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
We developed a new polymer gel dosimeter. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (9G), which are less toxic than methacrylic acid or acrylamide, were used as constituents polymerizing after irradiations. A cellulose derivative, hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), was selected and crosslinked to form gel matrix by an irradiation of 2-MeV electron beam, which doesn't soften at higher temperature. Hydrogel of HPC is enough transparent to observe light scattering and absorption of products of radiation-induced polymerization. As a result of  Co
Co  -ray irradiation of a few Gy, white turbidity arisen inside the gel, detailed behavior of which depended on composition of constituent monomers. It appeared at rather lower dose and its increase saturated at around 10 Gy of
-ray irradiation of a few Gy, white turbidity arisen inside the gel, detailed behavior of which depended on composition of constituent monomers. It appeared at rather lower dose and its increase saturated at around 10 Gy of  -irradiation when 9G was predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam of 135 MeV/u although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after
-irradiation when 9G was predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam of 135 MeV/u although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English