Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 20(Suppl.3), p.684 - 685, 2014/08
A novel wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) having a X-ray energy range of 50-210 eV has been developed. One feature is that the SXES is parallel detection of the signals so that it can be used like a conventional energy dispersive spectrometer. The other is a high energy resolution, which is about 0.2 eV at Al-L comparable to those revealed by XPS and EELS. These features enable us to obtain meaningful information about chemical bonding in various bulk samples. The SXES can detect Li-K emission spectrum. In the case of an anode electrode of a lithium ion battery (LIB), two types of lithium peaks are observed: one lower energy peak at 50 eV and the other higher energy peak at 54 eV. It was found that the former peak corresponds to the amount of charging, whereas the latter corresponds to the metallic state of lithium.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.77 - 80, 2013/09
We have been developing a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instrument for electron microscopes (TEM, EPMA/SEM) with an extension of detectable energy range to 50-4000 eV. An introduction of valence electron spectroscopy with microscopy will supply fruitful information on bonding electrons, which cannot be obtained by EELS and EDS. For extend the lowest (or highest) detection energy upto 50 eV (or 4000 eV), a new laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating, JS50XL, (or JS4000) has designed and manufactured. JS50XL and JS4000 having 1200 and 2400 lines/mm as well as coated by Au and a new multilayer-structure of W/B C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
C for a wide-band energy region of 2000-3800 eV, respectively. Those gratings were installed and tested in a SXES spectrometer attached to a TEM. The extension in lowest detection energy was confirmed by Mg-L emission (JS50XL). The energy resolution was 0.2 eV at Fermi edge of 49.5 eV. It can be also seen a sharp Fermi edge for Li-K emission spectrum of metal-Li. The high energy resolution was confirmed by Te-La emission at 3.8 keV (JS4000). The full width at half maximum of the peak was 27 eV. The detection energy range was successfully extended by using the two new VLS-gratings.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terauchi, Masami*; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2013-001, p.13 - 15, 2013/09
A very unique high performance soft X-ray emission spectrometer (SXES) has successfully been developed which can be attached not only to transmission electron microscopes (TEMs), but also to scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) as well as electron probe microanalyzers (EPMAs). To extend the analyzed energy ranges, a newly designed laminar-type varied-line-spacing (VLS) grating JS50XL, for a lower energy range, 50-170 eV, and a multilayered VLS grating JS4000, for a higher energy range, 2000-4000 eV, have been developed and installed to this spectrometer. Application software has also been developed for a commercial use of SXES in several fields such as battery materials, steel and alloys, and electron devices. The appearance of this spectrometer attached to EPMA and a few results acquired are shown in the following figures. This development has been conducted as one of the projects of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8848, p.884812_1 - 884812_14, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.03(Optics)We have developed an objective soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph to be able to attach to electron microscopes. This spectrograph has two attractive features. One is that it is designed to cover a wide energy range of 50-4000 eV by using four varied-line-spacing holographic gratings optimized for 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV. They can be accommodated in the single spectrograph. The other is a newly invented W/B C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of
C multilayer coating covering the 2000-4000 eV range. It can enhance the diffraction efficiency above a practical level of 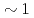 % at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
% at a constant incidence angle in the whole energy range.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 19(Suppl.2), p.1258 - 1259, 2013/08
A new wavelength dispersive soft X-ray emission spectrometer (WD-SXES) consisting of newly developed diffraction gratings has been developed for soft X-ray emission spectroscopy. The WD-SXES with two types of diffraction gratings nominally covering an energy range between 50 and 210 eV has been installed to electron probe X-ray microanalyzers, JEOL JXA-8100, for commercial use. The energy resolution of this WD-SXES is nominally 0.3 eV, which is one order of magnitude better than that of conventional WDSs with layered dispersion elements. It is to be noted that the corresponding edge of Al B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
B is shifted to higher energy side by about 1 eV. One of the energy range was selected from 72 to 73.5 eV whereas the other was from 73.5 to 75 eV. The contrast in the former map is reversed in the later map as expected even though the energy difference between two maps is only 1.5 eV. The study confirms the high potential for the characterization especially for chemical state mapping.
 ][1]benzothiophene monolayer on bismuth-terminated Si(111) vicinal surfaces with wettability optimization
][1]benzothiophene monolayer on bismuth-terminated Si(111) vicinal surfaces with wettability optimizationOtomo, Manabu; Tsuchida, Yuya*; Muraya, Naoki*; Yanase, Takashi*; Sakai, Seiji; Yonezawa, Tetsu*; Nagahama, Taro*; Hasegawa, Tetsuya*; Shimada, Toshihiro*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117(22), p.11555 - 11561, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.72(Chemistry, Physical)We report in-plane orientation control of newly developed high-mobility organic semiconductor: 2,7-diphenyl[1]benzothieno[3,2- ][1]benzothiophene (DPh-BTBT). As previously reported on monolayer pentacene, it was revealed that bunched steps on vicinal Si(111) with bismuth termination break the surface symmetry and reduce three-fold symmetry of DPh-BTBT grains into quasi-single orientation. Interestingly, the critical step height necessary for the orientation control was different from that of pentacene. We examined several mechanisms of orientation control and concluded that the facet nano structure fabricated by step bunching is working as an anisotropic template. We will also show the wettability control of bismuth terminated silicon surface and show that the growth mode of DPh-BTBT is dependent on the surface nanostructure of Bi-Si.
][1]benzothiophene (DPh-BTBT). As previously reported on monolayer pentacene, it was revealed that bunched steps on vicinal Si(111) with bismuth termination break the surface symmetry and reduce three-fold symmetry of DPh-BTBT grains into quasi-single orientation. Interestingly, the critical step height necessary for the orientation control was different from that of pentacene. We examined several mechanisms of orientation control and concluded that the facet nano structure fabricated by step bunching is working as an anisotropic template. We will also show the wettability control of bismuth terminated silicon surface and show that the growth mode of DPh-BTBT is dependent on the surface nanostructure of Bi-Si.
 and Sn-L
and Sn-L emissions of indium tin oxide
emissions of indium tin oxideTerauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy, 62(3), p.391 - 395, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.48(Microscopy)A new multilayer-coated varied line-spaced grating, JS4000, was fabricated and tested for extending the upper limit of a grating X-ray spectrometer for electron microscopy. This grating was designed for 2-3.8 keV at a grazing incidence angle of 1.35 deg. It was revealed that this new multilayer structure enables us to take soft-X-ray emission spectra continuously from 1.5 keV to 4 keV at the same optical setting. The full-width at half maximum of Te-L
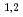 (3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L
(3.8 keV) emission peak was 27 eV. Sn-L (3444 eV) and In-L
(3444 eV) and In-L
 (3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
(3487 eV) peaks, which cannot be resolved by a widely used energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; Terauchi, Masami*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 425(15), p.152008_1 - 152008_4, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:79.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a flat-field spectrograph equipped with a wide-band multilayer grating and prefocusing mirror for the 2-4 keV range. To realize a spectrograph without any mechanical movement, the multilayer has a newly invented layer structure to uniformly enhance the diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the grating (or prefocusing mirror) at a fixed angle of incidence in the whole energy region. The multilayer structure consisting of W and B C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65
C layers has been deposited by ion beam sputtering method on a varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating. Also the same multilayer has been done on a spherical substrate. The average diffraction efficiency (or reflectivity) of the multilayer grating (or spherical mirror) is in excess of 3% at 88.65 (or 4% at 88.00
(or 4% at 88.00 ) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
) in the 2.1-3.8 keV range. The throughput of the spectrograph with multilayer optics can be evaluated to be 2-5000 times higher than that with conventional optics coated by a gold layer.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.33 - 37, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.86(Physics, Applied)Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Applied Optics, 51(13), p.2351 - 2360, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:52.47(Optics)Laminar and blazed types holographic varied-line-spacing spherical gratings for use in a versatile soft X-ray flat-field spectrograph attached to an electron microscope are designed, fabricated, and evaluated. The absolute diffraction efficiencies of laminar (or blazed) master and replica gratings at 86.00 incidence evaluated by synchrotron radiation show over 5% (or 8%) in the 50-200 eV range with the maxima of 22% (or 26-27%). Also the resolving power evaluated by a laser produced plasma source is in excess of 700 at the energy near the
incidence evaluated by synchrotron radiation show over 5% (or 8%) in the 50-200 eV range with the maxima of 22% (or 26-27%). Also the resolving power evaluated by a laser produced plasma source is in excess of 700 at the energy near the  emission spectrum of lithium (
emission spectrum of lithium ( 55 eV) for all gratings. Moreover, the
55 eV) for all gratings. Moreover, the  emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution is successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution is successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
 emission spectrum of Li
emission spectrum of LiImazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Memoirs of the SR Center Ritsumeikan University, (14), p.131 - 144, 2012/05
We have developed a wavelength-dispersive soft X-ray spectrograph covering an energy region of 50-4000 eV to attach to a conventional electron microscope. The energy range was properly divided into four ranges of 50-200 eV, 155-350 eV, 300-2200 eV, and 2000-4000 eV, and a versatile spectrograph equipped with interchangeable multiple gratings optimized in the respective energy ranges has been developed. In particular, the grating that covers the 50-200 eV range can be used for the measurement of the  emission spectrum (
emission spectrum ( 55 eV) of lithium. The diffraction efficiency evaluated by synchrotron radiation and resolving power measured by laser produced plasma sources are over 5% and in excess of 700, respectively. The
55 eV) of lithium. The diffraction efficiency evaluated by synchrotron radiation and resolving power measured by laser produced plasma sources are over 5% and in excess of 700, respectively. The  emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution has been successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
emission spectrum of metallic Li with high spectral resolution has been successfully observed with the spectrograph attached to a transmission electron microscope.
Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Proceedings of Microscopy and Microanalysis 2011 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2011/08
Soft X-ray spectroscopy with high-energy resolution gives useful information of the chemical bonding states in compounds. Terauchi et al. recently reported a high-energy resolution of 0.2 eV in the Al-L emission spectrum using the previously developed soft X-ray Emission spectrometer (SXES) with a transmission electron microscope. This spectrometer can design to detect the energy from 60 to 1200 eV. In order to progress this result, we had attempted to enhance the detection energy range. Especially to detect the Li-K emission spectrum, we are developing a spectrometer with newly designed aberration corrected gratings. The newly developed grating JS50XL can cover the X-ray energy range from 50 to 200eV with the high energy resolution. It actually means to detect Li-K (55 eV), Al-L (70 eV), Si-L (100 eV), B-K (180 eV) and high order of C-K (279 eV), N-K (392 eV), O-K (525 eV) and so on. This SXES can be equipped not only with TEM, but also with EPMA. Moreover, we found out that attached EPMA with SXES has another strong feature that the X-ray intensity is in directly proportional to probe current. This feature is very useful for the trace element analysis. In the case of Li-K, Be-K and B-K emissions, the detection limits have been evaluated to be a few tens of ppm. For example trace boron analysis is expected to evaluate the newly developed materials quantitatively. This developed spectrometer is hopeful to observe chemical bonding state and trace element analysis in many kinds of fields. In this presentation we report the results for fundamental and actual samples. This development is conducting as one project of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; Handa, Nobuo*; Murano, Takanori*; Koike, Masato; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Imazono, Takashi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; et al.
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 17(Suppl.2), p.604 - 605, 2011/07
We have been developing a soft X-ray emission spectroscopy (SXES) instrument for TEM. SXES combined with microscopy should be a hopeful method to reveal physical properties and chemical bonding states of identified small specimen areas of various compounds. Original SXES instruments for conventional transmission electron microscopes basically designed to detect from 60 eV to 1200 eV (or 2000 eV in extended version). For applying to material science, a much wider energy range is necessary. Thus, a new SXES development for electron microscope has started to obtain an energy range from 50 eV to 3800 eV. An extension in lower energy region was achieved by a new aberration corrected (varied-line-spaced: VLS) grating. Conventional gratings in soft-X-ray energy region have gold surface. Au has M-absorption edge at 2.2 keV and shows only a small reflectance higher than the energy. Thus, a new multilayer-coated (MLC) VLS grating has designed and manufactured for obtaining SXES spectra up to 4 keV at a grazing incident angle of 1.35 deg. This development is conducting as one project of Collaborative Development of Innovative Seeds (Practicability verification stage) by Japan Science and Technology Agency.
Hatano, Toshihisa; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Hasegawa, Koichi; Kaifuku, Yuichiro*; Abe, Tetsuya
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 54(5), p.313 - 316, 2011/05
In the quantitative measure of air pollution gas and impurity gas in the aluminum recycle material etc, it is requested to show the amount of the gas directly by the weight value from the viewpoint of global standard. Therefore, standard gas sources expressed in units of weight are needed. The vapor-liquid equilibrium type of gas permeation sources (hereafter "P-tube") is used well in the atmosphere as calibration gas of the measuring equipment and a standard gas source for low concentration of gas. The study aims to estimate performance of P-tubes in the vacuum. Specifically, weight change of P-tubes were measured with the vacuum balance and at the same time concentration of gas constituents were also measured by Electron Ionization-Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (hereafter, EI-QMS). The relation of both was examined. The prospect was obtained that the P-tube was able to be used as a standard gas source in the vacuum though the warming was needed.
Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Li, Z.; Ishii, Yasuo; Tome, Hayato*; Sato, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; et al.
Chemistry Letters, 38(11), p.1084 - 1085, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.93(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We report on the characteristic anion-exchange behavior of the superheavy element dubnium (Db) with atomic number Z = 105 in HF/HNO solution at the fluoride ion concentration [F
solution at the fluoride ion concentration [F ] = 0.003 M. The result clearly demonstrates that the fluoro complex formation of Db is significantly different from that of the group-5 homologue Ta in the 6th period of the periodic table while the behavior of Db is similar to that of the lighter homologue Nb in the 5th period.
] = 0.003 M. The result clearly demonstrates that the fluoro complex formation of Db is significantly different from that of the group-5 homologue Ta in the 6th period of the periodic table while the behavior of Db is similar to that of the lighter homologue Nb in the 5th period.
Hayashi, Kimio; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Onose, Shoji; Ishida, Takuya; Nakamichi, Masaru; Katsuyama, Kozo; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Hasegawa, Teiji; Kodaka, Hideo; Takatsu, Hideyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-007, 168 Pages, 2009/03
In-pile functional tests of breeding blankets have been planned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), using a test blanket module (TBM) which will be loaded in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER). In preparation for the in-pile functional tests, JAEA has been being performed irradiation experiments of lithium titanate (Li TiO
TiO ), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
), which is the first candidate of solid breeder materials for the blanket of the demonstration reactor (DEMO) under designing in Japan. The present report describes (1) results of a detailed design and trial fabrication tests of a dismantling apparatus for irradiation capsules which were used in irradiation experiments by the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) of JAEA, and (2) results of a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility for post-irradiation examinations (PIEs). In the detailed design of the dismantling apparatus, datailed specifications and the installation methods were examined, based on results of a conceptual design and basic design. In the trial fabrication, cutting tests were curried out by making a mockup of a cutting component. Furthermore, a preliminary investigation of a glove box facility was carried out in order to secure a facility for PIE work after the capsule dismantling, which revealed a technical feasibility.
Maekawa, Fujio; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Oi, Motoki; Sakai, Kenji; Teshigawara, Makoto; Hasegawa, Shoichi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.335 - 337, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron beam line (BL10) of JSNS, NOBORU, has been constructed in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC. A primal mission of NOBORU is to study neutronic performance of JSNS. We will measure the memorable first neutron pulse of JSNS at the Day-one by using NOBORU, and then measure neutron pulse shape, spectrum, intensity distribution, etc. for facility diagnostics. Since NOBORU also has an aspect as a test port, it welcomes trial uses to develop innovative instruments. Trial experiments to demonstrate several innovative instruments at NOBORU are under planning.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Oi, Motoki; Sakai, Kenji; Teshigawara, Makoto; Hasegawa, Shoichi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 589(2), p.310 - 317, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:95.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)NOBORU, NeutrOn Beam-line for Observation and Research Use, has been constructed in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. NOBORU is designed to "Observe" a 1 MW Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS), i.e., to study the neutronic performance of JSNS. NOBORU also will be used for "Research" activities, i.e., as a test port for R&D activities and trial users who have new ideas. In this paper, the design and application of NOBORU are described, and its expected performance is investigated by Monte Carlo simulations.
 solutions
solutionsToyoshima, Atsushi; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Akiyama, Kazuhiko*; Goto, Shinichi*; Ishii, Yasuo; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Sato, Tetsuya; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 96(3), p.125 - 134, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:85.1(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Formation of an anionic fluoride-complex of element 104, rutherfordium (Rf) produced in the  Cm(
Cm( O,5n)
O,5n) Rf reaction was studied by an anion-exchange method based on an atom-at-a-time scale. It was found that the hexafluoro complex of Rf, [RfF
Rf reaction was studied by an anion-exchange method based on an atom-at-a-time scale. It was found that the hexafluoro complex of Rf, [RfF ]
] , was formed in the studied fluoride ion concentrations of 0.0005 - 0.013 M. Formation of [RfF
, was formed in the studied fluoride ion concentrations of 0.0005 - 0.013 M. Formation of [RfF ]
] was significantly different from that of the homologues Zr and Hf, [ZrF
was significantly different from that of the homologues Zr and Hf, [ZrF ]
] and [HfF
and [HfF ]
] ; the evaluated formation constant of [RfF
; the evaluated formation constant of [RfF ]
] is at least one-order of magnitude smaller than those of [ZrF
is at least one-order of magnitude smaller than those of [ZrF ]
] and [HfF
and [HfF ]
] .
.
Arai, Takashi; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hatano, Toshihisa; Nemoto, Masahiro; Abe, Tetsuya
Heisei-18-Nendo Nagoya Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Sochi Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.76 - 79, 2007/03
Recently, the accident because of drunken driving is taken up in the topic of news, and the concern is had at the amount of the drinking and the drinking time etc. of the inside of the body. It is said that there is a correlation in the alcoholic density included in an alcoholic amount and the expiration in blood so far, and is reported on the equipment that measures an alcoholic density of the expiration based on this. We also are executing the breath analysis as an example of applying QMS (four pile polar mass spectrometer) gas analyzer "Gravimas". This time, an alcoholic density in the expiration was measured, the performance of this device to alcoholic detection was examined, and the change at the time of an alcoholic density in the expiration high sensitivity was measured. These results suggest the utility of the breath analysis that uses QMS.