Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Fumihiko; Okita, Hidefumi; Hotchi, Hideaki*; Saha, P. K.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Seiya, Kiyomi*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.64 - 68, 2023/11
The J-PARC 3GeV synchrotron (RCS) provides high intensity proton beams to the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) and the Main Ring (MR). The harmonic number (h) of the RCS is 2 and the RCS normally accelerates two bunches. For some experiments at the MLF, a single bunch is preferred. In this case, one of the rf bucket is filled with protons and the other is empty. Therefore the beam intensity is halved. If the RCS can accelerate with h=1, the intensity per bunch can be doubled, enabling to provide single bunch beams to the MLF with the maximum intensity. This possibly increases the MR beam power by injecting high intensity single bunches eight times. In this presentation, we report mainly on the consideration of h=1 acceleration in the RCS by longitudinal simulations.
Miyakawa, Kazuya; Hayano, Akira; Sato, Naomi; Nakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-009, 103 Pages, 2023/09
This borehole investigation was carried out to confirm the validity of the distribution of low flow areas deep underground estimated based on the geophysical survey in FY 2020, as a part of an R&D supporting program titled "Research and development on Groundwater Flow Evaluation Technology in Bedrock" under contract to the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (2021, 2022 FY, Grant Number: JPJ007597). The borehole name is Horonobe Fossil seawater Boring-1 and is referred to as HFB-1 borehole. HFB-1 is a vertical borehole drilled adjacent to the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL), which was drilled from the surface to a depth of 200 m in FY2021 and from a depth of 200 m to 500 m in FY2022. This report summarizes information related to the drilling of HFB-1 and various data (rock core description, geophysical logging, chemical analysis, etc.) obtained from the borehole investigation.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 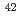 Ca, and
Ca, and 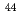 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Arai, Yoichi; Hasegawa, Kenta; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Minowa, Kazuki*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Hagura, Naoto*; Katsuki, Kenta*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Konishi, Yasuhiro*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Suzuki, Gen*; Ishikawa, Tetsuo*; Oba, Takashi*; Hasegawa, Arifumi*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Miyatake, Hirokazu*; Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 63(6), p.796 - 804, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.14(Biology)To elucidate the association between radiation dose and thyroid cancer after the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, it is essential to estimate individual thyroid equivalent doses (TEDs) to children. In a previous study, we reported a methodology for reconstructing TEDs from inhalation based on individual behavioural survey sheets combined with a spatiotemporal radionuclides database constructed by an atmospheric transport, diffusion, and deposition model (ATDM). In the present study, we further refined our methodology and estimated the combined TEDs from inhalation and ingestion among children in 16 municipalities around the nuclear power station utilizing 3,256 individual whereabouts questionnaire survey sheets. Distributions of estimated TEDs were similar to estimates based on direct thyroid measurements in 1080 children in Iwaki City, Kawamata Town, Iitate Village, and Minamisoma City. Mean TEDs in 1-year-old children ranged from 1.3 mSv in Date City to 14.9 mSv in Odaka Ward in Minamisoma City, and the 95th percentiles varied from 2.3 mSv in Date City to 28.8 mSv in Namie Town. In the future, this methodology can be useful for a case-control study of thyroid cancer after the FDNPS accident.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Yanagi, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*
RIST News, (67), p.3 - 15, 2021/09
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011049_1 - 011049_6, 2021/03
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011050_1 - 011050_6, 2021/03
R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and aluminum and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Yee-Rendon, B.; Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011043_1 - 011043_5, 2021/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been working in the research and development of an Accelerator Driven Subcritical System (ADS) for the transmutation of nuclear waste. The ADS proposed by JAEA consists of a CW proton linac of 30 MW coupling with a subcritical core reactor. The accelerator will be operated with a beam current of 20 mA. Normal conducting Radio-Frequency Cavities (NRFC) and Superconducting Radio-Frequency Cavities (SRFC) will be used to achieve final energy of 1.5 GeV, and the SRFC will be employed for the main part of the acceleration: from 2 MeV to 1.5 GeV. In the first stage of the accelerator development, the focus was the design and optimization of the SRFC models and the beam optics. For the SRFC sections, the acceleration will be done by using Half Wave Resonators (HWR), Single Spokes (SS), and Elliptical cavities (Ellip) operating with a frequency of 162, 324, and 648 MHz, respectively. The beam optics were optimized satisfying the equipartitioning condition to control the emittance growth, which helped to reduce the beam halos and the beam loss.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(10), p.1141 - 1151, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)To estimate the structural damages of materials in accelerator facilities, displacement per atom (dpa) is widely employed as a damage index, calculated based on the displacement cross-section obtained using a calculation model. Although dpa is applied as standard, the experimental data of the displacement cross-section for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV are scarce. Among the calculation models, difference of about factor 8 exist, so that the experimental data of the cross-section are crucial to validate the model. To obtain the displacement cross-section, we conducted experiments at J-PARC. The displacement cross-section of copper and iron was successfully obtained for a proton projectile with the kinetic energies, 0.4 - 3 GeV. The results were compared with those obtained using the widely utilized Norgertt-Robinson-Torrens (NRT) model and the athermal-recombination-corrected (arc) model based on molecular dynamics. It was found that the NRT model overestimates the present displacement cross-section by 3.5 times. The calculation results obtained using with the arc model based on the Nordlund parameter show remarkable agreement with the experimental data. It can be concluded that the arc model must be employed for the dpa calculation for the damage estimation of copper and iron.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06006_1 - 06006_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.061004_1 - 061004_6, 2020/02
no abstracts in English
 I impacted by atmospheric
I impacted by atmospheric  I releases from a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant
I releases from a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plantOta, Masakazu; Terada, Hiroaki; Hasegawa, Hidenao*; Kakiuchi, Hideki*
Science of the Total Environment, 704, p.135319_1 - 135319_15, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.02(Environmental Sciences)Land-surface transfers of  I are modeled and incorporated into a land-surface model (SOLVEG-II), and the model was applied to the observed transfer of
I are modeled and incorporated into a land-surface model (SOLVEG-II), and the model was applied to the observed transfer of  I at a vegetated field impacted by atmospheric releases of
I at a vegetated field impacted by atmospheric releases of  I from Rokkasho reprocessing plant during 2007 to investigate the importance of each
I from Rokkasho reprocessing plant during 2007 to investigate the importance of each  I-transfer pathway. The model calculation revealed that contamination of leaves of wild bamboo grasses was mostly caused by foliar adsorption of
I-transfer pathway. The model calculation revealed that contamination of leaves of wild bamboo grasses was mostly caused by foliar adsorption of  I (81%) induced via wet deposition of
I (81%) induced via wet deposition of  I. Wet deposition of
I. Wet deposition of  I was the main
I was the main  I-input to the soil, ten-fold the dry deposition of
I-input to the soil, ten-fold the dry deposition of  I
I ; however, the deposition of
; however, the deposition of  I during 2007 was only 2% of the model-assumed
I during 2007 was only 2% of the model-assumed  I that pre-existed in the soil; indicating the importance of long-term accumulation of
I that pre-existed in the soil; indicating the importance of long-term accumulation of  I in soils. The model calculation also revealed that root uptake of
I in soils. The model calculation also revealed that root uptake of  I, not methylation, control the long-term turnover of soil
I, not methylation, control the long-term turnover of soil  I.
I.
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akihiro; Machida, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Yanagi, Hideaki*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 210, p.105803_1 - 105803_10, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.8(Environmental Sciences)To improve the accuracy of simulations for air dose rates over fallout contaminated areas, the distribution of the radionuclides within the environment should be modelled realistically, e.g. considering differences in radioactivity levels between agricultural land, urban surfaces, and forest compartments. Moreover simulations should model the shielding of  rays by buildings, trees and land topography. Here we outline a system for generating three dimensional models of urban and rural areas in Fukushima Prefecture. The
rays by buildings, trees and land topography. Here we outline a system for generating three dimensional models of urban and rural areas in Fukushima Prefecture. The  Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity distribution can be set flexibly across the different components of the model. The models incorporate realistic representations of local buildings, based on nine common Japanese designs, individual conifer and broadleaf trees, and the topography of the land surface. Models are generated from Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and Digital Surface Model (DSM) datasets, and refined by users assisted with ortho-photographs of target sites. Completed models are exported from the system in a format suitable for the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) for the calculation of air dose rates and other radiological quantities. The system is demonstrated by modelling a suburban area 4 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant that has yet to be decontaminated. Air dose rates calculated in PHITS were correlated with measurements taken across the site in a car-borne survey.
Cs radioactivity distribution can be set flexibly across the different components of the model. The models incorporate realistic representations of local buildings, based on nine common Japanese designs, individual conifer and broadleaf trees, and the topography of the land surface. Models are generated from Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and Digital Surface Model (DSM) datasets, and refined by users assisted with ortho-photographs of target sites. Completed models are exported from the system in a format suitable for the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) for the calculation of air dose rates and other radiological quantities. The system is demonstrated by modelling a suburban area 4 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant that has yet to be decontaminated. Air dose rates calculated in PHITS were correlated with measurements taken across the site in a car-borne survey.
Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Yee-Rendon, B.; Meigo, Shinichiro; Maekawa, Fujio; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kako, Eiji*; Umemori, Kensei*; Sakai, Hiroshi*; Konomi, Taro*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2019) (Internet), p.399 - 402, 2019/11
Kim, M.; Malins, A.; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Machida, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Yanagi, Hideaki*
Isotope News, (765), p.30 - 33, 2019/10
Here we outline a system for generating three dimensional models of urban and rural areas in Fukushima Prefecture. The  Cs and
Cs and  Cs radioactivity distribution can be set flexibly across the different components of the model. The models incorporate realistic representations of local buildings, individual conifer and broadleaf trees, and the topography of the land surface. The system is demonstrated by modelling a suburban area 4 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant that has yet to be decontaminated. Air dose rates calculated in PHITS were correlated with measurements taken across the site in a car-borne survey.
Cs radioactivity distribution can be set flexibly across the different components of the model. The models incorporate realistic representations of local buildings, individual conifer and broadleaf trees, and the topography of the land surface. The system is demonstrated by modelling a suburban area 4 km from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant that has yet to be decontaminated. Air dose rates calculated in PHITS were correlated with measurements taken across the site in a car-borne survey.
Yee-Rendon, B.; Tamura, Jun; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Maekawa, Fujio; Meigo, Shinichiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.107 - 111, 2019/07