Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 38(2), p.347 - 358, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Analytical)To develop remote isotopic analysis for the nuclids with small isotope shifts, Doppler-free fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca was performed using laser ablation plume. Counter-propagating laser beams from two external cavity diode lasers were used to irradiate the plume in order to excite the ground-state Ca atoms to the  D
D state through a double resonance scheme of
state through a double resonance scheme of  S
S

 P
P

 D
D . Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the
. Subsequently, we measured fluorescence spectra associated with the relaxation from the  D
D to
to  P
P states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step
states. The linewidth measured at 1 ms delay after ablation under helium gas pressure of 70 Pa was found to be less than 70 MHz, which was about 1/30 of the linewidth of the Doppler-limited fluorescence spectrum. A broad Gaussian pedestal was observed at less than 600 micro-second delay in the temporal variation in fluorescence spectra, and it was most likely due to the velocity-changing collision. Additionally, the pressure broadening rate coefficient for the second-step  P
P

 D
D transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,
transition was determined to be 46.0 MHz/torr from the spectra measured under various gas pressures. We evaluated analytical performances such as linearity of the calibration curve, limit of detection, and measurement accuracy using fluorescence signals of three naturally occurring Ca isotopes (i.e.,  Ca,
Ca, 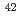 Ca, and
Ca, and 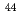 Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Ca). The limit of detection of isotopic abundance was estimated to be 0.09% from the 3-sigma criteria of the background. These results suggest that this spectroscopic technique is promising for remote isotopic analysis of nuclides with small isotope shifts.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy & Radiative Transfer, 265, p.107549_1 - 107549_7, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.28(Optics)Following the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, an isotope-selective analysis method using laser resonance ionization has been developed for strontium-90. In this study, we focused on ionization via autoionization states in terms of high isotopic selectivity and ionization efficiency, and the DC Stark shifts caused by the external electric field were measured for these states. It was found that the external electric field in the ionization region has to be of the order of 0.1 V/cm or less to suppress its effect on the observed spectra.
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Laser Applications, 33(1), p.012001_1 - 012001_16, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Tadokoro, Takahiro*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai-Shi, 122(1211), p.18 - 20, 2019/10
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinichi; Okumura, Masahiko*; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Enokida, Yoichi*; Umeki, Hiroyuki*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Kawasaki, Daisuke*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Furuta, Kazuo*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(2), p.131 - 148, 2016/12
A symposium "Science of nuclear fuel cycle and backend - Research and education -" was held at the Univer-sity of Tokyo in June 25, 2016. This aimed at developing the research on nuclear fuel cycle and backend. The time and the number of participants of the symposium were limited, but the active discussion was conducted, and the common perception for the future was shared among the experienced participants in those fields. This paper provides the discussions made in the symposium, and also, as a memory to Professor Ahn, the University of California, Berkeley, his prominent achievements in academic research and education.
Nagame, Yuichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Ishii, Yasuo; Sato, Tetsuya; Hirata, Masaru; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shinichi; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 93(9-10), p.519 - 526, 2005/00
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Umeki, Hiroyuki; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; ; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Suzuki, Atsuyuki*
WSES/IEEE Kaigi, 0 Pages, 2001/00
None
; Sakamoto, Yukio; Tanaka, Shunichi; ; Fukahori, Tokio; ; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Tanaka, Susumu; Nakamura, Takashi*; Shin, Kazuo*; et al.
JAERI-Data/Code 94-012, 90 Pages, 1994/09
no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
Because of environmental pollution of the radioactive materials released from TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, considerable attention has been focused on food safety in Japan. Whereas the principal pollutants for foods are radioactive  Cs and
Cs and  Cs, the radioactive
Cs, the radioactive  Sr, one of the alkaline earth elements like Ca and its radiation can damage bone marrow, is also one of the most important nuclide considering the possible occurrence of biological concentration through food chain. This
Sr, one of the alkaline earth elements like Ca and its radiation can damage bone marrow, is also one of the most important nuclide considering the possible occurrence of biological concentration through food chain. This  Sr is the pure
Sr is the pure  -ray emitter of which energy is 0.546 MeV (28.78 years) and is known as the nuclide for which analysis is difficult. For radiometric analysis, to eliminate various
-ray emitter of which energy is 0.546 MeV (28.78 years) and is known as the nuclide for which analysis is difficult. For radiometric analysis, to eliminate various  emitters which potentially interfere the
emitters which potentially interfere the  Sr analysis, not only a repeated application of ion-exchange and coagulating sedimentation processes but also a period of longer than 2 weeks are needed to establish radioactive equilibrium between
Sr analysis, not only a repeated application of ion-exchange and coagulating sedimentation processes but also a period of longer than 2 weeks are needed to establish radioactive equilibrium between  Sr and its daughter nuclide
Sr and its daughter nuclide  Y. To realize a prompt
Y. To realize a prompt  Sr analysis for marine foods, we are developing a new analytical technique by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy (RIS) and ion trap detection. In the present study, we have evaluated ionization efficiency and analytical performances using highly efficient and isotope-selective RIS scheme which we determined in our previous study.
Sr analysis for marine foods, we are developing a new analytical technique by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy (RIS) and ion trap detection. In the present study, we have evaluated ionization efficiency and analytical performances using highly efficient and isotope-selective RIS scheme which we determined in our previous study.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Iwata, Yoshihiro*; Jung, K.*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
For the radioactivity evaluation regarding to the accident of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, time-consuming and skills-required sample pretreatments for  Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for
Sr analysis (radiometric or ICP-MS analyses) is serious issue. We are developing a ultra-sensitive and rapid analytical technique for  Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5
Sr by combining resonance ionization spectroscopy, in which only the atoms of specific isotope can be ionized using the slight difference in level energy, and ion trap technique, in which only the ions of specific isotope can be trapped for a long duration to observe them with high sensitivity. In this study, we applied a continuous-wave isolated-core excitation technique (cw-ICE) for the first time to search for highly efficient and isotope-selective ionization schemes, especially for the Rydberg series converging to the 5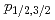 ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5
ionic levels, of which information is quite scarce. As a result, we have revealed a detailed level-structure of autoionizing 5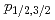 (nl) series of Sr atoms.
(nl) series of Sr atoms.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
In the field of atomic energy, it is necessary to know isotopic abundances of various radioactive isotopes as well as nuclear fuel materials such as uranium and plutonium. To date radiochemical analysis and mass spectrometry such as ICP-MS are widely used as methods for obtaining these values, and established as a standard method. However, when it is necessary to know the abundance of extremely small amount of radioactive isotope existing in nature, when it is necessary to shorten the time for the pretreatment of samples and measurement, or when it is necessary to perform analysis under extremely high radiation fields or analysis of samples with high radioactivity for the decommissioning of FDNPP, there are cases where it is not applicable with standard analytical techniques alone. Spectroscopic analysis using continuous-wave diode lasers has excellent selectivity and sensitivity to isotopes and atomic states, possibility to simplify sample pretreatment, and the possibility of remote or noncontact analysis, and we are studying to use it as a method to complement standard analytical methods. In this talk, we will report the present status of the development of laser ablation absorption spectroscopy for remote analysis of samples with high radioactivity and that of 3-step resonance ionization mass spectrometry for detecting  Sr with food regulation level in marine foods, and also discuss about their future prospects.
Sr with food regulation level in marine foods, and also discuss about their future prospects.
 Sr analysis in real samples using laser resonance ionization
Sr analysis in real samples using laser resonance ionizationIwata, Yoshihiro*; Cheon, D.*; Miyabe, Masabumi; Nagaoka, Mika; Matsubara, Natsumi; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ito, Chikara; Yamada, Tomonori; Daido, Hiroyuki*; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Tomonori; Daido, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Miyabe, Masabumi; Daido, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara; Yamada, Tomonori; Shibata, Takuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Ito, Chikara; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Tomonori; Ishizuka, Ippei*; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Hanari, Toshihide; Omori, Shinya*; Kurosawa, Koichi*; Sasaki, Go*; Nakada, Masahiro*; Sakai, Hideaki*; Shibata, Takuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English