Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Motoki*; Nakanishi, Yohei*; Abe, Jun*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Iwase, Hiroki*; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Katsuhiro*; et al.
Polymer Journal, 55(11), p.1165 - 1170, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)Abeykoon, S.*; Howard, C.*; Dominijanni, S.*; Eberhard, L.*; Kurnosov, A.*; Frost, D. J.*; Boffa Ballaran, T.*; Terasaki, Hidenori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 128(9), p.e2023JB026710_1 - e2023JB026710_17, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Small amounts of iron sulphide minerals are found in most rocks from the Earth's mantle and as inclusions trapped in natural diamonds. Hydrogen may dissolve into iron sulphide minerals under high pressures and temperature, but is most likely lost once pressure and temperature are removed. In this study, we determined deuterium contents in iron sulphide, held under high pressure and temperature conditions, using neutron diffraction measurements with 6-ram multi-anvil press at PLANET, J-PARC. Deuterium contents in iron sulphide were measured at high-P, up to 11.4 GPa and high-T to 1300 K in in situ neutron diffraction experiments. The total deuterium content increases with both P and T. The results are used to estimate hydrogen contents of iron sulphide minerals in the deep continental lithospheric mantle, which are found to be in the range 1700-2700 ppm. This corresponds to approximately 2-3 ppm of hydrogen in the bulk mantle.
 Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Masakazu; Takahara, Shogo; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Nagakubo, Azusa; Hirouchi, Jun; Hayashi, Naho; Abe, Tomohisa; Funaki, Hironori; Nagai, Haruyasu
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 264, p.107198_1 - 107198_15, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)One of the current major radiation exposure pathways from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident-fallout is inhalation of the re-suspended  Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of
Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of  Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric
Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric  Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of
Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of  Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air
Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air  Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher
Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher  Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore
Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore  Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle
Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle  Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,
Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,  Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore
Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore  Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric
Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric  Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
 Ni
Ni D
D at high
at high 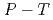 conditions
conditionsShito, Chikara*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Abe, Jun*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
American Mineralogist, 108(4), p.659 - 666, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:64.83(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The phase relation and crystal structure of Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D ) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under
) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under 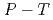 conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal (
conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal ( ) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe
) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe Ni
Ni D
D unlike fcc FeH
unlike fcc FeH (D
(D ). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium
). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium 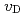 was determined as 2.45(4)
was determined as 2.45(4) 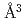 and 3.31(6)
and 3.31(6) 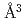 for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD
for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD . The
. The 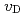 value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that
value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that 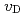 is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Klotz, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Fern ndez-D
ndez-D az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(40), p.e2208717119_1 - e2208717119_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.35(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here we present the first elucidation of the disordered structure of ice VII, the dominant high-pressure form of water, at 2.2 GPa and 298 K from both single-crystal and powder neutron diffraction techniques. We reveal the three-dimensional atomic distributions from the maximum entropy method and unexpectedly find a ring-like distribution of hydrogen in contrast to the commonly-accepted discrete sites. In addition, total scattering analysis at 274 K clarified the difference in the intermolecular structure from ice VIII, the ordered counterpart of ice VII, despite an identical molecular geometry. Our complementary structure analyses robustly demonstrate the unique disordered structure of ice VII. Furthermore, these noble findings are related to the proton dynamics which drastically vary with pressure, and will contribute to an understanding of the structural origin of anomalous physical properties of ice VII under pressures.
 plantation
plantationAbe, Yukiko*; Liang, N.*; Teramoto, Munemasa*; Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tange, Takeshi*
Geoderma Regional (Internet), 29, p.e00529_1 - e00529_11, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.4(Soil Science)This study aimed to clarify the causes of spatial variation in soil respiration rate on volcanic ash soil. From January 2013 to August 2019, soil respiration rates were measured at 40 measuring points periodically at a 35-year-old  plantation in Tokyo, Japan. In August 2019, the carbon content of the litter layer, total carbon content of soil organic matter (SOM), carbon content of the low-density fraction (LF-C) of SOM, fine root biomass, and bulk density of soil were measured at all measuring points. Results of the multiple regression analysis showed that the model with only the LF-C as an explanatory variable had the highest capability for predicting the respiration rate at a soil temperature of 20
plantation in Tokyo, Japan. In August 2019, the carbon content of the litter layer, total carbon content of soil organic matter (SOM), carbon content of the low-density fraction (LF-C) of SOM, fine root biomass, and bulk density of soil were measured at all measuring points. Results of the multiple regression analysis showed that the model with only the LF-C as an explanatory variable had the highest capability for predicting the respiration rate at a soil temperature of 20 C, indicating that LF-C, which is considered to be readily available to soil microorganisms, can be the main factor responsible for the spatial variation in soil respiration rate.
C, indicating that LF-C, which is considered to be readily available to soil microorganisms, can be the main factor responsible for the spatial variation in soil respiration rate.
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Hisano, Naoki*; Abe, Jun*; Suzuki, Akio*
American Mineralogist, 107(3), p.325 - 335, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.72(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The basaltic glass structure were investigated to 18 GPa using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction. The O-O coordination number (CN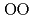 ) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r
) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r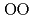 ) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN
) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN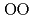 stops increasing and r
stops increasing and r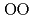 begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN
begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN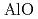 ) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN
) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN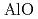 increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN
increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN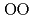 increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at
increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at  2 GPa.
2 GPa.
Abe, Jun*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 93(2), p.025103_1 - 025103_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)
 3H(D)
3H(D) O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehonite
O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehoniteYamamoto, Genichiro*; Kyono, Atsushi*; Abe, Jun*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(2), p.96 - 103, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:51.59(Mineralogy)Neutron diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and thermal analysis were performed to investigate the composition, structure, and formation conditions of the magnesium carbonate hydrate nesquehonite. The time-of-flight neutron diffraction revealed the crystal structure of the monoclinic space group  2
2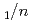 with lattice parameters of
with lattice parameters of  =7.72100(12)
=7.72100(12)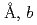 =5.37518(7)
=5.37518(7)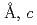 =12.1430(3)
=12.1430(3)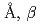 =90.165(4)
=90.165(4) , in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
, in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
 3H
3H O rather than Mg(HCO
O rather than Mg(HCO )(OH)
)(OH) 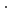 2H
2H O.
O.
Sano, Asami; Kakizawa, Sho*; Shito, Chikara*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
High Pressure Research, 41(1), p.65 - 74, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.35(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We applied Kawai-type multi-anvil assemblies (MA6-8) for time-of-flight neutron-diffraction experiments to achieve high pressures and high temperatures simultaneously. To achieve sufficient signal intensities, the angular access to the sample was enlarged using slits and tapers on the first-stage anvils. Using SiC-binder sintered diamond for the second-stage anvils that transmits neutrons, sufficient signal intensities were achieved at a high-pressure of  23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
23.1 GPa. A high-temperature experiment was also conducted at 16.2 GPa and 973 K, validating the use of tungsten carbide for the second-stage anvils. The present study reveals the capability of the MA6-8 cells in neutron-diffraction experiments to attain pressures and temperatures beyond the limits of the conventional MA6-6 cells used in the high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET at the MLF, J-PARC.
Temleitner, L.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Nakajima, Yoichi*; Pusztai, L.*
Molecules (Internet), 26(5), p.1218_1 - 1218_12, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.77(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Total structure factors of per-deuterated methanol and heavy water, CD OD and D
OD and D O, have been determined across the entire composition range at pressures of up to 1.2 GPa, by neutron diffraction. Largest variations due to increasing pressure were observed below
O, have been determined across the entire composition range at pressures of up to 1.2 GPa, by neutron diffraction. Largest variations due to increasing pressure were observed below 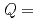 5
5 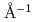 , mostly as shifts of the first and second maxima. Molecular dynamics computer simulations been conducted at the experimental pressures to interpret neutron diffraction results. The peak shifts mentioned above could be qualitatively reproduced by simulations. In order to reveal the influence of changing pressure on the local intermolecular structure, simulated structures have been analyzed in terms of hydrogen bond related partial radial distribution functions and size distributions of hydrogen bonded cyclic entities. Distinct differences between pressure dependent structures of water-rich and methanol-rich composition regions have been revealed.
, mostly as shifts of the first and second maxima. Molecular dynamics computer simulations been conducted at the experimental pressures to interpret neutron diffraction results. The peak shifts mentioned above could be qualitatively reproduced by simulations. In order to reveal the influence of changing pressure on the local intermolecular structure, simulated structures have been analyzed in terms of hydrogen bond related partial radial distribution functions and size distributions of hydrogen bonded cyclic entities. Distinct differences between pressure dependent structures of water-rich and methanol-rich composition regions have been revealed.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
High Pressure Research, 40(3), p.325 - 338, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:38.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To understand the practical effects of pressure-transmitting media (PTM) on neutron diffraction using Paris-Edinburgh presses, diffraction patterns of MgO were collected to approximately 20 GPa using PTMs of Pb, AgCl, 4:1 methano-ethanol (ME) mixture with and without heating, N , and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N
, and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N , and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
, and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
High Pressure Research, 39(3), p.417 - 425, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have developed a technique for neutron diffraction experiments at pressures up to 40 GPa using a Paris-Edinburgh press at the PLANET beamline in J-PARC. To increase the maximum accessible pressure, the diameter of the dimple for sample chamber at the top of the sintered diamond anvils is sequentially reduced from 4.0 mm to 1.0 mm. As a result, the maximum pressure increased and finally reached 40 GPa. By combining this technique with the beam optics which defines the gauge volume, diffraction patterns sufficient for full-structure refinements are obtainable at such pressures.
Abe, Jun*; Sekine, Kotaro*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Aizawa, Kazuya
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.283 - 286, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.02(Physics, Condensed Matter)Abe, Yuta; Nagai, Keiichi; Maie, Mitsuyoshi*; Nakano, Natsuko*; Kawashima, Yuichi*; Takesue, Naohisa*; Saito, Junichi
Dai-23-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.301 - 308, 2017/12
PLANET is a neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. Combining the intense neutron source of J-PARC and high-pressure devices designed for time-of-flight powder neutron diffraction enables precise structure analysis of crystal, liquid and amorphous solids over wide pressure and temperature region of 0-20 GPa and 77-2000K. This beamline is effective for various studies in geophysics, planetary science, physics and chemistry. This paper overviews the beamline and introduces recent results obtained at PLANET.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Harjo, S.; Tsuchida, Noriyuki*; Abe, Jun*; Gong, W.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.15149_1 - 15149_11, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:100 Percentile:93.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)