Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(3), p.031504_1 - 031504_17, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Environmental Sciences)In Japan, the radiation-dose limit for the lens of the eye was revised in April 2021. Consequently, for workers, the numerical values of the equivalent dose to the lens of the eye are equal to those of the effective dose. Radiation workers, radiation safety officers and licensees must comply with regulations related to radiation protection and optimize protection. The new guidelines on dose monitoring of the lens of the eye developed by the Japan Health Physics Society recommend for the dose to be estimated near the eye for accurate estimation, when the dose to the lens approaches or exceeds the management criteria. However, there is limited information regarding the non-uniform exposure of nuclear power plant workers. In this study, the dose equivalents of high-dose-rate workplaces and the personal doses of 88 workers were estimated at four Japanese commercial nuclear power plant sites (RWR: 3 units and BWR: 3 units) and the dose to the lens of the eye and the exposure situations of the workers were analyzed.
Tsurudome, Koji; Suzuki, Hajime; Aoki, Katsunori
JAEA-Review 2021-031, 186 Pages, 2021/12
Tono Geoscience Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting mine closure activities at Tono Mine based on "Plan for closure activities of the Tono Mine" since FY2010. The closure activities of the Tono Mine are carried out in accordance with the Mining Act, the Mine Safety Act and the Industrial Safety and Health Act. In particular, in order to examine the technologies applied to the closure activities of the Tono mine, also the surrounding environmental monitoring, "Technical Committee on Mine Closure Activities of the Tono Mine" was organized at Tono Geoscience Center in FY2013 and the results in the previous fiscal year and the plan for the current fiscal year have been reported and discussed at the annual meeting. As a result, it has been confirmed that the closure activities are making progress as planned and that the environment around the mine meets the legally required standards from the monitoring results. This document is a compilation of meeting materials of all eight committee meetings held between FY2013 and FY2019.
Aoki, Katsunori; Yamanaka, Hiroki*; Watanabe, Kazuhiko*; Sugihara, Kozo
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-018, 45 Pages, 2021/02
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is pursued by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the crystalline host rock (granite) as a part of geoscientific study of JAEA, and underground facilities of MIU are constructed down to 500m blow the ground surface. As small amount of Uranium is normally contained in granite, high concentration of radon is sometimes detected in the air of the underground facilities constructed in granitic rocks depending on their ventilation conditions. Radon concentrations in underground facilities of MIU have been measured according to the excavation progress of underground facilities or the change of ventilation system. It is recognized that the data obtained by the actual measurement of radon concentration in such underground facilities are rare and valuable. This repot summarizes the measured data from fiscal 2010 to fiscal 2020, together with the information of ventilation conditions and air temperature which affect radon concentrations in underground facilities. The variation of the equilibrium factors of radon is also examined with the actually measured data. As a result, it has been found that radon concentration in the drift is high in summer and low in winter according to the natural ventilation caused by the seasonal temperature difference between in and out of the underground facilities. Furthermore, the temporary increase in the equilibrium factor of radon in the drift at the start of ventilation is supposed to be due to the aerosol increase by the ventilation flow, such as the dust blown up.
 Sr+
Sr+ Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioning
Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioningTsujimura, Norio; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yamazaki, Takumi; Momose, Takumaro; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
KEK Proceedings 2020-5, p.21 - 28, 2020/11
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Measurements, 138, p.106399_1 - 106399_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tsujimura, Norio; Hoshi, Katsuya; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106305_1 - 106305_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Tsujimura, Norio; Yokoyama, Sumi*
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106304_1 - 106304_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:45.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)In FY 2017, the Japanese Nuclear Regulatory Agency (NRA) established the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund for funding projects on nuclear safety regulation, and adopted the two-year research project entitled "Study on standard eye lens monitoring, suitable dose management and radiation protection for nuclear and medical workers". The study is a two-phase study: a laboratory study on the eye lens dosemeter's characteristics to photons, and a field study executed at actual workplaces at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. This paper summarizes the results of the first-phase study, which was designed to clarify the eye lens dosemeter positioning and the shielding effect of full face mask respirators used at the station. No marked difference was observed in readings of the dosemeters attached on the different positions on the head phantom. Two types of full face mask respirators provided insignificant shielding effect for photons of 83 keV to 662 keV.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 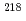 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Aoki, Katsunori
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 4, p.788 - 792, 2014/04
The equivalent dose rate per positron fluence for the human eye lens is calculated using a Monte Carlo simulation code, EGS5, with two mathematical models (a computational head voxel phantom and a simple eye model). The eye lens doses for medical staff and carers as received from a radiopharmaceutical such as 18F-FDG, which is used in PET examinations, when spilled on the floor, and from positrons passing through a thin injection tube are calculated using a simple eye model. At energies less than 1 MeV, the equivalent dose for the eye lens per electron and positron fluence as calculated using the simple eye model was a maximum of three orders of magnitude lower than that for the head voxel phantom. These values for the simple eye model were equal to the calculation results obtained using the eye lens model in ICRP Publication 116 and those reported in past studies. The eye lens dose rates from the point and tube sources of 18F-FDG as calculated using our simple eye model are about 0.57 and 0.37  Sv min
Sv min MBq
MBq at 5 cm, respectively. The doses at 10 cm were one-third to half of those at 5 cm.
at 5 cm, respectively. The doses at 10 cm were one-third to half of those at 5 cm.
Maeda, Makoto*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Iyomoto, Naoko*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Takasaki, Koji; Nakamura, Keisuke; Aoki, Katsunori; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*; Tanaka, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Keisuke; Maeda, Makoto*; Aoki, Katsunori; Yasumune, Takashi; Takasaki, Koji; Maehata, Keisuke*; Iyomoto, Naoko*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*; Tanaka, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Keisuke; Aoki, Katsunori; Takasaki, Koji; Maeda, Makoto*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Iyomoto, Naoko*; Ishibashi, Kenji*; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*; Tanaka, Keiichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoki, Katsunori; Ogura, Hideki; Kubota, Mitsuru; Tsurudome, Koji; Ikeda, Koki; Nagasaki, Yasushi; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Furuta, Sadaaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoki, Katsunori; Ogura, Hideki; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Ikeda, Koki; Nagasaki, Yasushi; Tsurudome, Koji; Furuta, Sadaaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopyYoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Hoshi, Katsuya; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsujimura, Norio; Yokoyama, Sumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Nishino, Sho; Yokoyama, Sumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oguchi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ezaki, Iwao*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Oguchi, Hiroyuki*; Tsujimura, Norio; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoki, Katsunori; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Tsujimura, Norio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English