Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otsuka, Satoshi; Shizukawa, Yuta; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Yano, Yasuhide; Onizawa, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Onuma, Masato*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.288 - 298, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:78.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has been developing 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) tempered martensitic steel(TMS) as a candidate material for the fuel cladding tubes of sodium-cooled fast reactors(SFRs). The reliable prediction of in-reactor creep-rupture strength is critical for implementing the 9Cr-ODS TMS cladding tube in the SFR. This study investigated the quantitative correlation between the creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700
C and the dispersions of nanosized oxides by analyzing the creep data and the material's nanostructure. The possibility of deriving a formula for estimating the in-reactor creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMSs based on an analysis of the nanostructure of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS TMSs was also discussed. The creep properties of 9Cr-ODS TMS at 700  C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
C closely correlated with the dispersion of nanosized oxide particles. The correlation between creep-rupture lives and nanosized oxide particle dispersion was determined using existing creep models. The elucidation of correlation between the stress exponent of secondary creep rate and the nanostructure is essential to enhance future modeling reliability and formulation.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Shizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Sato, Isamu*; Maeda, Koji
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2017/00
Electrochemical corrosion behavior under salt water in a type 304L stainless steel used to a part of BWR core materials was investigated to evaluate the possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence for the fuel assemblies which experienced seawater exposure in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) accident. Especially, focusing on the upper end plug part having the 304L SS crevice structure, measurement of repassivation potential for crevice corrosion (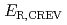 ) were carried out using the crevice test pieces fabricated by 304L SS plates. From the results,
) were carried out using the crevice test pieces fabricated by 304L SS plates. From the results, 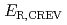 was lower than the spontaneous potential (
was lower than the spontaneous potential ( ) when the conditions of 2500 ppm chloride ion concentration at over 50
) when the conditions of 2500 ppm chloride ion concentration at over 50  C or that of 2500 ppm at over 80
C or that of 2500 ppm at over 80  C, which are included in the SFP water quality conditions. Therefore, in the 304L SS parts of the 1F fuel assemblies that experienced seawater exposure, there is a possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence.
C, which are included in the SFP water quality conditions. Therefore, in the 304L SS parts of the 1F fuel assemblies that experienced seawater exposure, there is a possibility of crevice corrosion occurrence.
Shizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki; Maeda, Koji
no journal, ,
The upper plug of a fuel rod used for the spent fuel pool (SFP) of Unit 4 in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Plant (1F) consists of Zircaloy-2 bolt and SUS304L nut, and it forms the screw-gap structure. Therefore, when seawater left in this gap structure by a seawater injection after an accident, crevice corrosion might occur. It may have an influence on the integrity of a fuel assembly stored in common pool. In this study, the systematic determining the repassivation potential for crevice corrosion of SUS304L and Zircaloy-2 samples. From the result, SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen indicates the tendency of corrosion to progress at 50 C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm. SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen and SUS304L/Zircaloy-2 clearance specimen show the tendency not to corrode at 80
C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm. SUS304L/SUS304L clearance specimen and SUS304L/Zircaloy-2 clearance specimen show the tendency not to corrode at 80 C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm.
C, Chloride ion concentration 10 ppm.
Kaito, Takeji; Yano, Yasuhide; Shizukawa, Yuta; Oka, Hiroshi; Tanno, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi
no journal, ,
 C absorber material for fast reactor after irradiation
C absorber material for fast reactor after irradiationShizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Inoue, Toshihiko; Maeda, Koji; Yoshida, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Oka, Hiroshi; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
no journal, ,
In JAEA's Materials Monitoring Facility (MMF), various post-irradiation examination (PIEs) have been carried out on the long-life core, structural and absorber materials irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo. The PIEs have revealed many important technological insights, i.e. the effects of irradiation on mechanical properties, microstructures, and physical properties of fast reactor materials such as modified austenitic steel, radiation-resistant ferritic steels including oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel, B C, and so on. The test specimens loaded and irradiated in material irradiation rig of Joyo can be tested in the hot-cell of MMF. In addition, the various samples could be machined from the wrapper tubes of driver and fuel test subassemblies irradiated in Joyo using by an electrical discharge machine (EDM). These samples can be characterized using the equipment such as tensile, miniature Charpy and TEM in the hot cell of MMF. In this presentation, we will introduce the details of feasible PIE equipment in the hot-cell of MMF, and examples of typical PIE data acquired by these equipment.
C, and so on. The test specimens loaded and irradiated in material irradiation rig of Joyo can be tested in the hot-cell of MMF. In addition, the various samples could be machined from the wrapper tubes of driver and fuel test subassemblies irradiated in Joyo using by an electrical discharge machine (EDM). These samples can be characterized using the equipment such as tensile, miniature Charpy and TEM in the hot cell of MMF. In this presentation, we will introduce the details of feasible PIE equipment in the hot-cell of MMF, and examples of typical PIE data acquired by these equipment.
 C control materials
C control materialsShizukawa, Yuta; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Inoue, Toshihiko; Maeda, Koji; Yoshida, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Otsuka, Satoshi; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Fujita, Koji; Shizukawa, Yuta; Hashidate, Ryuta; Onizawa, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Ito, Chikara
no journal, ,
Implementation of fusion energy system and fast reactor cycle system requires the development of advanced materials resistant to the severe core environment where high-temperature and high-dose neutron irradiation are superposed. A lot of efforts have been made worldwide for research and development of oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steels with a variety of specification; Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has focused on the development of 9Cr,11Cr-ODS tempered martensitic steel (TMS) for high-burnup fuel cladding tube of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). This paper overviews the current status on 9Cr,11Cr-ODS TMS cladding tube development in JAEA, and discusses the cross-cutting issues in material development for advanced nuclear power systems.
Tanno, Takashi; Fujita, Koji; Shizukawa, Yuta
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Koji; Shizukawa, Yuta; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide
no journal, ,
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developed 11 Cr martensitic steel PNC-FMS as the candidate material for wrapper tubes of fast reactors. Developing database of property changes by thermally aging is necessary to clarify the irradiation effects from post irradiation experimental data. Tensile tests and hardness measurement of PNC-FMS aged up to 45,000 hours were carried out. Tensile test and hardness test after the thermal aging showed that the strength of specimens aged at 600 C or higher decreased with aging time. It was shown that the decrease trend was described by linear correlation with Larson-Miller parameter. This means that the strength decrease should have been made by microstructural degradation due to the diffusion-controlled process.
C or higher decreased with aging time. It was shown that the decrease trend was described by linear correlation with Larson-Miller parameter. This means that the strength decrease should have been made by microstructural degradation due to the diffusion-controlled process.
Tanno, Takashi; Shizukawa, Yuta; Fujita, Koji
no journal, ,
The evaluation of the fracture toughness of thermal-aged PNC-FMS was conducted using the miniature three-point bending fracture toughness evaluation technique under development. The results implied that although the Charpy impact properties of PNC-FMS after thermal aging for 6000 hours at 600 C degraded, the fracture toughness at room temperature did not degraded. Furthermore, as a result of comparing the cases where fatigue pre-crack was introduced to the test specimen before and after thermal aging, it was found that there was no significant difference under the present thermal aging conditions.
C degraded, the fracture toughness at room temperature did not degraded. Furthermore, as a result of comparing the cases where fatigue pre-crack was introduced to the test specimen before and after thermal aging, it was found that there was no significant difference under the present thermal aging conditions.
Shizukawa, Yuta; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English