Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirouchi, Jun; Kujiraoka, Ikuo; Takahara, Shogo; Takada, Momo*; Schneider, T.*; Kai, Michiaki*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 44(2), p.021510_1 - 021510_10, 2024/06
no abstracts in English
Nakanishi, Chika*; Ota, Masakazu; Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo
JAEA-Research 2023-012, 29 Pages, 2024/02
The OSCAAR program is a probabilistic risk assessment program for reactor accidents developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. To improve the model included in the OSCAAR program, which is about long-term exposure caused by the resuspension of radioactive materials deposited on soil surfaces, we calculated resuspension factors for Cs-137. The one- dimensional atmosphere-SOiL-VEGetation model, SOLVEG-R was utilized to compute resuspension factor. The wind velocity was kept constant in this study since it significantly affects particle resuspension behavior. Our calculations indicate that wind velocities below 6 m s resulted in little variation in the annual mean resuspension factor at a height of 1 m. However, as wind velocities increased above 6 m s
resulted in little variation in the annual mean resuspension factor at a height of 1 m. However, as wind velocities increased above 6 m s , the resuspension factor significantly increased. The resuspension factors ranged from 10
, the resuspension factor significantly increased. The resuspension factors ranged from 10 to 10
to 10 m
m for wind velocities ranging from 1 m s
for wind velocities ranging from 1 m s to 7 m s
to 7 m s .
.
 Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Masakazu; Takahara, Shogo; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Nagakubo, Azusa; Hirouchi, Jun; Hayashi, Naho; Abe, Tomohisa; Funaki, Hironori; Nagai, Haruyasu
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 264, p.107198_1 - 107198_15, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)One of the current major radiation exposure pathways from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident-fallout is inhalation of the re-suspended  Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of
Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of  Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric
Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric  Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of
Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of  Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air
Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air  Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher
Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher  Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore
Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore  Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle
Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle  Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,
Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,  Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore
Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore  Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric
Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric  Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(4), p.041503_1 - 041503_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:27.23(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is one of the countermeasures against radiation exposure during nuclear accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering for inhalation exposure is often expressed by the reduction factor, which is defined as the ratio of the indoor to the outdoor cumulative radioactivity concentrations or doses. The indoor concentration is mainly controlled by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. Meanwhile, the air exchange rate depends on surrounding environmental conditions: the wind speed, leakage area normalized by the floor area of the house, and gross building coverage ratio. In this study, the ranges of the uncertainty of the reduction factors for particles and I were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I
were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Kato, Nobuyuki*; Matsui, Yasuto*; Yoneda, Minoru*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 41(3), p.S139 - S149, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.53(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is one of the countermeasures for protection against radiation exposures in nuclear accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering is often expressed by the reduction factor, that is the ratio of the indoor to the outdoor cumulative radioactivity concentrations or doses. The indoor concentration is mainly controlled by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. The penetration factor and indoor deposition rate depend on the surface and opening materials. We investigated experimentally these parameters of I and particles. The experiment was performed in two apartment houses, three single-family houses, and chambers. The obtained penetration factor ranged 0.3
and particles. The experiment was performed in two apartment houses, three single-family houses, and chambers. The obtained penetration factor ranged 0.3  1 for particles of 0.3
1 for particles of 0.3  1
1  m and 0.15
m and 0.15  0.7 for I
0.7 for I depending on the air exchange rate. The indoor deposition rate for a house room ranged 0.007
depending on the air exchange rate. The indoor deposition rate for a house room ranged 0.007  0.2 h
0.2 h for particles of 0.3
for particles of 0.3 1
1  m and 0.2
m and 0.2 1.5 h
1.5 h for I
for I depending on floor materials.
depending on floor materials.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Yoshimura, Kazuya
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 232, p.106572_1 - 106572_6, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.54(Environmental Sciences)Information on the radioactivity distribution inside and outside houses is useful for indoor external dose assessments. In this study, we collected both soil samples around the target houses and house material samples (i.e., of the floor, inner wall, ceiling, outer wall, and roof). The radioactivity of the samples was measured using a high-purity germanium detector. The surface contamination densities of the floor, inner wall, ceiling, outer wall, and roof relative to the ground were 3  10
10
 7
7  10
10 , 6
, 6  10
10
 4
4  10
10 , 7
, 7  10
10
 3
3  10
10 , 2
, 2  10
10
 1
1  10
10 , and 4
, and 4  10
10
 2
2  10
10 , respectively. The relative surface contamination densities varied depending on the material, its location, and the orientation of the surface.
, respectively. The relative surface contamination densities varied depending on the material, its location, and the orientation of the surface.
Hirouchi, Jun; Tokashiki, Yuji*; Takahara, Shogo; Manabe, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2021-001, 284 Pages, 2021/03
Doses to the public are calculated with internal dose coefficients based on the publications of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in OSCAAR, which is a level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment code developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The gastrointestinal absorption fraction, 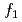 , which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that
, which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that 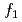 has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of
has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of 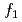 has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of
has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of 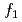 on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various
on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various 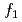 , and derive the relationship between the coefficient and
, and derive the relationship between the coefficient and 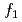 . As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
. As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2019 (ASRAM 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2019/09
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Takahara, Shogo; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Hirouchi, Jun; Iijima, Masashi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Health Physics, 114(1), p.64 - 72, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.55(Environmental Sciences)Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Iijima, Masashi; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Munakata, Masahiro
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 140, p.127 - 131, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.18(Chemistry, Physical)Takahara, Shogo; Watanabe, Masatoshi; Oguri, Tomomi; Kimura, Masanori; Hirouchi, Jun; Munakata, Masahiro; Homma, Toshimitsu
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-016, 65 Pages, 2017/02
We surveyed on structural and material data on 22 facilities which are listed in local disaster management plan in Matsue city. These facilities can be divided into educational facilities, communal facilities and gymnastic hall. Height and floor-area of rooms, as well as window-area were collected as the structural data. We also collected information on constructional materials, and density of those. In addition, mass-thicknesses of the constructional materials were evaluated based on our surveys, and compared to the previous studies which were made in Japan, U.S., and European countries. Consequently, it was found that there is no significant difference of mass-thickness of constructional materials between the results of our surveys and the previous studies. However, for gymnastic hall, since thin metal plates are used for roofs, we can point out that the mass-thickness of roofs are much lower than those for other concrete facilities and clay tile roofing wooden houses.
Takahara, Shogo; Kimura, Masanori; Kinase, Sakae; Ishikawa, Jun; Suyama, Kenya; Hosoyamada, Ryuji; Homma, Toshimitsu
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 3, p.25 - 29, 2012/10
Dose assessment is one of the important issues to make decisions in contaminated areas resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. The doses to inhabitants of contaminated areas should be assessed prospectively and retrospectively taking into account the impact from various exposure pathways. The external exposure from deposited radioactive materials of short-lived and long-lived is one of the most important pathways. In the present study, the radionuclide compositions have been evaluated by source term analysis taking into account 54 radionuclides. This analysis consists in evaluating the inventory and the fraction of the radionuclides that were released into the atmosphere. On the assumption that dose rate may be decreased due to the radioactive decay as well as weathering effects, we have assessed the dose for future and past at the contaminated areas. The assessed values are almost consistent with the measured ones during the first month.
Sawada, Atsushi; Uchida, Masahiro; Shimo, Michito*; Yamamoto, Hajime*; Takahara, Hiroyuki*; Doe, T. W.*
Engineering Geology, 56(1-2), p.75 - 96, 2002/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:42.51(Engineering, Geological)None
Sawada, Atsushi; Uchida, Masahiro; Shimo, Michito*; Yamamoto, H.*; Takahara, Hiroyuki*; Doe, T. W.*
SKB TR-01-24, p.151 - 164, 2002/00
None
Takahara, Shogo; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Hirouchi, Jun; Iijima, Masashi*; Munakata, Masahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro; Kimoto, Shigeru*; Yoneda, Minoru*; Matsui, Yasuto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English