Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
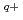 with He
with HeKawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Imai, Makoto*; Sataka, Masao; Komaki, Kenichiro*; Shibata, Hiromi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 205, p.528 - 532, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.7(Instruments & Instrumentation)Auger and Coster-Kronig electron spectra from highly excited states produced by low-energy highly charged ions with gas targets have been investigated both theoretically and experimentally. In this case, the highly excited states were formed by electron capture processes. We have studied collision processes of high-energy highly charged ions with a gas target using zero-degree electron spectroscopy at the tandem accelerator of JAERI, Tokai. In the present, we have measured Auger and C-K electron spectra from highly excited states produced by 1-3 MeV/u O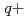 (q=3-5) + He collisions, where the highly excited states in Oq+ ions were formed by electron excitation. We have compared and discussed the Auger and C-K electron spectra obtained by electron-capture and electron-excitation processes. It is found that the C-K spectra for high-energy Oq+ ions show relatively low-l states and the Auger spectra also have different structures from those for low-energy highly charged Oq+ ions.
(q=3-5) + He collisions, where the highly excited states in Oq+ ions were formed by electron excitation. We have compared and discussed the Auger and C-K electron spectra obtained by electron-capture and electron-excitation processes. It is found that the C-K spectra for high-energy Oq+ ions show relatively low-l states and the Auger spectra also have different structures from those for low-energy highly charged Oq+ ions.
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Takeshima, Naoki*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Naramoto, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2001-039, TIARA Annual Report 2000, p.188 - 189, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yamaguchi, Sadae*; Naramoto, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.143 - 145, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Takahiro, Katsumi*; Kawatsura, Kiyoshi*; Zhang, K.*; Rotter, F.*; Schwen, D.*; Ronning, C.*; Hofs ss, H.*; Krauser, J.*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; et al.
ss, H.*; Krauser, J.*; Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to study the allotropic effect on ripple formation on carbon surfaces induced by sputter erosion, three types of carbon materials, highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), single crystalline diamond and tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C) films, were irradiated with 5 keV Xe at an incident angle of 30 degree. The irradiation fluence was 2
at an incident angle of 30 degree. The irradiation fluence was 2 10
10 cm
cm for all irradiations. No ripples were formed on diamond and ta-C surfaces, while ripples with a wavelength of
for all irradiations. No ripples were formed on diamond and ta-C surfaces, while ripples with a wavelength of  100 nm occurred on HOPG. Electron energy loss spectroscopy revealed that the surfaces of all carbon materials became amorphous with similar densities upon irradiation. Therefore, the presented results clearly show that rippling depends on the nature of the underlying carbon materials. The mechanism for rippling of carbon materials will be discussed.
100 nm occurred on HOPG. Electron energy loss spectroscopy revealed that the surfaces of all carbon materials became amorphous with similar densities upon irradiation. Therefore, the presented results clearly show that rippling depends on the nature of the underlying carbon materials. The mechanism for rippling of carbon materials will be discussed.
Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Takahiro, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Nagata, Shinji*
no journal, ,
Optical absorption due to localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of Au nanoparticles (Au NPs) is being applied to optical chemical sensors. In this work, ion sputtering and plasma cleaning have been employed to control the LSPR absorption. Au NPs on quartz and Si substrates were fabricated by RF magnetron sputtering method. The samples were characterized by UV-Vis extinction spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The peak position of LSPR absorption was shifted toward shorter wavelength after ion irradiation and plasma treatment. The SEM observation revealed that the average size of Au NPs did not change before and after ion irradiation and plasma treatment. The XPS analysis showed that the blue-shift of LSPR absorption was resulted from the elimination of hydrocarbons adhered on particle surfaces. We concluded that plasma and ion sputtering treatments are effective method to obtain Au NPs with clean surfaces.