Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sako, Hiroyuki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Sakaguchi, Takao*; Chujo, Tatsuya*; Esumi, Shinichi*; Gunji, Taku*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hwang, S.; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 956, p.850 - 853, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.66(Physics, Nuclear)Takahashi, Naoki; Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Harada, Akio; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Ueno, Takashi; Kurihara, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Soju; Takamatsu, Misao; Maeda, Shigetaka; Iseki, Atsushi; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Homu Peji (Internet), 64 Pages, 2016/00
no abstracts in English
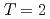 mirrors
mirrors  Ca and
Ca and  S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplines
S; A Test for isospin symmetry of shell gaps at the driplinesDoornenbal, P.*; Reiter, P.*; Grawe, H.*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Al-Khatib, A.*; Banu, A.*; Beck, T.*; Becker, F.*; Bednarczyk, P.*; Benzoni, G.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 647(4), p.237 - 242, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:86.95(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The first excited state of  Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured
Ca was measured at GSI for the first time. The measured 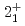 energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus
energy is found to be 3015(16) keV, which is lower than its mirror nucleus  S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the
S by as large as 276 keV. The structure of those nuclei is studied by the shell model. It is found that those nuclei can be well described by the 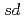 valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the
valence space. The large energy shift between them is caused by the Thomas-Ehrman effect. We presented that the energy shift in the 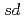 shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
shell region can be explained by the shell model with a phenomenological treatment of the Thomas-Ehrman effect.
Emoto, Takehiko; Torii, Tatsuo; Nozaki, Tatsuo; Saito, Kei; Emori, Shuichi; Ando, Hideki
PNC TN9410 96-299, 74 Pages, 1996/08
The technique has been developed to measure the dose-rate distribution of radiation easily. The detector is made of plastic scintillation fibers (of following PSFs). The technique is based on the time of flight method, that is to measure the time difference of scintillation reaching from a incidence position to both ends of fibers. Measuring devices were built as trials. The position resolution was measured with collimated  ray. The dose-rate linearity and the energy response were measured with an irradiation equipment of
ray. The dose-rate linearity and the energy response were measured with an irradiation equipment of  ray. Then, the devices were applied to the dose-rate distribution measurements in facilities. The tests were carried out to turn the technique into practicable use. Main results are as follows; (1) The continuos dose-rate distribution of
ray. Then, the devices were applied to the dose-rate distribution measurements in facilities. The tests were carried out to turn the technique into practicable use. Main results are as follows; (1) The continuos dose-rate distribution of  ray can be measured with a single detector. The result of a measurement is illustrated on the screen of a device immediately. (2) The upper limit of counting rate measuring range is 10
ray can be measured with a single detector. The result of a measurement is illustrated on the screen of a device immediately. (2) The upper limit of counting rate measuring range is 10 cps. The upper limit of
cps. The upper limit of  ray dose-rate measuring range is 1 mSv/h (calculated value) for a detector of "0.25 mm
ray dose-rate measuring range is 1 mSv/h (calculated value) for a detector of "0.25 mm 
 1 peace, 10 m length". (3) The detection efficiency does not depend on the
1 peace, 10 m length". (3) The detection efficiency does not depend on the  ray energy between 500 keV and 1.5 MeV. (4) The practical length of PSFs is up to about 10 m for the dose-rate distribution measurement. (5) When the dose-rate distribution has sharp peaks, the output distribution of measurement is slightly flattened against the actual distribution based on the detector characteristic of position resolution. The unfolding method can correct this effect. (6) It is possible to discriminate the energy and type of radiation, if the pulse height output of a photomultiplire is corrected in each incidence position with the multi-parameter measuring method.
ray energy between 500 keV and 1.5 MeV. (4) The practical length of PSFs is up to about 10 m for the dose-rate distribution measurement. (5) When the dose-rate distribution has sharp peaks, the output distribution of measurement is slightly flattened against the actual distribution based on the detector characteristic of position resolution. The unfolding method can correct this effect. (6) It is possible to discriminate the energy and type of radiation, if the pulse height output of a photomultiplire is corrected in each incidence position with the multi-parameter measuring method.